T3 Blood
Optimize your health with a precise Triiodothyronine (T3) Test. Get accurate thyroid insights for better well-being.


What is a T3 Blood Test?
A T3 blood test, also known as a Triiodothyronine blood test, is a medical diagnostic tool used to measure the levels of the hormone Triiodothyronine (T3) in a person's bloodstream. T3 is one of the two major hormones produced by the thyroid gland, the other being thyroxine (T4), and plays a crucial role in regulating the body's metabolism. This test is vital in assessing thyroid function and can provide valuable insights into a person's overall health.
The T3 blood test is typically ordered by healthcare providers to evaluate thyroid function and diagnose thyroid disorders. It is especially useful in determining if the thyroid gland is overactive (hyperthyroidism) or underactive (hypothyroidism). Hyperthyroidism is characterized by elevated T3 levels, leading to symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and nervousness. Conversely, hypothyroidism, which results from low T3 levels, can cause symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, and depression.
Additionally, the T3 test can be employed to monitor the effectiveness of treatment for thyroid conditions, such as thyroid hormone replacement therapy. Regular monitoring allows healthcare providers to adjust medication doses to ensure the patient's thyroid hormone levels remain within the normal range.
The importance of the T3 blood test extends beyond thyroid health. Abnormal T3 levels can impact various bodily functions, including the cardiovascular and nervous systems, metabolism, and energy production. Early detection and treatment of thyroid disorders can help prevent complications and improve the patient's overall quality of life.
The T3 blood test is a crucial diagnostic tool used to assess thyroid function and diagnose thyroid disorders. It provides essential information for healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding treatment and monitoring. Maintaining healthy thyroid hormone levels is paramount for overall well-being, as thyroid function influences a wide range of bodily processes. Regular check-ups and consultations with a healthcare professional can help ensure that T3 levels are within the normal range, promoting optimal health and preventing potential complications.
Triiodothyronine (T3) Test Template
Triiodothyronine (T3) Test Example
How Does it Work?
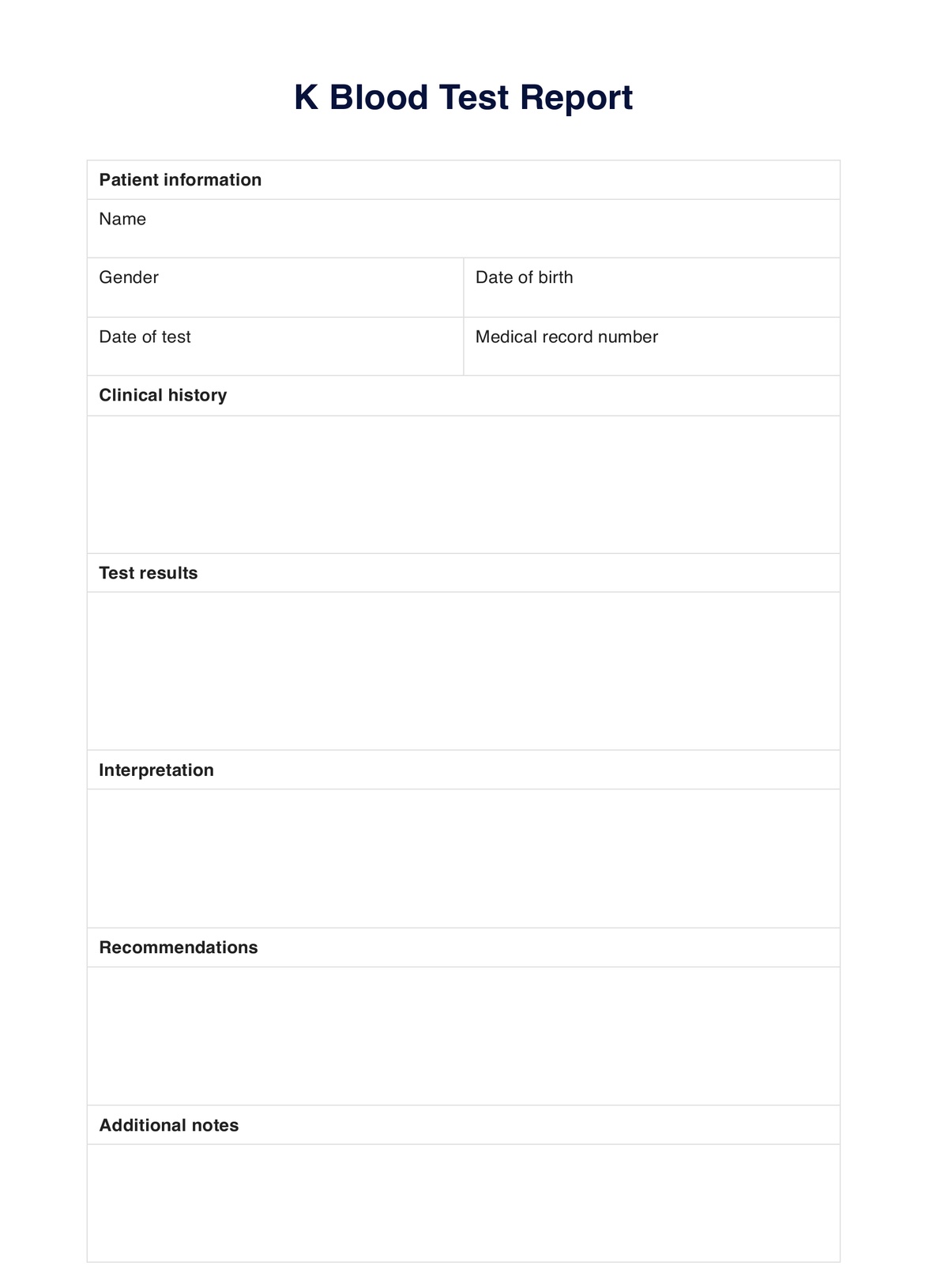
Using and filling out a printable T3 Blood Test form involves several key steps, ensuring accurate collection of patient data and test information. This form serves as a vital tool for healthcare practitioners to request, conduct, and interpret T3 blood tests.
Step 1: Obtain the Form
Begin by obtaining the printable T3 Blood Test form, which can be typically sourced from the healthcare facility or printed from a secure and reliable medical records system. It is essential to ensure that you are using an up-to-date and approved form to maintain accuracy and compliance.
Step 2: Patient Information
The form starts with capturing essential patient information. This includes the patient's name, date of birth, gender, and a unique medical record number, if available. Accurate patient information is crucial for linking the test results to the right individual.
Step 3: Test Request and Provider Details
Indicate the specific test requested, in this case, the T3 Blood Test. Mention the name of the healthcare provider who is ordering the test. This is vital for accountability and tracking.
Step 4: Test Procedure Details
Include the specimen type required for the T3 Blood Test, usually whole blood. Specify the collection time and site. These details help ensure a standardized and consistent collection process.
Step 5: Test Results
After the blood sample is collected and analyzed in the laboratory, the T3 level is recorded on the form. This level should be compared to the laboratory reference range to determine whether it falls within the expected normal range.
Step 6: Interpretation
Provide an interpretation of the test results. If the T3 level is within the normal range, explain that this indicates healthy thyroid function. If the result is outside the normal range, suggest the possible implications, such as hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, and recommend further evaluation.
Step 7: Additional Information
Offer additional context and information, emphasizing that the T3 Blood Test is only one part of a comprehensive thyroid evaluation. Clinical symptoms and other thyroid function tests may be necessary to make a thorough assessment.
Step 8: Signature
The healthcare provider signs the form, indicating their approval and responsibility for the test and its interpretation.
This printable T3 Blood Test form serves as a critical tool for documenting and tracking thyroid health. It helps maintain accurate patient records and ensures that healthcare practitioners can provide the best possible care.
When Would you use this Test?
The T3 Blood Test is a vital diagnostic tool primarily used by healthcare practitioners, especially endocrinologists, internists, and primary care physicians, to assess thyroid function and diagnose thyroid-related disorders. Here are several scenarios when it is appropriate to utilize this resource:
Symptoms of Thyroid Dysfunction
When a patient presents with symptoms such as unexplained weight changes, fatigue, rapid heartbeat, cold intolerance, or mood disturbances, healthcare providers may consider ordering a T3 Blood Test. These symptoms can be indicative of thyroid dysfunction.
Thyroid Disorder Screening
In routine healthcare check-ups, physicians may use the T3 Blood Test as part of a comprehensive thyroid panel to screen for thyroid disorders, even in the absence of specific symptoms. This is especially important for individuals with a family history of thyroid disease or known risk factors.
Monitoring Thyroid Treatments
For patients already diagnosed with thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, the T3 Blood Test is a valuable tool for monitoring the effectiveness of ongoing treatment. It helps ensure that medication dosages are adjusted correctly to maintain optimal thyroid hormone levels.
Evaluation of Abnormal Thyroid Function
When other thyroid function tests, such as T4 and Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone test (TSH), indicate abnormal results, the T3 Blood Test may be ordered to provide additional insight into the nature and severity of the thyroid dysfunction. It aids in diagnosing specific conditions like Graves' disease or Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
Assessment of Non-Thyroidal Illness (NTI)
In some cases, non-thyroidal illnesses, such as critical illness, severe infection, or malnutrition, can affect T3 levels. Healthcare practitioners may use the T3 Blood Test to determine if such illnesses are impacting the thyroid function and contributing to the patient's health issues.
Reproductive Health
In cases where women are experiencing fertility issues, the T3 Blood Test can be employed to assess thyroid health, as thyroid dysfunction can impact reproductive health.
What do the Results Mean?
A Free T3 Blood Test, also known as a Free Triiodothyronine Blood Test, measures the concentration of unbound (free) triiodothyronine hormone in the bloodstream. The results of this test provide essential insights into a patient's thyroid function. Here's a breakdown of common Free T3 results and their implications:
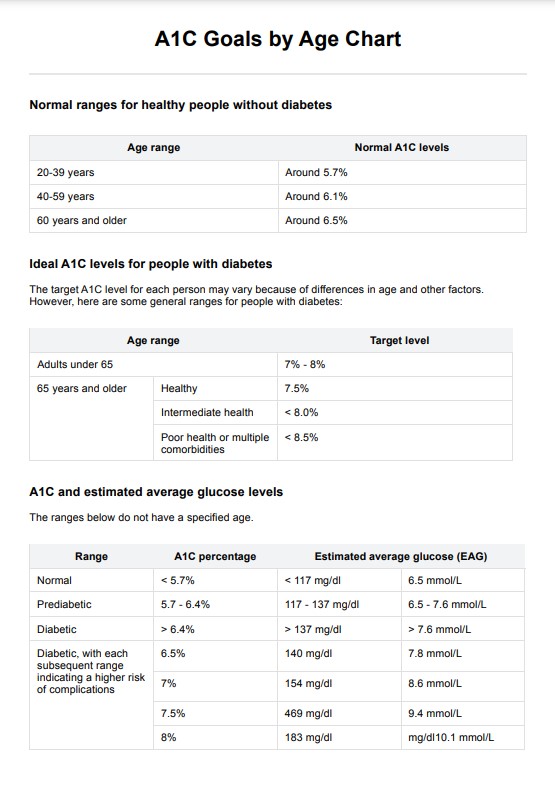
Normal Range (euthyroid)
A Free T3 level falling within the laboratory's reference range typically suggests that the patient's thyroid function is within the normal range. This means the thyroid is producing an appropriate amount of T3 to support metabolic processes, energy production, and overall well-being.
High Free T3 (Hyperthyroidism)
Elevated levels of Free T3 can be indicative of hyperthyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland is overactive and producing excessive thyroid hormones. Symptoms may include rapid heartbeat, unexplained weight loss, anxiety, and heat sensitivity. In this case, further evaluation and treatment may be necessary to address the underlying thyroid disorder.
Low Free T3 (Hypothyroidism)
Low levels of Free T3 may indicate hypothyroidism, where the thyroid gland is underactive and not producing enough thyroid hormones. Hypothyroidism can lead to symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, and depression. Treatment, often in the form of thyroid hormone replacement therapy, is typically recommended to restore thyroid function to normal levels.
T3 Toxicosis
In rare cases, extremely high Free T3 levels can be observed in T3 toxicosis, which may occur in patients with certain medical conditions or thyroid disorders like Graves' disease. This condition may require specific management and treatment to regulate thyroid hormone levels.
Non-Thyroidal Illness (NTI)
Abnormal Free T3 levels can sometimes occur during non-thyroidal illnesses (NTI), such as severe illness, malnutrition, or stress. In NTI, the body may alter thyroid hormone levels as a response to the illness itself, rather than due to a primary thyroid disorder. Further evaluation is needed to determine the underlying cause.
Pregnancy and Reproductive Health
Pregnancy can also impact Free T3 levels, and healthcare providers need to consider these changes when evaluating thyroid function in pregnant women.
Research & Evidence
The T3 Blood Test is a well-established diagnostic tool rooted in decades of medical research and clinical application. Its history is closely intertwined with the understanding of thyroid function and thyroid disorders. The history of the T3 Blood Test is deeply rooted in the evolution of thyroid function testing. Recent research and evidence, especially from 2018 to 2021, underscore the clinical significance of T3 measurements, both total and free, in diagnosing and managing thyroid disorders. These resources and guidelines provide the foundation for the continued use of the T3 Blood Test as a valuable diagnostic tool in healthcare practice.
The T3 Blood Test is part of a broader set of thyroid function tests that have been developed and refined over the years. The concept of measuring thyroid hormones in the blood dates back to the mid-20th century, with the pioneering work of Harris and Haring in 1954, laying the foundation for modern thyroid function testing.
Recent studies have emphasized the importance of Free T3 levels in evaluating thyroid function. For example, a study by Lee et al. (2018) investigated the role of Free T3 in differentiating subclinical hyperthyroidism from euthyroidism in older adults. Another study by Biondi and Wartofsky (2019) highlighted the clinical significance of Free T3 in diagnosing and managing hypothyroidism. Research conducted by Panicker et al. (2020) examined the relationship between T3 levels and cardiovascular risk, shedding light on the implications of thyroid function on heart health.
The American Thyroid Association (ATA) guidelines, last updated in 2021, provide evidence-based recommendations for using thyroid function tests, including T3, in clinical practice. The Endocrine Society's clinical practice guidelines (Garber et al., 2020) emphasize the importance of T3 testing in diagnosing and managing thyroid disorders.
References
Lee, Y. K., et al. (2018). The Role of Free Triiodothyronine in Differentiating Subclinical Hyperthyroidism from Euthyroidism in Older Adults. International Journal of Endocrinology, 2018(Ap), 1-6.
Biondi, B., & Wartofsky, L. (2019). Treatment with thyroid hormone. Endocrine Reviews, 40(4), 1163-1213.
Panicker, V., et al. (2020). Thyroid Function and Cardiovascular Disease. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 105(4), 1-22.
Garber, J. R., et al. (2020). Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hypothyroidism in Adults: Cosponsored by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American Thyroid Association. Endocrine Practice, 26(1), 1-160.
Commonly asked questions
T3 Tests are performed to assess thyroid function. They are used to diagnose thyroid disorders like hyperthyroidism (elevated T3 levels) and hypothyroidism (low T3 levels). T3 Tests are also used to monitor the effectiveness of thyroid treatments.
The T3 Test involves drawing a blood sample, usually from a vein in the arm. The collected blood is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. Results are typically available within a few days.
Normal T3 levels typically fall within the laboratory reference range, which is usually between 80 to 200 nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL). It's important to note that reference ranges may vary slightly between different laboratories.




















-template.jpg)