The priority nursing diagnosis for a patient with a tracheostomy is a risk for impaired gas exchange, addressing airway compromise, or altered respiratory function.
Tracheostomy Nursing Care Plan
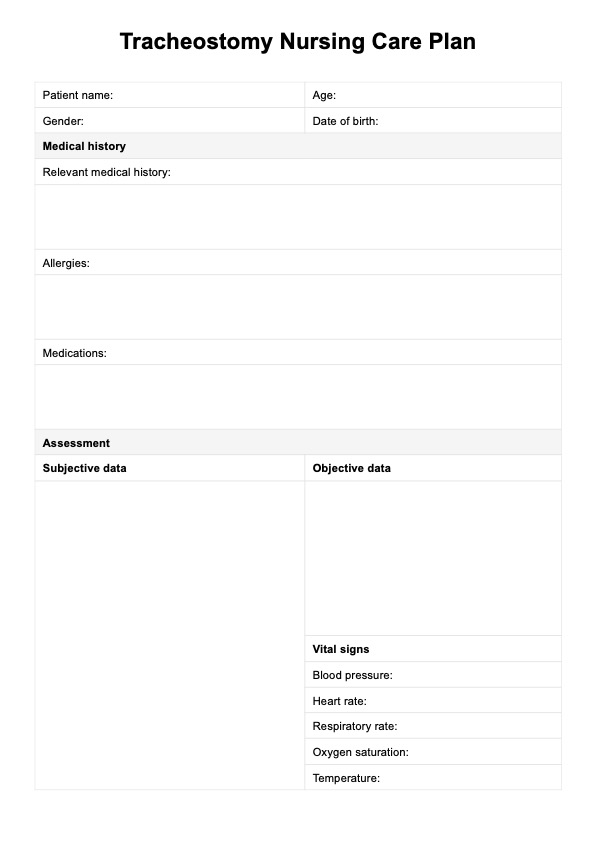
Learn about creating a comprehensive Tracheostomy Nursing Care Plan through Carepatron's free downloadable PDF guide and detailed example.
Use Template
Tracheostomy Nursing Care Plan Template
Commonly asked questions
Nursing interventions include managing tracheal secretions, ensuring tube patency, performing the suctioning procedure, educating on tracheostomy care, and providing emotional support.
Standard care includes thorough site care, regular respiratory assessments, the use of sterile gloves during procedures, and monitoring for complications like infections or obstructions.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











