DN4 Questionnaire
Learn about the DN4 Questionnaire, its purpose, and how to use it with Carepatron's free PDF download. Get an example questionnaire to guide you in assessing neuropathic pain.


What is neuropathic pain?
Neuropathic pain is a complex and chronic pain condition that arises from damage or dysfunction within the nervous system. Unlike pain that results from an injury, neuropathic pain stems from nervous or somatic lesions, which can be due to various factors such as diabetes, spinal cord injury, or infections like shingles. This type of pain is often characterized by unusual sensations, such as painful colds or a burning feeling, and can be persistent and debilitating.
Neuropathic pain components include both spontaneous and evoked pain, with symptoms sometimes occurring without any apparent trigger. The neuropathic pain component is essential to understand because it requires different management strategies compared to other types of chronic pain. The clinical examination for neuropathic pain typically involves assessing these unique symptoms and identifying the underlying neuropathic characteristics.
To aid in the differential diagnosis of neuropathic pain syndromes, healthcare practitioners use tools like the neuropathic pain diagnostic questionnaire, specifically the version of the Douleur Neuropathique en 4 Questions (DN4) Questionnaire. Pain medicine tailored to neuropathic pain components often includes medications that target nerve pain specifically, effectively addressing both central neuropathic pain and peripheral neuropathic pain.
Understanding neuropathic pain and its distinct characteristics is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment, ensuring that individuals receive the appropriate care for their specific pain condition.
Characteristics of neuropathic pain
Neuropathic pain presents with distinct characteristics that set it apart from other types of pain. These symptoms can vary widely but share common features that help in identifying neuropathic pain.
- Burning sensation: A persistent burning feeling that can be intense and debilitating.
- Painful cold: Sensations of painful colds are often described as a freezing or icy feeling.
- Electric shock-like pain: Sudden, sharp, and jolting pains similar to an electric shock.
- Tingling or "pins and needles": A constant or intermittent tingling sensation, also known as paresthesia.
- Allodynia: Pain caused by stimuli that don’t normally provoke pain, such as a light touch.
- Hyperalgesia: An increased sensitivity to pain, making even mild pain feel severe.
- Numbness: Areas of reduced sensation, which can be coupled with pain in other areas.
- Spontaneous pain: Pain that occurs without any obvious trigger or cause.
- Altered sensation: Changes in the way sensations are felt, such as feeling pain instead of touch.
Understanding these characteristics is essential for accurately diagnosing and managing neuropathic pain, ensuring effective treatment strategies for those affected.
Causes of neuropathic pain
Neuropathic pain stems from various conditions or injuries affecting the nervous system. One common cause is nerve damage resulting from diseases like diabetes, autoimmune disorders, or infections such as herpes zoster (shingles). Trauma to the spinal cord or diseases affecting it can also lead to neuropathic pain.
Additionally, strokes causing brain damage, particularly in areas involved in pain processing, can result in neuropathic pain. Conditions like multiple sclerosis (MS) where the immune system targets nerve coverings contribute to neuropathic pain.
Tumors pressing on nerves or treatments like chemotherapy in cancer patients can also induce neuropathic pain. Even surgical procedures can sometimes lead to nerve damage and subsequent neuropathic pain.
Understanding these varied causes is essential for diagnosing and treating neuropathic pain effectively.
DN4 Questionnaire Template
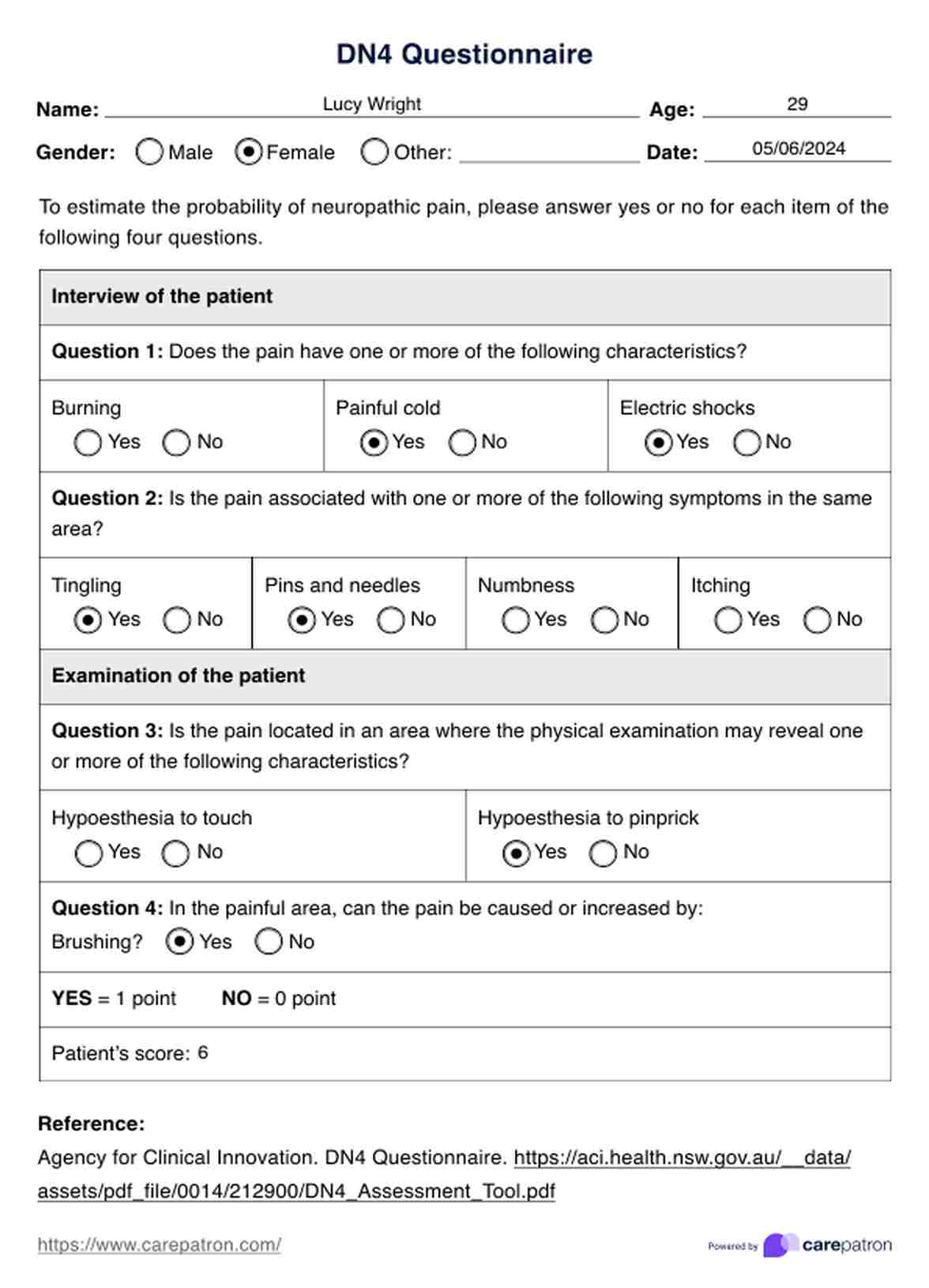
DN4 Questionnaire Example
What is the DN4 Questionnaire?
The Douleur Neuropathique en 4 Questions or DN4 Questionnaire is a widely used tool for assessing neuropathic pain in clinical practice. Developed by Bouhassira et al., it provides a structured approach to identifying neuropathic pain components within chronic pain syndromes. The questionnaire consists of ten items, seven focusing on neuropathic symptoms and three on physical exam findings.
Its primary aim is to differentiate between neuropathic and non-neuropathic pain components, aiding in diagnosing and managing neuropathic pain disorders. Identifying symptoms such as burning sensations, electric shock-like pains, and numbness, alongside physical exam findings like hypoesthesia and allodynia, the DN4 Questionnaire helps clinicians in their differential diagnosis.
Incorporating the DN4 Questionnaire into clinical practice enhances the systematic assessment of neuropathic pain, leading to more targeted and effective treatment approaches.
What to expect when using this questionnaire
Medical practitioners can expect a straightforward and structured approach to assessing neuropathic pain when using the DN4 Questionnaire. The questionnaire provides a systematic way to identify neuropathic pain components within chronic pain syndromes, aiding in differential diagnosis and treatment planning.
Expect clear and concise questions that address neuropathic symptoms. The DN4 Questionnaire streamlines the assessment process, efficiently helping clinicians differentiate between neuropathic and non-neuropathic pain components.
Additionally, medical practitioners can anticipate reliable and validated results, as the DN4 Questionnaire has undergone rigorous testing and validation in various patient populations. Its user-friendly format allows for easy administration in clinical settings, enhancing the overall assessment of neuropathic severity of pain and guiding appropriate management strategies.
How is this questionnaire scored, and how are the results interpreted?
The scoring and interpretation of the DN4 Questionnaire follow a structured process based on the patient's responses. Each item in the questionnaire is carefully designed to assess specific neuropathic pain symptoms and physical examination findings.
The DN4 Questionnaire is a quick and easy tool used to identify potential neuropathic pain. Here's how it's scored and interpreted:
Scoring:
- Each question has a yes or no answer.
- One point is awarded for each "yes" answer.
- No points are given for "no" answers.
- Add up the points from all ten questions.
Interpretation:
- A score of 4 or higher out of 10 suggests a likelihood of neuropathic pain.
- Scores below 4 are considered negative for neuropathic pain.
Scoring typically involves assigning points to each item based on whether the symptom or finding shows either a positive predictive value or a negative predictive value. The total score is then calculated by summing up the points across all items.
While the DN4 is a helpful screening tool, it's not a definitive diagnosis. A score above the threshold indicates a need for further evaluation by a healthcare professional. The doctor will likely perform a physical examination and may order additional tests to confirm or rule out neuropathic pain.
The development and validation of the DN4 Questionnaire involved a meticulous process, including concept definition, translation steps, and testing with patients. Three items—painful colds, tingling, and pins and needles—were mainly discussed during the conceptual definition and translation steps. Collaboration with the developer facilitated the definition of their meaning and the finding of conceptual equivalents.
How does our DN4 Questionnaire template work?
Carepatron's DN4 Questionnaire template provides medical practitioners with a user-friendly and efficient tool for assessing neuropathic pain in their patients.
The template streamlines administering and scoring the DN4 Questionnaire, enhancing the overall assessment of severity of the pain and guiding appropriate treatment strategies.
Step 1. Access the template
Medical practitioners can access the DN4 Questionnaire template through Carepatron's platform. The template is readily available for use, eliminating manual creation or customization.
Step 2: Administer the questionnaire
Practitioners can easily administer the DN4 Questionnaire to patients directly through the Carepatron platform. The questionnaire is presented in a clear and structured format, allowing patients to provide responses to each item efficiently.
Step 3: Score the questionnaire
Once patients have completed the questionnaire, Carepatron's DN4 template, calculate the total score based on the responses provided.
Step 4: Documentation and follow-up
Practitioners can easily record the questionnaire's score within the template, ensuring comprehensive patient records and enabling seamless clinical documentation.
Benefits of using this questionnaire
Utilizing the DN4 Questionnaire in medical practice offers several benefits for both medical practitioners and patients diagnosed with neuropathic pain conditions.
Enhanced diagnostic accuracy
The DN4 Questionnaire provides a structured approach to assessing neuropathic pain components, aiding in the accurate diagnosis of neuropathic pain conditions. By systematically evaluating symptoms and physical examination findings, clinicians can differentiate between neuropathic and non-neuropathic pain complaints more effectively.
Efficient screening tool
Carepatron's version of the DN4 Questionnaire offers a user-friendly and efficient screening tool for neuropathic pain. Its clear and concise format allows for quick administration and scoring, saving valuable time during patient assessments.
Improved treatment planning
By identifying neuropathic pain components using the DN4 Questionnaire, medical practitioners can tailor treatment plans to target specific symptoms and underlying causes. This personalized approach to treatment leads to better outcomes for patients, alleviating their neuropathic pain and improving their quality of life.
High predictive value
The DN4 Questionnaire demonstrates high positive and negative predictive values for identifying neuropathic pain components. Its ability to accurately detect neuropathic pain, especially in patients with a history of nerve trauma or neuropathic conditions, enhances diagnostic confidence and guides appropriate management strategies.
Neuropathic pain treatments
Neuropathic pain can be challenging to manage, but several treatment options can help alleviate symptoms and improve patients' quality of life.
Medications
Medications are often the first line of treatment for neuropathic pain. Commonly prescribed medications include anticonvulsants such as gabapentin and pregabalin, which work by stabilizing nerve activity and reducing pain signals. Tricyclic antidepressants like amitriptyline can also be effective in managing neuropathic pain by altering the way pain signals are processed in the brain.
Physical therapy
Physical therapy techniques such as stretching exercises, massage therapy, and nerve stimulation can help reduce neuropathic pain symptoms. Physical therapists can also educate patients on proper posture and body mechanics to minimize pain and improve function.
Nerve blocks
Nerve blocks involve injecting anesthetic or anti-inflammatory medications directly into the affected nerves to block pain signals. This procedure can provide temporary relief from neuropathic pain and may be repeated as needed for long-term management.
Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS)
SCS involves implanting a device near the spinal cord that delivers electrical impulses to interfere with pain signals, reducing the perception of pain. This treatment is often reserved for patients who have not responded to other therapies and can provide significant relief for chronic neuropathic pain.
Complementary therapies
Complementary therapies such as acupuncture, biofeedback, and mindfulness meditation may help reduce neuropathic pain symptoms and improve overall well-being. While these therapies may not provide complete pain relief on their own, they can complement traditional treatments and enhance their effectiveness.
Commonly asked questions
The DN4 Questionnaire, or Douleur Neuropathique en 4 Questions, is a tool used to assess neuropathic pain. It consists of ten items, seven focusing on symptoms and three on physical examination findings.
The DN4 Questionnaire has high sensitivity for detecting neuropathic pain, making it a valuable tool for screening patients with suspected neuropathic pain conditions.
To score the neuropathic pain questionnaire, assign points to each item based on the patient's responses and calculate the total score. A higher score indicates a higher likelihood of neuropathic pain.