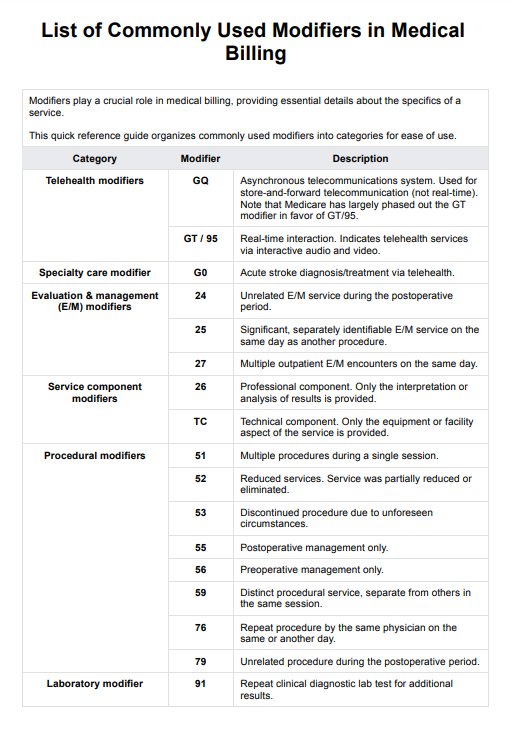
CPT modifiers are two-character codes added to CPT codes to provide additional information about a medical service or procedure. They help specify circumstances such as whether the service involved the same provider, a diagnostic procedure, or a separately identifiable evaluation and management service. Modifiers can also indicate technical details, such as a technical component, payment impacting modifiers, or services provided during the same operative session.
List of Commonly Used Modifiers in Medical Billing
Unlock precision in medical billing with Carepatron. Download our free List of Modifiers in Medical Billing PDF for accurate coding and improved reimbursements.
List of Commonly Used Modifiers in Medical Billing Template
Commonly asked questions
Modifiers are categorized as informational modifiers or payment modifiers. Informational modifiers clarify details without affecting reimbursement, such as anatomical modifiers that specify the separate structure where a service was performed. In contrast, payment impacting modifiers influence reimbursement rates, like those used for a primary procedure or durable medical equipment.
Yes, a qualified health care professional can use more than one modifier for the same procedure to describe different aspects of the service provided, as long as the modifiers are appropriate. For example, if an unusual non-overlapping service was performed or a repeat procedure was conducted by the same physician on the same day, using a payment modifier can clarify these circumstances. However, it is crucial to check payer-specific guidelines and the American Medical Association's coding rules to ensure the correct application of multiple modifiers and avoid claim rejections.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











