Arm Squeeze Test
Learn all about the Arm Squeeze Test with examples on our website. Get Carepatron's free PDF download today!


What is cervical nerve root compression?
Cervical nerve root compression, often called cervical radiculopathy, is a condition characterized by the compression or irritation of nerve roots in the cervical spine, particularly in the middle third of the neck. This compression can result from various factors such as cervical spine disease, including herniated discs or bone spurs, leading to symptoms that commonly manifest as neck pain, shoulder pain, and upper arm discomfort.
Understanding cervical nerve root compression is crucial, especially in patients presenting with shoulder pathology or upper arm compared to shoulder pain. Often, the symptoms of cervical radiculopathy can mimic those of other shoulder diseases, such as a rotator cuff tear, making it a somewhat doubtful diagnosis without proper clinical tests.
The Arm Squeeze Test is a valuable clinical tool in assessing patients with cervical nerve root compression. It involves applying pressure to the patient's upper arm while monitoring for any exacerbation of symptoms associated with median nerve compression. This test helps healthcare practitioners differentiate between shoulder pathology and cervical spine-related issues, aiding in accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning for patients with suspected cervical nerve root compression.
Symptoms of cervical nerve root compression
Cervical nerve root compression can manifest through various symptoms, indicating potential nerve impingement or irritation in the cervical spine. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for prompt diagnosis and management. Common manifestations include:
- Neck pain, often radiating to the shoulder or upper arm
- Tingling or numbness in the fingers, hand, or forearm
- Weakness in the muscles of the arm or hand
- Difficulty with fine motor skills, such as gripping objects or buttoning clothing
- Pain exacerbated by certain movements or positions, such as neck extension or turning the head to the affected side
- Sensory changes, such as hypersensitivity or altered sensation along the affected nerve distribution
- Muscle spasms or stiffness in the neck or upper back
These symptoms may vary in intensity and presentation depending on the severity and location of the nerve compression. It's essential for individuals experiencing these symptoms, especially in conjunction with shoulder pain or upper arm discomfort, to seek medical evaluation for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Causes
Cervical nerve root compression can arise from various underlying factors, leading to nerve impingement or irritation in the cervical spine. Understanding the potential causes is essential for identifying risk factors and guiding appropriate management strategies. Some common causes include:
- Herniated discs: Discs in the cervical spine may bulge or herniate, exerting pressure on nearby nerve roots.
- Degenerative changes: Age-related wear and tear on the cervical spine, such as osteoarthritis or spinal stenosis, can narrow the spinal canal and compress nerve roots.
- Bone spurs: Abnormal bony growths, known as osteophytes or bone spurs, can develop in response to degenerative changes, contributing to nerve compression.
- Traumatic injury: Accidents or trauma to the neck region can cause fractures, dislocations, or soft tissue injuries that impinge on cervical nerve roots.
- Tumors: Rarely, tumors or abnormal growths within or near the cervical spine can compress nerve roots, leading to symptoms of cervical radiculopathy.
- Inflammatory conditions: Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis can cause inflammation and structural changes in the cervical spine, potentially resulting in nerve compression.
Arm Squeeze Test Template
Arm Squeeze Test Example
What is the Arm Squeeze Test?
The Arm Squeeze Test is a clinical assessment tool used to aid in the diagnosis of cervical nerve root compression, particularly in patients presenting with symptoms such as shoulder pain or discomfort in the upper arm compared to the shoulder. This simple yet effective test involves applying pressure to the patient's upper arm while observing for any exacerbation of symptoms associated with median nerve compression.
In cases where cervical radiculopathy is suspected, distinguishing between shoulder pathology and cervical spine-related issues can be challenging due to overlapping symptoms. The Arm Squeeze Test serves as a valuable diagnostic aid in such scenarios, helping healthcare practitioners differentiate between conditions like rotator cuff tears and cervical root compression.
During the Arm Squeeze Test, pressure applied to the patient's upper arm may elicit characteristic symptoms indicative of cervical nerve compression, such as radiating pain or tingling sensations along the affected nerve distribution. By reproducing these symptoms, the test provides valuable clinical information, aiding in the confirmation or exclusion of cervical spine involvement in cases where the diagnosis is uncertain.
Given its simplicity and efficacy, the Arm Squeeze Test is significant in clinical practice, particularly when faced with a doubtful diagnosis of cervical radiculopathy versus other shoulder diseases. Incorporating this test into diagnosing patients with neck pain or shoulder pathology can facilitate accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
How is this conducted?
The Arm Squeeze Test is a straightforward clinical procedure that can be easily performed by healthcare practitioners to aid in the assessment of cervical nerve root compression. Below are the steps involved in conducting the Arm Squeeze Test:
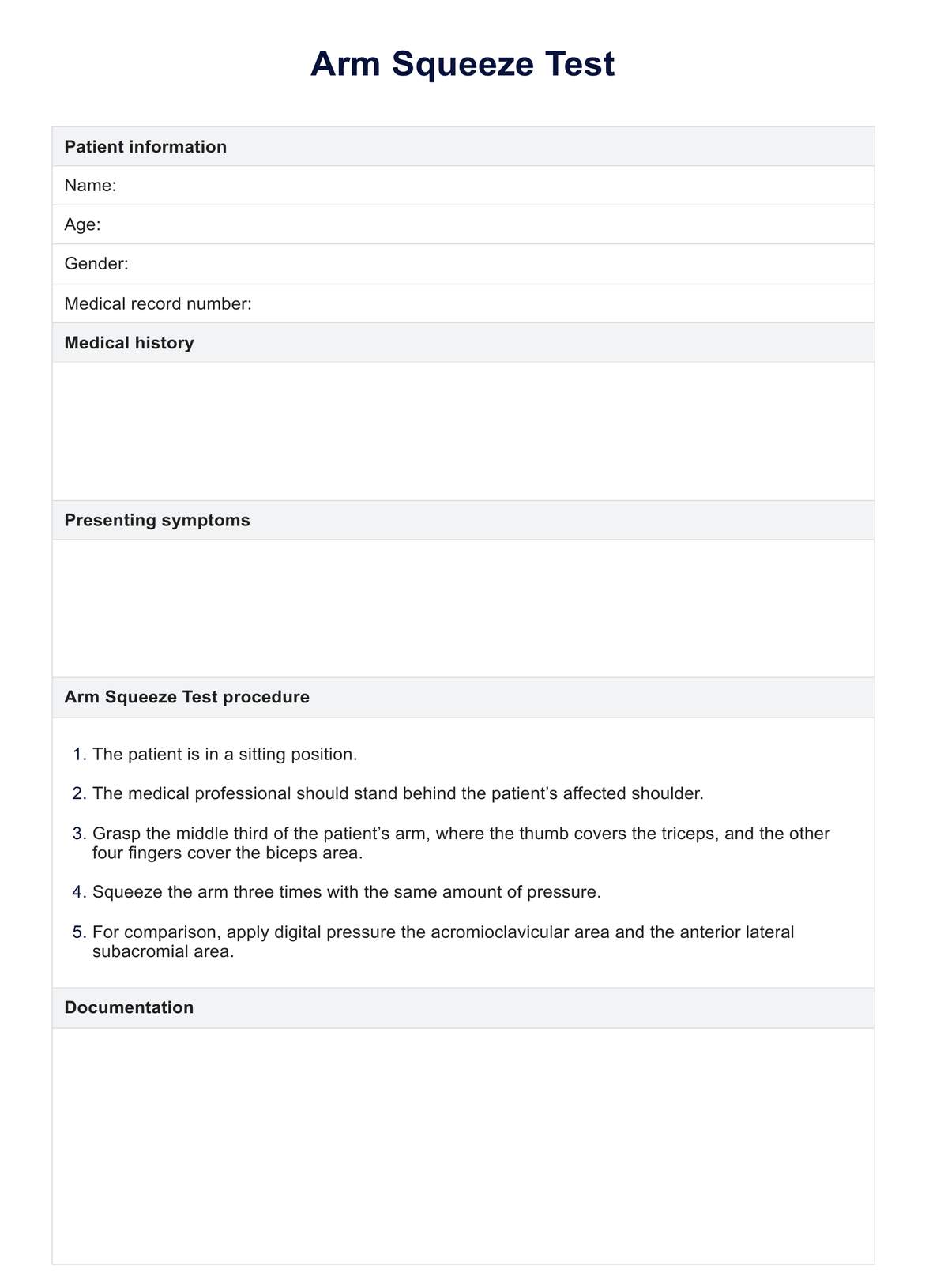
- The patient is in a sitting position.
- The medical professional should stand behind the patient’s affected shoulder.
- Grasp the middle third of the patient’s arm, where the thumb covers the triceps, and the other four fingers cover the biceps area.
- Squeeze the arm three times with the same amount of pressure.
- For comparison, apply digital pressure to the acromioclavicular and anterior lateral subacromial areas.
How are the results interpreted?
Interpreting the results of the Arm Squeeze Test is crucial for accurately assessing cervical nerve root compression and guiding further diagnostic and treatment decisions. Below are the key points to consider when interpreting the results:
- The patient scores pain for each of the three areas on the VAS scale.
- The test is considered positive if pain during the arm squeeze is three or more points higher than the other two sides.
- The test is considered negative if the pain is not felt once the upper arm on the affected side is squeezed with enough pressure.
Next steps after interpreting results
Following the interpretation of Arm Squeeze Test results, the next steps involve guiding further diagnostic and treatment interventions based on the findings. This may include:
- Referral for further evaluation: If the Arm Squeeze Test suggests cervical nerve root compression, consider referring the patient for additional diagnostic tests such as imaging studies (e.g., MRI or CT scan) to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of nerve compression.
- Treatment planning: Develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to the patient's specific needs. This plan may include conservative measures such as physical therapy, pain management strategies, and activity modification.
- Specialist consultation: If indicated by the Arm Squeeze Test results, consider involving specialists such as orthopedic surgeons or neurologists for further evaluation and management of cervical spine-related issues.
- Patient education: Provide the patient with information about their condition, treatment options, and self-care strategies to empower them in managing their symptoms effectively.
How to use our Arm Squeeze Test template
Utilizing Carepatron's Arm Squeeze Test template simplifies conducting and documenting the test, streamlining workflow efficiency for medical practitioners. Below are the steps to effectively use the template:
Step 1: Accessing the template
Log in to your Carepatron account and navigate to the Templates section. Search for the Arm Squeeze Test template or browse the available templates in the website's template library.
Step 2: Recording patient information
Input the patient's demographic details, including name, age, gender, and medical record number, into the designated fields. Include relevant medical history, presenting symptoms, and previous diagnostic test results to provide comprehensive context for the Arm Squeeze Test.
Step 3: Performing the Arm Squeeze Test
Follow the standardized procedure outlined in the template for conducting the Arm Squeeze Test, ensuring consistency and accuracy in test administration. Document the patient's response to the test, including any reproduction or exacerbation of cervical nerve root compression symptoms.
Step 4: Interpreting test results
Evaluate the results of the Arm Squeeze Test based on the observed symptoms and patient feedback. Use the template's guidance to interpret the findings and determine the presence or likelihood of cervical radiculopathy or other cervical spine-related issues.
Step 5: Documenting next steps
Based on the interpretation of test results, outline the recommended next steps for further evaluation or treatment. Document referrals to specialists, additional diagnostic tests, or treatment interventions as indicated by the Arm Squeeze Test findings.
Benefits of conducting this test
Conducting the arms squeeze clinical test offers several advantages in diagnosing cervical nerve root compression and related conditions. Here are five key benefits:
Early detection of cervical nerve root compression
By incorporating the arms squeeze test into routine clinical assessments, healthcare practitioners can promptly detect cervical nerve root compression signs, allowing for early intervention and preventing potential complications.
Accurate diagnosis amidst doubtful presentations
In cases where symptoms overlap with other shoulder diseases, such as rotator cuff tears, the arm squeeze exam is a new clinical test to aid in accurate diagnosis, helping clinicians differentiate between cervical root compression and alternative diagnoses.
Differentiation of shoulder pathology from cervical issues
The arm squeeze evaluation enables clinicians to distinguish between shoulder pathology and cervical spine-related issues, particularly in patients presenting with shoulder pain or discomfort in the middle third of the arm compared to the shoulder.
Enhanced diagnostic confidence
The arm clinical test enhances diagnostic confidence by providing objective evidence of moderate compression of cervical nerve roots, guiding appropriate treatment planning and improving patient outcomes.
Streamlined workflow efficiency
Incorporating the Arm Squeeze Test into routine clinical practice streamlines workflow efficiency for healthcare providers, offering a standardized approach to assessing patients with suspected cervical nerve root compression and facilitating timely diagnosis and management.
Cervical nerve root compression treatments
Cervical nerve root compression can cause significant discomfort and impairment, requiring appropriate treatment interventions to alleviate symptoms and restore function. Here are five common treatments for cervical nerve root compression:
Medication management
Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and oral corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and improve mobility associated with cervical nerve compression.
Physical therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing cervical nerve root compression. It focuses on strengthening and stretching exercises to improve cervical spine stability, posture, and range of motion. Additionally, manual therapy techniques, such as cervical traction and mobilization, may be employed to alleviate nerve compression and symptoms.
Epidural steroid injections
Epidural steroid injections deliver corticosteroids directly into the epidural space surrounding the affected nerve root, providing targeted anti-inflammatory effects and pain relief. Despite conservative measures, this minimally invasive procedure can significantly relieve patients with persistent symptoms.
Surgical intervention
In cases of severe or refractory cervical nerve root compression, surgical intervention may be warranted to decompress the affected nerve root and stabilize the cervical spine. Surgical options include discectomy, laminectomy, foraminotomy, or spinal fusion, depending on the underlying pathology and extent of nerve compression.
Lifestyle modifications
Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining proper posture, avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms, and incorporating ergonomic changes in the workplace or home environment, can help alleviate pressure on the cervical spine and reduce the risk of recurrent nerve compression episodes.
Commonly asked questions
To perform an Arm Squeeze Test, apply gentle pressure to the patient's upper arm while observing for any exacerbation of symptoms associated with cervical nerve compression, such as pain, tingling, or numbness.
The four tests for cervical radiculopathy include the Spurlings test, Upper limb tension-1, distraction test, and involved side cervical rotation range of motion less than 60 degrees.
A cervical radiculopathy arm squeeze is a clinical test used to assess for cervical nerve root compression by applying pressure to the patient's upper arm and monitoring for reproduction or exacerbation of symptoms associated with nerve compression.