Eysenck's three personality types are extraversion, neuroticism, and psychoticism. These types represent the key dimensions in his personality theory, with extraversion reflecting sociability and the person being fairly self-confident, neuroticism indicating emotional stability, and psychoticism assessing tough-mindedness and aggression.
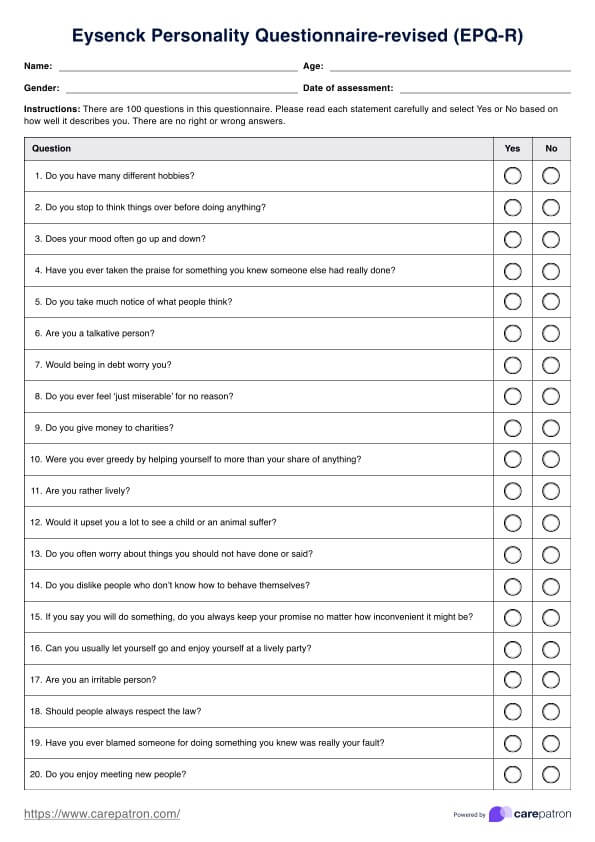
Eysenck Personality Questionnaire
Download Carepatron's free Eysenck Personality Questionnaire-revised (EPQ-R) PDF and learn how to use this assessment tool for personality evaluation.
Eysenck Personality Questionnaire Template
Commonly asked questions
The Eysenck Personality Questionnaire (EPQ) is a self-report assessment tool designed to measure the three core personality traits of Extraversion, Neuroticism, and Psychoticism, based on Eysenck's biological theory of personality. It is widely used in both clinical settings and personality research to evaluate individual personality characteristics.
The Eysenck personality test is considered a reliable tool, supported by numerous studies that demonstrate consistent results across various populations. However, like all personality assessments, its reliability can be influenced by factors such as the respondent's honesty and self-awareness.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











