Neurological Exam Checklist
Enhance your neurological assessment process with our Neurological Exam Checklist Template. Download a copy here!


What is a neurological exam checklist?
A neurological examination checklist is a structured and systematic tool used by healthcare professionals to evaluate and document a patient’s neurological status. This comprehensive neurological exam assesses critical components of the nervous system, including mental status, cranial nerve function, motor strength, sensory perception, reflexes, and gait. By following this checklist, clinicians can identify neurological deficits, such as multiple cranial nerve deficits or other signs of dysfunction, that may indicate conditions like traumatic brain injury or neurological disease.
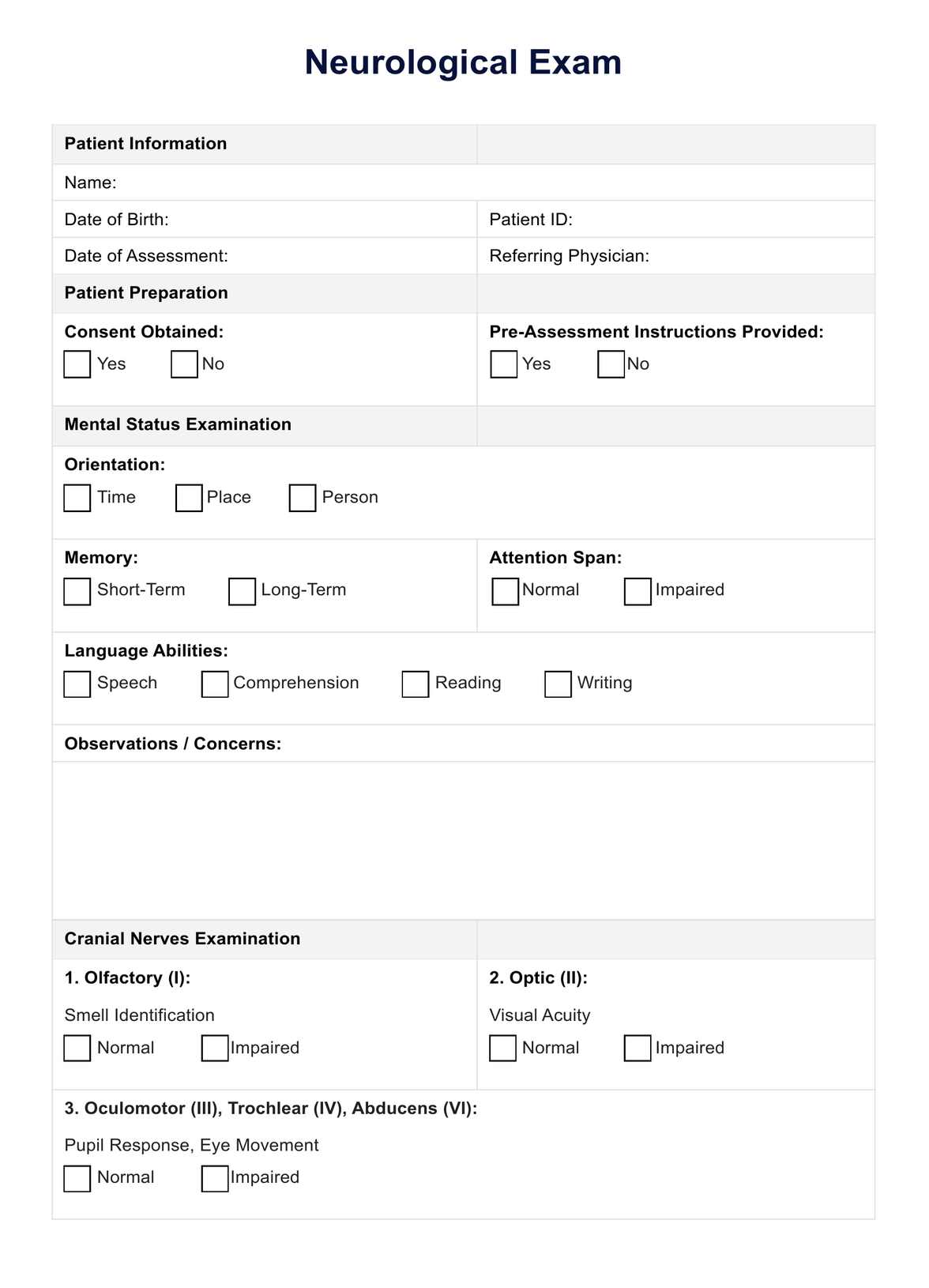
The neurological assessment checklist ensures thorough testing of the twelve cranial nerves, including cranial nerve I (olfactory nerve), cranial nerve ii (optic), cranial nerve VII (facial nerve), and cranial nerve XI (accessory). It also examines motor coordination, reflex responses, and sensory awareness. The checklist aids in detecting abnormalities in the central and peripheral nervous systems and supports clinical assessments during initial nurse-patient interactions and follow-up evaluations.
This tool can be helpful in the initial nurse-patient interaction and is essential for identifying neurological concerns and guiding treatment plans. The checklist also enhances communication among healthcare providers and ensures a standardized approach to neurological examinations in diverse clinical settings.
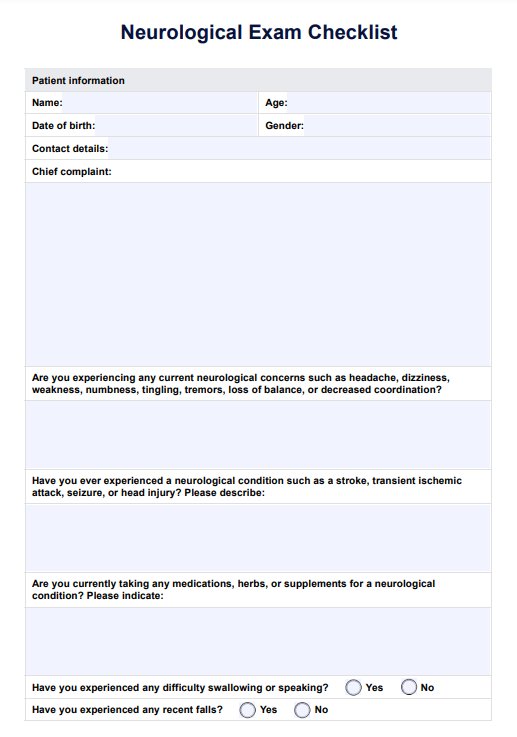
Neurological Exam Checklist Template
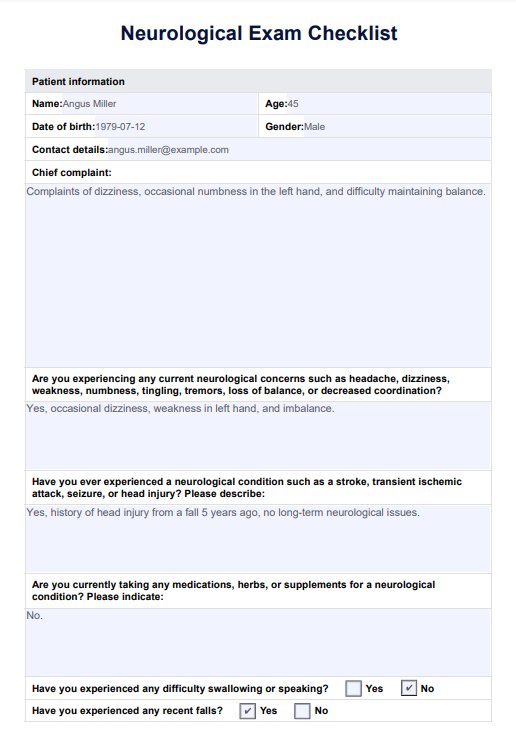
Neurological Exam Checklist Example
How does the Neurological Exam Checklist Template work?
The neurological exam checklist follows a structured approach to effectively assess a patient's neurological health. By systematically evaluating key areas such as mental status, cranial nerve function, motor coordination, sensory perception, reflexes, and gait, healthcare professionals can obtain critical insights into the patient's neurological condition and identify areas of concern.
Step 1: Access template from Carepatron
Start by accessing the Neurological Exam Checklist Template from this page by clicking on "Use template" or "Download." This ensures you have a standardized and comprehensive tool for the assessment.
Step 2: Gather patient information
Collect essential patient details, including name, age, date of birth, gender, and contact information, to personalize the checklist and ensure accurate record-keeping.
Step 3: Assess neurological functions
Systematically evaluate key neurological areas, including the level of consciousness, cranial nerve assessment, muscle strength, coordination, balance, sensory responses (touch, pain, temperature, proprioception), and reflexes.
Step 4: Document observations
Record all findings in the checklist accurately. Include any abnormalities or deviations from typical responses to establish a clear baseline for monitoring and future comparisons.
Step 5: Analyze findings
Review the documented results to identify any patterns or signs of neurological issues. Use this analysis to guide potential diagnostic steps and develop appropriate treatment plans.
Step 6: Communicate results
Discuss the findings with the patient in a professional and understandable manner. Address concerns, explain the implications of the results, and outline the next steps in their care plan.
When would you use this template?
Our neuro exam template can be helpful in the following contexts:
Initial patient evaluations
A Neurological Exam Checklist Template is essential for gathering baseline data during a patient's first assessment. It provides a comprehensive overview of the patient's neurological function, including mental status, motor function, cranial nerve assessments, and reflexes. This baseline is critical for identifying any deviations in the patient's neurological status over time and ensuring thorough clinical assessments.
Monitoring disease progression
For patients with neurological conditions like Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, or multiple sclerosis, a Neurological Exam Checklist Template enables consistent tracking of disease progression. By regularly assessing motor function, sensory exam results, and reflexes, healthcare professionals can detect changes in the nervous system and adjust treatment plans or medications accordingly.
Evaluating neurological symptoms
When patients present with neurological symptoms such as weakness, dizziness, headaches, or numbness, a Neurological Exam Checklist Template provides a systematic approach to evaluation. By focusing on sensory perception, motor coordination, and cranial nerve function, this checklist can help narrow down potential causes, including peripheral or central nervous system issues. For example, the checklist is particularly useful in identifying dizziness-related concerns.
Guiding diagnostic tests
Neurological exam findings play a vital role in directing further diagnostic testing. Abnormalities detected during assessments, such as in cranial nerve function or deep tendon reflexes, can guide advanced diagnostic tools like MRI, CT scans, EEG, or nerve conduction studies. These findings ensure that tests are targeted and yield actionable insights by pinpointing specific areas of concern.
Informing treatment decisions
The results from a neurological exam checklist directly inform treatment strategies for neurological conditions. Whether recommending therapies, rehabilitation programs, or medications, the comprehensive findings support tailored care. For conditions like traumatic brain injury or multiple cranial nerve deficits, these insights are integral to designing effective and personalized treatment plans.
What do normal results mean?
- Mental status: Normal mental status indicates that the patient is alert and oriented and exhibits no cognitive impairments, including inattention or difficulty communicating. Abnormal results, such as confusion, disorientation, or memory deficits, may indicate neurological dysfunction, including issues with the central nervous system (CNS).
- Cranial nerves: Normal cranial nerve function suggests that all twelve cranial nerves perform as expected, indicating proper sensory and motor function across the nervous system. Abnormalities in cranial nerve function, such as olfactory or facial nerve issues, could point to brain or brainstem problems.
- Motor function: Normal motor function means the patient exhibits adequate muscle strength and coordination with smooth, purposeful limb movements. Weakness, spasticity, or incoordination may suggest issues with the motor system, including the brain, spinal cord, or peripheral nervous system.
- Sensory function: Normal sensory function indicates that the patient perceives sensations such as touch, pain, temperature, vibration, and proprioception accurately. Numbness, tingling, or abnormal pain responses may signal issues with the sensory pathways of the spinal cord or peripheral nerves.
- Reflexes: Normal reflexes involve intact responses to stimuli, including deep tendon reflexes (DTRs) like the knee jerk and ankle jerk. Abnormal results, such as hyperreflexia or hyporeflexia, may suggest issues with the reflex arc or problems in the sensory and motor systems, potentially involving spinal cord or peripheral nerve dysfunction.
- Gait and station: A normal gait and station indicate that the patient can walk steadily and maintain balance. Abnormal results, such as shuffling, unsteadiness, or difficulty walking, may suggest cerebellar, basal ganglia, or peripheral nervous system dysfunction.
Commonly asked questions
Carepatron has a ready-to-download and use Neurological Exam Checklist template for your convenience.
Neurological Exam Checklist Templates are used in clinical assessment when healthcare professionals need to systematically assess a patient's neurological function.
Healthcare professionals use Neurological Exam Checklist Templates by systematically evaluating various aspects of the nervous system, including mental status, cranial nerves, motor function, sensory function, reflexes, and gait and station.













-template.jpg)