Healthcare audits serve several purposes, including ensuring quality care, identifying areas for improvement, preventing fraud and abuse, and guaranteeing adherence to regulations.
Healthcare Audit Checklist
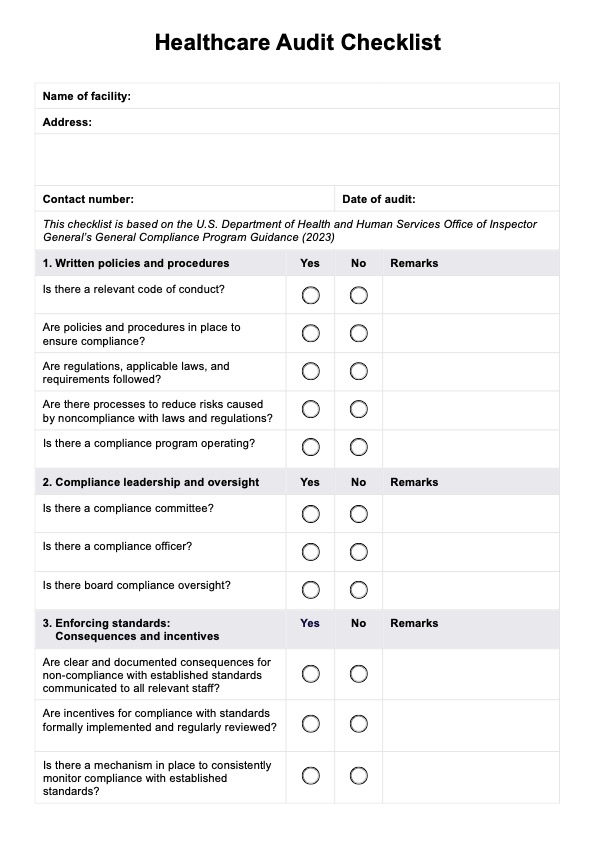
Ensure regulatory compliance and optimize patient care with our comprehensive Healthcare Audit Checklist. Download the template now.
Use Template
Healthcare Audit Checklist Template
Commonly asked questions
Auditors typically examine medical records, billing practices, and internal controls. They may also conduct interviews with staff and observe daily operations.
Healthcare audits come in different types: internal audits, external audits, clinical audits, random audits, federal government audits, and comprehensive audits.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











