Osteomyelitis Classification Table
Get Carepatron's free PDF download of an Osteomyelitis Classification Table along with examples for easy reference and understanding of this medical condition.


What is an osteomyelitis?
Osteomyelitis is a serious bone infection that can occur when bacteria or fungi invade the bone tissue, leading to inflammation and the destruction of healthy bone. This condition can manifest in different forms, such as acute osteomyelitis, which develops rapidly and presents severe symptoms, and chronic osteomyelitis, which persists over a longer period and can be more challenging to treat. Osteomyelitis can affect any bone in the body, but it is commonly seen in the long bones of the legs and arms, and in vertebral osteomyelitis, which affects the spine.
Bone infections often begin as a soft tissue infection that spreads to the bone. Individuals with certain conditions, such as foot infections or sickle cell disease, are at higher risk of developing osteomyelitis. Diagnosing osteomyelitis typically involves a combination of medical imaging, such as MRI, and laboratory tests, including a bone biopsy to identify the causative organism, often Staphylococcus aureus.
Types of osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis can be classified into several types based on the duration of the infection, how it was acquired, and its location. Understanding these classifications helps in diagnosing and formulating the appropriate treatment plan.
- Acute osteomyelitis: This type develops rapidly, usually within two weeks of an infection, trauma, or surgery. It is characterized by severe pain, fever, and swelling. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications.
- Chronic osteomyelitis: Occurring when the infection persists for months or even years, chronic osteomyelitis is often the result of an inadequately treated acute infection. Symptoms may include persistent pain, drainage from an open wound.
- Hematogenous osteomyelitis: Caused by pathogens spreading through the bloodstream, this type is more common in children and typically affects the long bones.
- Contiguous osteomyelitis: This type occurs when an infection spreads to the bone from an adjacent tissue infection or open wound. It is common in adults with diabetic infections or following trauma or surgery.
- Vertebral osteomyelitis: A specific form of osteomyelitis that affects the spine, it can lead to severe back pain and potential neurological complications if not treated promptly.
- Osteomyelitis in immunocompromised patients: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with sickle cell disease, diabetes, or undergoing chemotherapy, are at higher risk for developing osteomyelitis and may require specialized care.
Understanding the different types of osteomyelitis is essential for healthcare practitioners to provide accurate diagnoses and effective treatments.
Symptoms of osteomyelitis
Recognizing the symptoms of osteomyelitis is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. The symptoms can vary depending on the type of osteomyelitis and the specific bone affected. Here are the common symptoms associated with this condition:
- Persistent and severe pain in the affected bone area is a hallmark symptom of osteomyelitis.
- Infected areas often become swollen, red, and warm to the touch.
- High fever and chills as the body responds to the infection.
- General feelings of tiredness and malaise can accompany the infection.
- Drainage of pus through the skin from an open wound near the infected bone.
- Reduced mobility or reluctance to use the affected limb or joint, particularly in children.
- Infected areas can be tender to touch and palpation.
- Severe and persistent back pain.
- Unintended weight loss can occur, especially in chronic cases.
- Profuse sweating during the night can be a symptom of ongoing infection.
These symptoms warrant immediate medical attention to prevent complications and promote effective treatment.
Causes and risk factors of osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis is primarily caused by bacterial infections, with Staphylococcus aureus being the most common pathogen. The infection can spread to the bone through the bloodstream, nearby tissue, or an open wound or surgery.
Risk factors include having a compromised immune system, diabetes, recent injury or surgery, and intravenous drug use. Conditions such as sickle cell disease and peripheral artery disease also increase susceptibility. Poor circulation and chronic conditions that affect blood flow to bones, like diabetic foot ulcers, further elevate the risk of developing osteomyelitis.
Diagnosing osteomyelitis
Diagnosing osteomyelitis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Here are the key steps in the diagnostic process:
- Medical history and physical exam: The doctor will review the patient’s medical history and conduct a thorough physical examination, focusing on the affected area to check for signs of infection such as pain, swelling, and warmth.
- Blood tests: Elevated white blood cell levels and markers of inflammation, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), can indicate an infection.
- Imaging studies: X-rays are used initially to detect changes in bone structure; magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provides detailed images of bone and soft tissue to identify the extent of the infection; computed tomography (CT) scans are used when MRI is not suitable, to provide cross-sectional images of the affected bone.
- Bone biopsy: This is a crucial step in which a sample of bone tissue is taken and analyzed to identify the specific organism causing the infection, guiding appropriate antibiotic therapy.
- Bone scan: This is a nuclear imaging technique that helps detect areas of high bone activity, which indicates infection or inflammation.
- Culture tests: If drainage from the wound occurs, the fluid may be cultured to identify the bacteria or fungi responsible for the infection.
These diagnostic steps are essential for confirming osteomyelitis and formulating an effective treatment plan. You can also use the Clinical Evaluation template to conduct thorough assessments of your clients' conditions.
Osteomyelitis Classification Table Template
Osteomyelitis Classification Table Example
Classification systems of osteomyelitis
Classification systems for osteomyelitis are essential for accurately diagnosing the type and severity of the infection in the bone, which guides effective treatment strategies. These systems help healthcare practitioners distinguish between acute and chronic osteomyelitis and assess the extent of the disease.
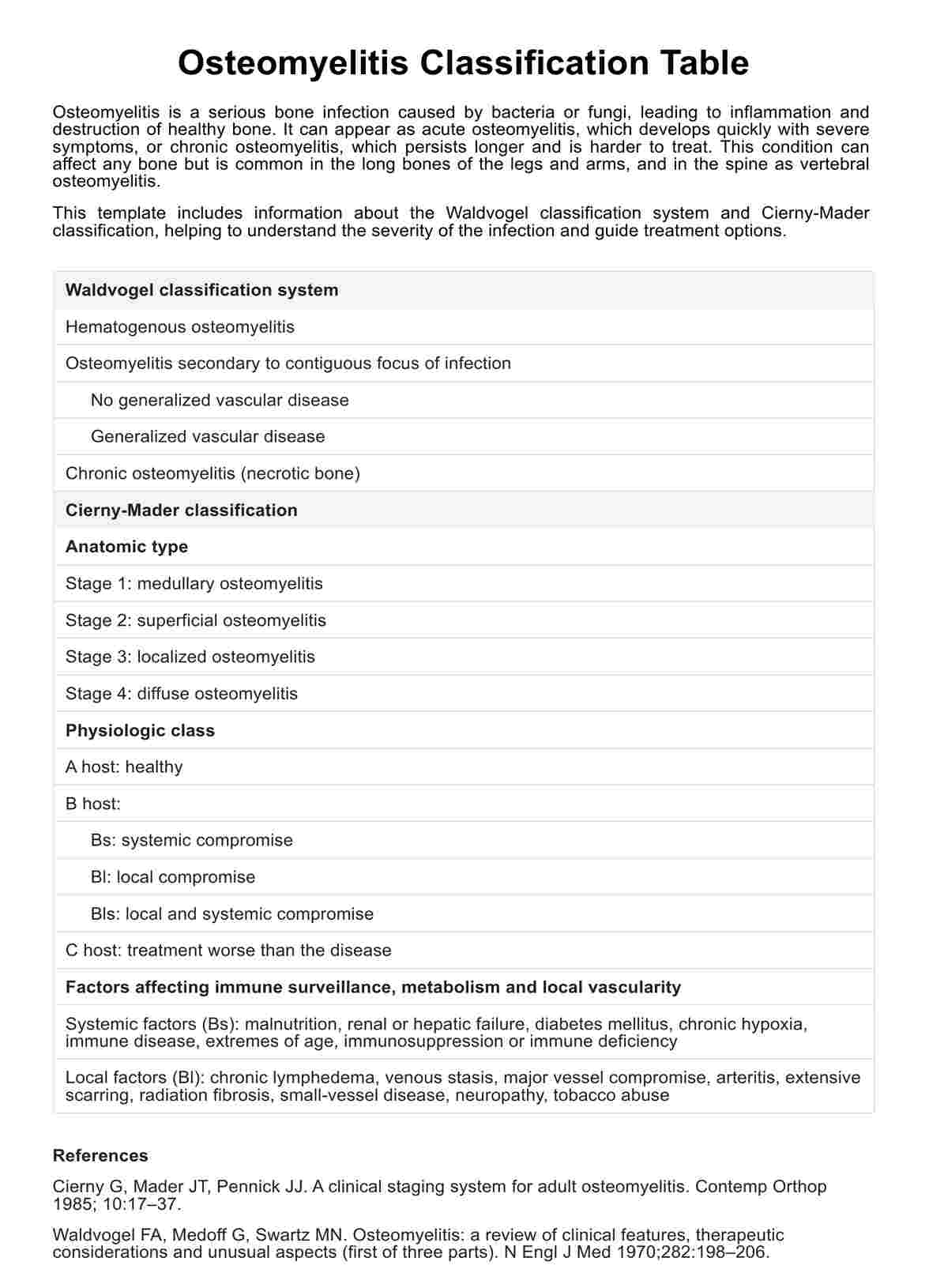
Waldvogel classification
The Waldvogel classification system categorizes osteomyelitis based on the infection's duration and mechanism. It divides osteomyelitis into acute osteomyelitis, which develops rapidly and requires prompt antibiotic therapy, and chronic osteomyelitis, characterized by persistent infection and necrotic bone. This system also identifies whether the infection is hematogenous, spreading through the bloodstream, or contiguous, spreading from adjacent tissue infection.
Cierny-Mader classification
The Cierny-Mader classification focuses on the anatomical and physiological aspects of infection in the bone. It categorizes osteomyelitis into four anatomical stages, considering factors like the involvement of soft tissues. This system is beneficial for planning surgical intervention and is often applied in cases such as vertebral osteomyelitis and diabetic foot infections.
Kingella classification
The Kingella classification emphasizes the microbiological and pathological aspects of osteomyelitis. It is beneficial for identifying infections caused by specific pathogens, such as Staphylococcus aureus. This system aids in determining the appropriate antibiotic therapy, especially for osteomyelitis in adults and individuals with underlying conditions like sickle cell disease.
What is an osteomyelitis classification?
An osteomyelitis classification is a systematic approach used by healthcare practitioners to categorize bone infections based on various factors such as the duration, cause, and location of the infection. This classification is vital for accurately diagnosing suspected osteomyelitis and determining the most effective treatment plan. For instance, acute osteomyelitis often requires prompt antibiotic treatment, while chronic cases might necessitate surgical debridement to remove necrotic tissue.
Osteomyelitis classifications also consider associated conditions, such as diabetes mellitus, which can complicate the infection due to vascular insufficiency. Blood cultures are typically used to identify the causative pathogens, especially in septic arthritis or spinal infections. Additionally, imaging techniques like MRI are employed to detect osteomyelitis and assess the involvement of soft tissue.
Through proper categorization of the infection, healthcare providers can better understand the severity and spread of the condition, particularly in complex cases involving vascular insufficiency or diabetic patients. This comprehensive approach ensures that patients receive tailored treatment, whether it involves antibiotics, surgery, or other interventions, to manage and resolve the infection effectively.
How to use our Osteomyelitis Classification Table template
Carepatron's Osteomyelitis Classification Table template includes the Waldvogel classification and Cierny-Mader classification, standing as an easy reference for healthcare professionals. It assists medical practitioners in systematically categorizing and managing osteomyelitis. Follow these steps to use the template effectively:
Step 1: Gather patient information
Begin by collecting comprehensive patient information, including medical history, symptoms, and risk factors such as diabetes mellitus or a history of vascular insufficiency. Document any signs of suspected osteomyelitis, such as localized pain, swelling, or fever.
Step 2: Conduct diagnostic tests
Perform necessary diagnostic tests to confirm the presence and type of osteomyelitis. This includes blood cultures to identify the causative bacteria, MRI scans to detect osteomyelitis and assess the involvement of soft tissue, and bone biopsies to determine the extent of the infection and presence of necrotic tissue.
Step 3: Classify the osteomyelitis
Using the information gathered, classify the osteomyelitis based on the template. This step helps in understanding the severity and nature of the bone infection.
Step 4: Develop a treatment plan
Based on the classification, develop a tailored treatment plan. Address underlying conditions, such as managing diabetes mellitus or improving vascular insufficiency, to support overall treatment efficacy.
Commonly asked questions
Osteomyelitis can be classified into acute, chronic, and subacute forms based on the duration and severity of the infection.
Osteomyelitis is a bone infection characterized by inflammation and destruction of bone tissue, often caused by bacterial or fungal pathogens.
The main cause of osteomyelitis is bacterial infection, with Staphylococcus aureus being the most common pathogen involved.