Celiac Disease Diet Plan
Get our free Celiac Disease Diet Plan to guide dietary recommendations and support symptom management in patients.


What is a celiac diet?
A celiac diet is a strict gluten-free diet that eliminates all gluten-containing foods to prevent immune reactions in individuals with celiac disease (Aljada et al., 2021). Gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye (Biesiekierski, 2017), triggers intestinal damage in affected individuals, leading to malabsorption and gastrointestinal symptoms. This diet requires avoiding grains, pasta, cereals, and processed foods unless explicitly labeled gluten-free.
Patients can consume naturally gluten-free foods such as meat, fish, fruits, vegetables, and grains like rice and quinoa. Many gluten-free foods have gluten-free versions, including breads and pasta. Adherence to a gluten-free diet is a lifelong necessity for individuals with celiac disease to manage symptoms, promote intestinal healing, and prevent complications.
Proper label reading and awareness of cross-contamination risks are crucial to maintaining a safe diet. Even small amounts of gluten from eating gluten can cause adverse effects, making strict compliance essential.
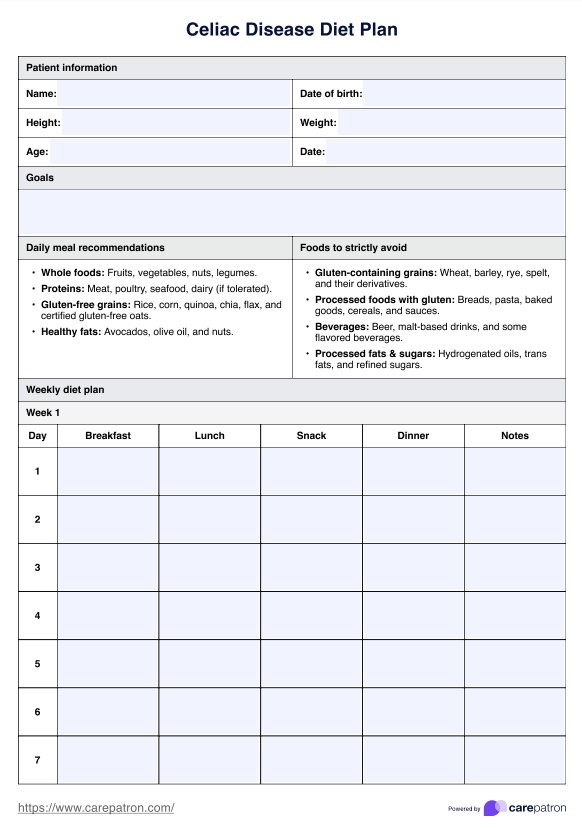
Celiac Disease Diet Plan Template
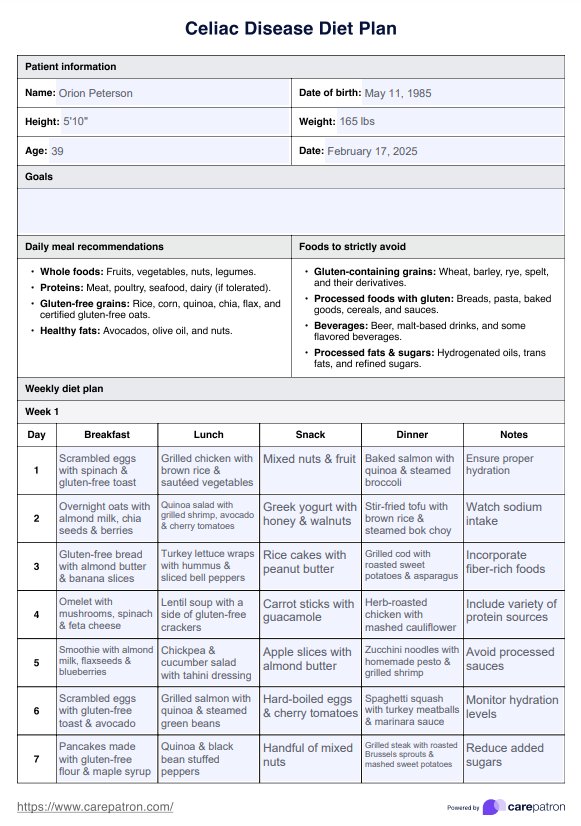
Celiac Disease Diet Plan Example
What is a Celiac Disease Diet Plan?
A Celiac Disease Diet Plan is a meal plan that eliminates gluten to prevent adverse immune reactions in people with celiac disease, gluten intolerance, or non-celiac gluten sensitivity. This gluten-free diet removes wheat, barley, and rye while incorporating nutritious foods that support digestive health. Individuals following this plan must choose gluten-free options such as gluten-free bread, grains, and naturally gluten-free products.
Adopting a healthy diet with balanced macronutrients is crucial, ensuring adequate fiber, protein, and vitamins. Since many gluten-free products lack certain nutrients, choosing whole, minimally processed foods is essential for maintaining long-term health.
Food to include
A Celiac Disease Diet Plan should emphasize nutritious foods that are naturally gluten-free and support a healthy diet. Eating gluten-free includes consuming fresh fruits and vegetables, which provide essential vitamins and fiber. Lean proteins such as poultry, fish, and seafood are excellent choices. Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt are typically safe unless lactose intolerance exists.
Legumes, beans, and nuts are great plant-based protein sources. Whole grains such as rice, corn, potato, flax, and chia are excellent alternatives to wheat-based products. Certified gluten-free flours like almond, coconut, and tapioca can be used for baking.
Many gluten-free products, including gluten-free bread and pasta, are available to replace wheat-based foods. Oats are acceptable if labeled gluten-free and consumed in moderation. Homemade soups and sauces without gluten-containing additives are also good dietary choices.
Foods to avoid
For individuals eating gluten-free, avoiding gluten-containing foods is crucial. This includes wheat, barley, rye, and any products derived from them. Processed carbohydrates such as conventional breads, pasta, cookies, and cakes should be replaced with gluten-free options. Gluten-free flour should be used instead of wheat flour in cooking and baking. Beverages like beer and malt alcohol contain gluten and must be excluded.
Many condiments, including soy sauce, salad dressings, and marinades, often contain hidden gluten and require careful label checking. Processed fats, including trans fats and hydrogenated oils, may also contribute to inflammation and should be limited. High-sugar foods should be minimized to maintain a balanced meal plan. Since many gluten-free products can be highly processed, selecting whole, nutritious foods is recommended to ensure a healthy diet while eating gluten-free.
How does it work?
Carepatron’s Celiac Disease Diet Plan makes dietary management easier, ensuring a structured approach to guiding patients. This gluten-free diet template helps you assess nutritional needs, educate patients, and develop personalized meal plans. Follow these steps to integrate the template into your practice.
Step 1: Access the template
Click "Use template" to open the Celiac Disease Diet Plan directly in Carepatron. This will prompt you to access the platform to download or customize the template seamlessly. For a fillable PDF version, click "Download."
Step 2: Introduce the diet plan to the patient
Explain the purpose of the gluten-free diet and its importance for people with celiac disease. Clarify the need to eliminate gluten-containing foods and emphasize the role of gluten-free products in preventing complications. Encourage patient compliance by outlining the health benefits of adhering to a structured meal plan.
Step 3: Discuss meal plans and goals with patient
Work with patients to establish dietary goals and personalize their gluten-free options based on preferences and nutritional needs. Use the template to structure a healthy diet, ensuring a balanced intake of nutritious foods, including gluten-free bread, grains, and proteins. Address any patient concerns about meal planning and nutrient adequacy.
Step 4: Provide additional patient education
Educate patients on reading food labels to identify labeled gluten-free items and avoid hidden gluten in soy sauce, condiments, and processed foods. Discuss cross-contamination risks, recommend trusted gluten-free flours, and guide them in selecting many gluten-free products that support a sustainable gluten-free diet.
Step 5: Save and implement
You can easily save the completed Celiac Disease Diet Plan within Carepatron for streamlined record-keeping. The template integrates into medical workflows, allowing you to revisit dietary plans, adjust recommendations, and track patient progress.
Benefits of using this diet plan
Our Celiac Disease Diet Plan helps you efficiently guide patients who need to follow a gluten-free lifestyle. The format allows you to customize dietary recommendations, ensuring patients eat foods that prevent complications associated with gluten triggers. The plan simplifies meal planning by categorizing safe and unsafe foods, reducing the risk of accidental exposure.
Registered dietitians and clinicians can use this template to create a balanced diet tailored to individual patient needs, ensuring adequate nutrient intake while eliminating gluten.
Additionally, the template educates patients on what foods contain gluten, such as processed grains, while incorporating nutritious alternatives. The approach improves patient compliance, streamlines documentation, and ensures consistency in dietary guidance, making it an essential tool for effective gluten-free diet management.
References
Aljada, B., Zohni, A., & El-Matary, W. (2021). The gluten-free diet for celiac disease and beyond. Nutrients, 13(11), Article 3993. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113993
Biesiekierski, J. R. (2017). What is gluten? Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 32(S1), 78–81. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.13703
Commonly asked questions
Healthcare professionals, including registered dietitians, gastroenterologists, and primary care providers, request this plan for patients diagnosed with celiac disease or gluten intolerance. It helps ensure patients follow a gluten-free diet while maintaining a balanced diet with proper nutrition.
While eliminating gluten-containing foods is essential, a Celiac Disease Diet Plan must also include nutritious foods to prevent deficiencies. Patients should consume fiber, protein, and essential vitamins while avoiding processed, high-sugar, gluten-free products that lack nutritional value.
Symptoms often improve within a few weeks of strictly eating gluten-free, but complete intestinal healing can take months to years, depending on severity. Continued adherence to the gluten-free diet is necessary to prevent symptoms and long-term complications.