Carepatron ensures high precision in monitoring, utilizing advanced algorithms and cross-referencing with medical benchmarks for accuracy.
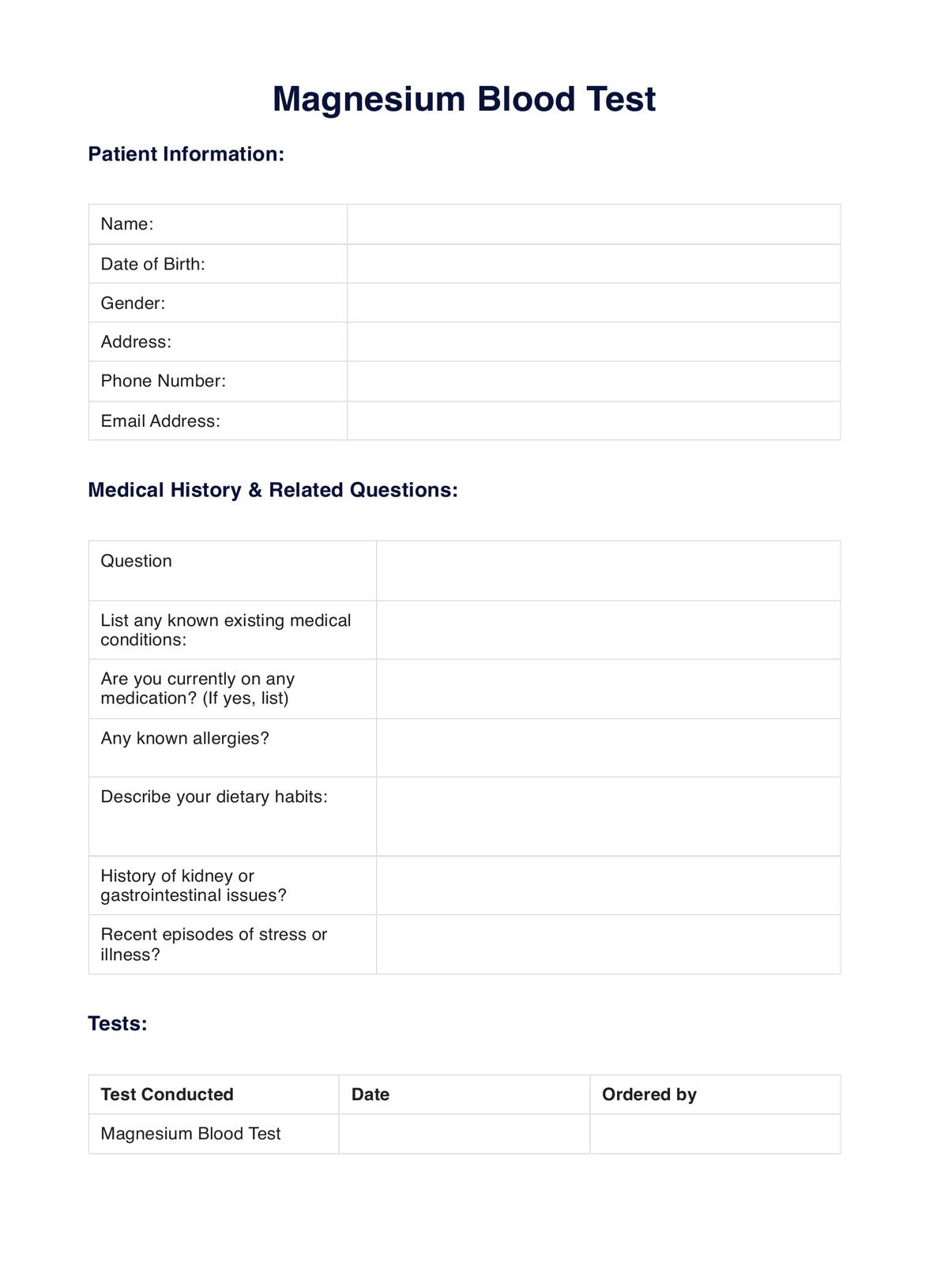
Magnesium Blood
Unlock efficient, compassionate care with Carepatron's Magnesium Blood App. Seamless monitoring, collaborative analysis, and improved patient outcomes await!
Use Template
Magnesium Blood Template
Commonly asked questions
Absolutely, Carepatron emphasizes collaborative healthcare and allows secure data sharing with consent.
Yes, Carepatron is versatile and designed for comprehensive health management, including various tests and health indicators.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











