Internalized Homophobia Scale
Learn how to measure and understand internalized homophobia with Carepatron's free PDF download of the Internalized Homophobia Scale.


What is the Internalized Homophobia Scale?
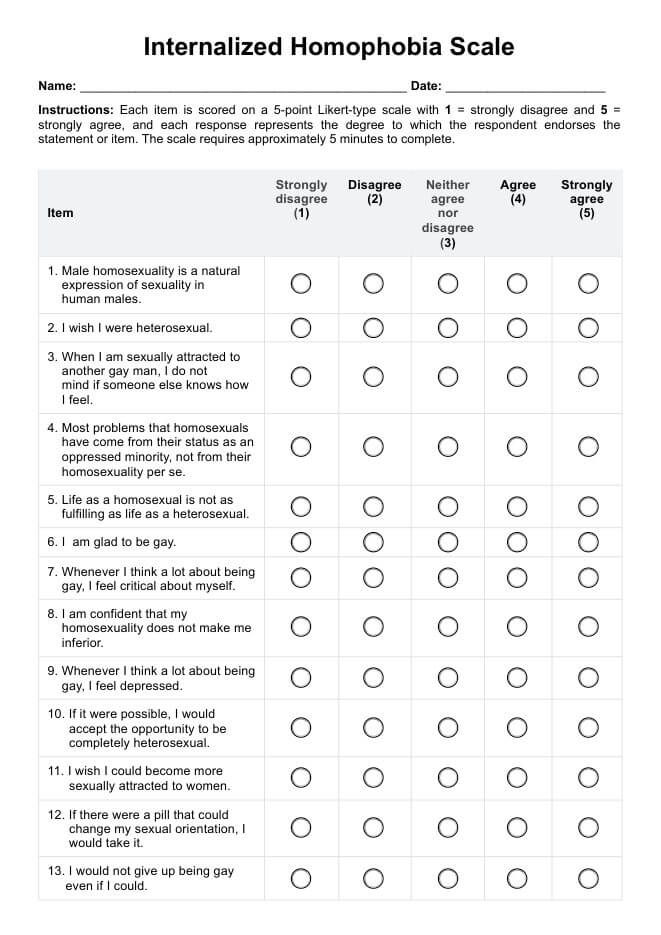
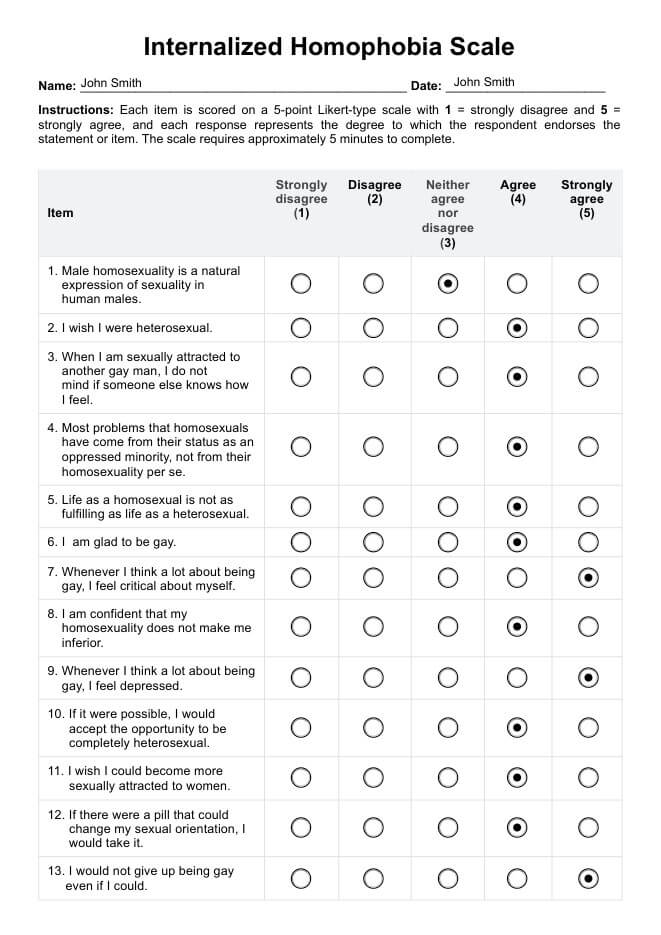
The Internalized Homophobia Scale (IHS) is a psychological instrument designed to assess internalized homophobia specifically among gay men. This scale evaluates the extent to which negative attitudes and beliefs about homosexuality become internalized and integrated into one's self-identity.
Comprising 20 items, the IHS includes 9 items from the Nungesser Homosexual Attitudes Inventory and 11 developed by the HIV Center for Clinical and Behavioral Studies at the New York State Psychiatric Institute. The scale functions as a self-report measure, with responses scored on a 5-point Likert scale from "Agree" to "Strongly disagree".
Measuring internalized homophobia is crucial as it reveals the extent to which individuals from sexual minority groups, particularly gay men, have internalized sexual stigma. This internalization can manifest as low self-esteem, demoralization, and general psychological distress based on perceived stigma. Studies have shown that those who experience high levels of internalized homophobia are more likely to feel uncomfortable with their sexual orientation and may struggle with avoidant coping mechanisms.
Internalized Homophobia Scale Template
Internalized Homophobia Scale Template
How to use our Internalized Homophobia Scale template
The Internalized Homophobia Scale template by Carepatron is designed to help healthcare professionals accurately assess and address the internalized stigma that individuals from sexual minorities may experience. This tool can be a vital part of mental health evaluations, providing insights that guide treatment and support. Below are the steps to effectively use the template in a clinical setting.
Access and download the scale template
To begin, access and download the Internalized Homophobia Scale template from Carepatron's platform. You may find the template from our Resource Library and download from there.
Review the scale content
Before using the scale with a patient, it's essential to review the content thoroughly. Familiarize yourself with the questions and the scoring system to ensure you can guide the patient through the process smoothly. The scale measures various aspects of internalized homophobia, so understanding the nuances of each item will help you interpret the results accurately and provide better support to the patient.
Introduce and use the scale with the patient
When introducing the Internalized Homophobia Scale to a patient, explain its purpose and importance in assessing internalized sexual stigma. Emphasize that the scale is a tool to help them understand how societal attitudes may have impacted their self-perception. Assure the patient that their responses will remain confidential and that the goal is to provide them with the best possible care and support.
Walk through and educate the patient on the scale
As the patient completes the scale, walk them through each question, ensuring they understand what is being asked. Educate them about the relevance of each section and how it relates to their experiences with internalized homophobia.
Discuss results with the patient
Once the scale is completed, take time to discuss the results with the patient. Highlight areas where internalized homophobia may be impacting their mental health and explore potential strategies for addressing these issues. This discussion is a key opportunity to provide education, support, and resources that can help the patient reduce the negative effects of internalized stigma and improve their overall well-being.
Scoring
The Internalized Homophobia Scale is scored by evaluating responses to 20 items, each designed to measure the level of internalized homophobia. Of these, 10 items are positively keyed, meaning higher agreement reflects higher internalized homophobia, while the other 10 items are negatively keyed, where they strongly agree meaning lower internalized homophobia.
The total score ranges from 20 to 100, with higher scores indicating greater levels of internalized homophobia. This scoring system helps healthcare professionals gauge the extent to which an individual has internalized negative societal attitudes about their sexual orientation.
Next steps after using the scale
After administering the Internalized Homophobia Scale, the next steps are crucial in supporting your patient effectively. Once the scale has been scored, it's essential to interpret the results in the context of the patient's overall mental health and well-being. This interpretation should take into account the patient’s score and how it reflects their internalized feelings of whom they're sexually attracted to. If the results indicate a high level of internalized homophobia, further exploration and intervention may be necessary.
Begin by discussing the findings with your patient in a sensitive and non-judgmental manner. Emphasize that the purpose of assessing internalized homophobia is to identify areas where the patient may need additional support. For patients who show high levels of internalized stigma, consider introducing additional tools like the gay and lesbian internalized homophobia scale, if applicable, to gain a broader understanding of their experiences.
Next, develop a treatment plan that addresses the specific issues identified by the scale. This may include counseling, cognitive-behavioral therapy, or other interventions aimed at reducing negative self-perceptions and perceived stigma. Using a rational theoretical approach to guide your treatment strategy, ensuring that it aligns with the patient's unique needs and experiences as a sexual minority.
Incorporate stigma measures into ongoing assessments to track progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed. Familiarity with the development and psychometric properties of the scale, as outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual, will ensure you are using evidence-based methods to support your patient.
Finally, encourage the patient to engage in activities and communities that affirm their identity and reduce feelings of isolation. Regularly revisit the scale or similar tools to measure improvements or shifts in the patient’s internalized homophobia, ensuring that the treatment plan remains effective and responsive to their evolving needs.
Commonly asked questions
Yes, homophobia can significantly contribute to anxiety by creating a hostile environment that exacerbates feelings of fear and insecurity about one’s sexual orientation. Individuals facing homophobia may experience heightened stress and apprehension, which can lead to chronic anxiety and mental health issues.
The stigma of homophobia refers to the negative attitudes and societal prejudices directed towards individuals based on their sexual orientation. This stigma can lead to discrimination, social exclusion, and internalized shame, affecting the overall well-being of those targeted.
Internalized homophobia can severely impact mental health by causing feelings of self-loathing, depression, and low self-esteem. When individuals internalize negative societal attitudes about their sexual orientation, it often results in significant emotional distress and psychological challenges.

















-template.jpg)