Readiness for Change Questionnaire
Assess your organization's readiness for change with Carepatron's free PDF download of a readiness for change questionnaire.


What is the Readiness for Change Questionnaire?
The Readiness for Change Questionnaire is a widely used tool designed to assess an individual’s willingness and preparedness to make significant changes in their drinking behavior, particularly in relation to substance use. Originally developed in the context of alcohol usage, this questionnaire is instrumental in identifying the contemplation stages of individuals who may be grappling with alcohol misuse or other forms of substance abuse. Through readiness assessment, healthcare practitioners can determine the level of motivation a person has to alter their specific behavior, which is crucial for an effective brief intervention.
The questionnaire helps in tailoring techniques to fit the specific needs of individuals who struggle with substance abuse. This personalized approach is essential when addressing substance- or alcohol-related problems, allowing for more effective and opportunistic interventions.
By evaluating where a person falls within the contemplation stage of behavior change, practitioners can better support them through the process of desired change. The Readiness for Change Questionnaire is not just limited to alcohol use but can be applied to various behaviors.
Our template contains a Readiness for Change Questionnaire for treating or managing substance use disorder or alcohol abuse, not assessing organizational readiness for change.
Readiness for Change Questionnaire Template
Readiness for Change Questionnaire Example
How to use our Readiness for Change Questionnaire template?
Using the Readiness for Change Questionnaire template from Carepatron can greatly enhance the process of assessing and supporting behavior change in patients. This tool is designed to streamline the process for healthcare professionals, making it easier to evaluate and respond to a patient’s readiness to change, particularly in areas like alcohol misuse and abuse.
Follow these steps to effectively integrate the template into your practice.
Step 1: Access and download the template
Start by accessing the Readiness for Change Questionnaire template by clicking "Use template." You can also save the template by clicking "Download."
Step 2: Review the template
Before using the template with a patient, take a moment to review the content thoroughly, especially the Scoring section. Familiarize yourself with the questions and the scoring to ensure you can guide the patient effectively.
Step 3: Administer the questionnaire to the patient
When meeting with a patient, introduce the Readiness for Change Questionnaire as a tool to help them explore their motivations and readiness for behavior change. Explain the purpose of the questionnaire, focusing on how it assesses excessive drinkers, substance abuse, and contemplation stages. This step is key to gaining the patient’s trust and ensuring they understand how the tool will assist in their journey towards change.
Step 4: Review results and monitor
After the patient completes the Readiness for Change Questionnaire, review the results together. Discuss the insights gained, particularly in relation to their readiness to change and any identified areas of concern such as hazardous alcohol consumption or alcohol-related problems. Use this information to plan appropriate interventions and monitor their progress over time, adjusting your approach as needed to support intervention strategies.
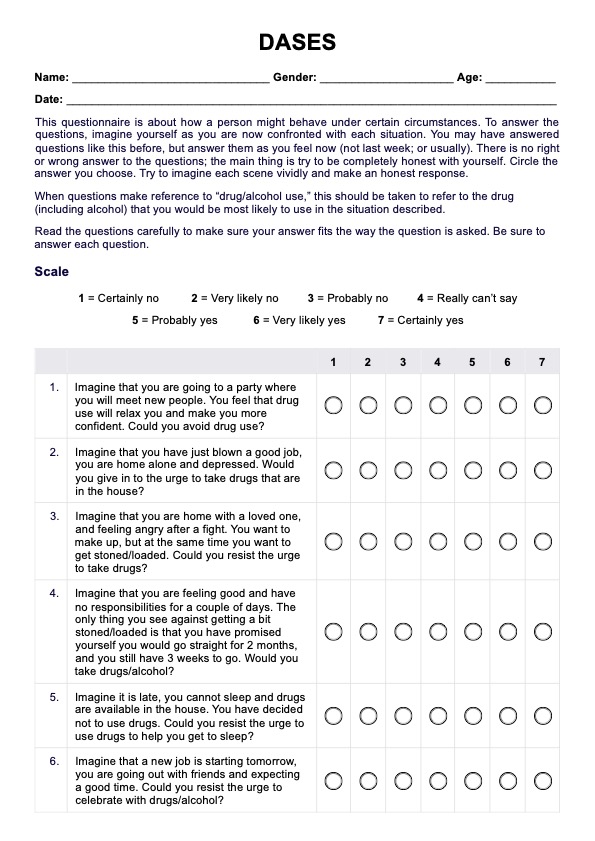
Scoring
The Readiness to Change Questionnaire is scored by adding up the item scores for each scale within the questionnaire (Precontemplation, Contemplation, and Action). The scoring range for each scale extends from -10 through 0 to +10. A negative score on a particular scale indicates an overall disagreement with the items measuring that specific stage of change, suggesting that the individual may not yet be ready for behavior modification. Conversely, a positive score reflects an overall agreement, indicating a higher level of readiness and motivation to engage in behavior change.
Next steps after conducting the assessment
After completing the Readiness for Change Questionnaire, the next steps are crucial in guiding your patient toward positive change. Begin by analyzing the results, focusing on the stage allocation that the assessment reveals. Understanding the patient’s current stage in the change model helps tailor your approach to their specific needs, whether they are in the early distinct stages of contemplation or already preparing for action.
Use the questionnaire as a helpful tool to facilitate change talk—conversations that encourage the patient to express their desire, ability, reasons, and need for change. This dialogue is vital to increase motivation and build self-efficacy, as it allows patients to recognize their capacity for change.
Next, consider the questionnaire's factor structure to ensure that all relevant aspects of change readiness have been addressed. Depending on the results, you may opt for a treatment version of the intervention that aligns with the patient’s readiness level. This might involve setting small, achievable goals that gradually build momentum toward more significant changes.
Commonly asked questions
When assessing readiness, ask questions like, "What are your reasons for considering this change?" and "How confident are you in your ability to make this change?" These questions help gauge motivation, self-efficacy, and the excessive drinkers' readiness to move forward in the change process.
To assess readiness to change, use structured tools like the Readiness for Change Questionnaire, which measures the patient’s current stage in the change process. Combine this with open-ended questions and motivational interviewing techniques to better understand the patient’s commitment and potential barriers to change.
The Stages of Change Questionnaire assesses an individual’s current stage in the behavior change process, from precontemplation to maintenance. It helps healthcare providers tailor interventions to the patient’s specific stage, enhancing the effectiveness of treatment plans.


















-template.jpg)