Eversion Stress Test
Discover how to effectively utilize the Eversion Stress Test to assess ankle stability, particularly the deltoid ligament. Download our free PDF guide.


What is a medial ankle sprain?
A medial ankle sprain occurs when the deltoid ligament, which supports the medial (inner) side of the ankle, is damaged. This type of sprain is less common than lateral ankle sprains but can be more severe due to the strength and structure of the deltoid ligament.
Causes typically include traumatic events such as sudden twists or impacts during physical activity. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and ankle instability, with risk factors including previous ankle injuries and activities involving abrupt changes in direction or uneven surfaces.
Eversion Stress Test Template
Eversion Stress Test Example
What is the Eversion Stress Test?
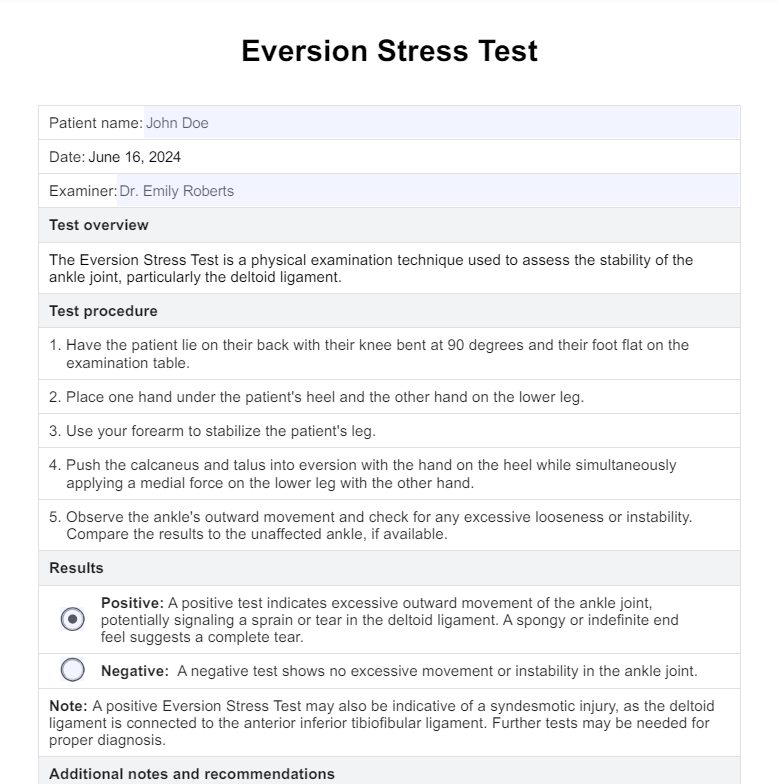
The Eversion Stress Test is a diagnostic tool used to evaluate the integrity of the deltoid ligament of the ankle joint. This physical examination helps determine the presence of injuries by assessing the stability of the ankle joint when an eversion, or outward turning force, is applied to the foot.
How to conduct the Eversion Stress Test?
To accurately perform the Eversion Stress Test, follow these detailed steps:
- Position the patient supine on the examination table, with the knee bent at a 90-degree angle and the foot flat, ensuring the patient's leg is relaxed. This neutral position is crucial for an accurate assessment.
- Secure the patient’s heel with one hand. Use your forearm to stabilize the lower leg. This prevents extraneous movement that could affect the results.
- With your free hand, gently apply an outward force to the patient's foot, turning it away from the body's midline. This maneuver assesses the integrity of the medial structures of the ankle, especially the deltoid ligament.
- Carefully observe the ankle's movement. Feel for any looseness or instability, which could indicate a sprain or tear in the ligaments. Note the degree of eversion and any pain elicited during this step.
- If possible, compare the findings with those of the unaffected ankle. This comparison helps determine the relative severity of the injury and provides a baseline for recovery.
- Record your observations meticulously to ensure continuity in diagnosis and treatment. For enhanced diagnostic accuracy and to support your clinical examination findings with visual aids, download our detailed Eversion Stress Test.
By following these steps, healthcare professionals can ensure a thorough and precise assessment of the ankle range. This is critical in sports medicine and orthopedic settings, where the accurate diagnosis of ankle injuries is paramount.
Results and next steps of the Eversion Stress Test
Positive results typically show excessive mobility or pain, indicating possible ligament damage. Following a positive test, it is recommended to perform additional imaging tests, such as an MRI, for a comprehensive assessment. Documenting the findings using our detailed template ensures precise monitoring and follow-up.
Benefits of using our template
Our template offers the following benefits:
Offers a standardized method of documentation
Our free Eversion Test template lets you document your tests in a systematic and standardized manner. With clearly defined sections and headings, you can easily organize your documentation and ensure consistency across all your tests. This makes it easier for your team to understand and follow the test procedure, leading to more accurate results.
Saves time and effort
Creating a test document from scratch can be time-consuming and requires significant effort. Our template provides a ready-made structure that you can easily customize according to your specific needs. This not only saves time but also ensures that no important details are missed while documenting the test process.
Improves communication
Using our template ensures that all team members are on the same page when it comes to understanding the test process. The standardized format makes it easier for everyone to understand and follow the documented steps, leading to better communication within your healthcare team. This can also help avoid misunderstandings or errors that may occur due to miscommunication.
Fully digital and easily accessible
Our template is available in a digital format, making it easily accessible. This eliminates the need for physical copies of documents, reducing clutter and making it easier to update or share important information with your patient.
Management and treatment of medial ankle sprains
The management of medial ankle sprains involves a combination of rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). This should be initiated immediately after the injury occurs to reduce pain and swelling. Over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can also help with pain relief and inflammation reduction.
In addition to RICE therapy, it is important to limit weight-bearing activities on the injured foot and use crutches if necessary. This will help to prevent further damage and allow the ligaments to heal properly.
Physical therapy
Once the initial pain and swelling have subsided, physical therapy can be beneficial in strengthening the muscles around the ankle joint and improving range of motion. A physical therapist may also use techniques such as manual therapy, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation to aid in healing.
Bracing
In cases of more severe sprains or for athletes returning to sports that involve twisting movements, a brace or taping may be recommended for additional support. This can help to prevent re-injury and provide stability during activity.
Surgery
In rare cases where the ligaments are severely torn or there is a significant instability in the joint, surgery may be necessary. This typically involves repairing the damaged ligaments and may require a period of immobilization followed by physical therapy to regain strength and range of motion.
Prevention
To prevent medial ankle sprains, it is important to maintain strong muscles around the ankle joint through regular exercise and stretching. Wearing appropriate footwear for specific activities can also help prevent injury. It is also essential to warm up before any physical activity and avoid sudden changes in direction or uneven surfaces.
Commonly asked questions
The Eversion Stress Test evaluates the deltoid ligament's integrity, which is crucial for diagnosing medial ankle sprains, unlike other tests that may assess different aspects of ankle stability.
While it can be performed independently, it is recommended to use this test with other diagnostic tools for a comprehensive evaluation of ankle injuries.
The Eversion Stress Test uniquely evaluates the integrity of the deltoid ligament, whose physical examination is essential for diagnosing medial ankle sprains. Unlike other tests focusing on lateral ankle stability or different ligament groups, this test specifically assesses medial stability, providing targeted insights into the deltoid ligament's condition and the ankle's medial aspect.

.jpg)