Muscular Strength Test
Explore the Muscular Strength Test template, a comprehensive tool for healthcare professionals to effectively assess and enhance patient muscle strength.


What is a Muscular Strength Test?
Muscular strength testing involves a series of evaluations designed to measure the force and endurance of muscles when they contract, utilizing methods like the Oxford Scale for comprehensive assessment. These tests use either body weight or other sources of resistance, such as resistance bands, free weights, or from another person.
They are also fundamental in sports medicine, physical therapy, and exercise science for assessing an individual's muscular capabilities and overall physical fitness. The purpose of conducting muscular strength tests is to identify strengths and weaknesses in the musculoskeletal system, guide rehabilitation programs, and evaluate the effectiveness of training regimens.
The research and history behind muscle strength testing are extensive, tracing back to the early 20th century when scientists and physicians began to recognize the importance of muscle strength in patient recovery and athletic performance. Over the years, various methods have been developed to measure muscular strength, including manual resistance, mechanical devices, and computerized systems.
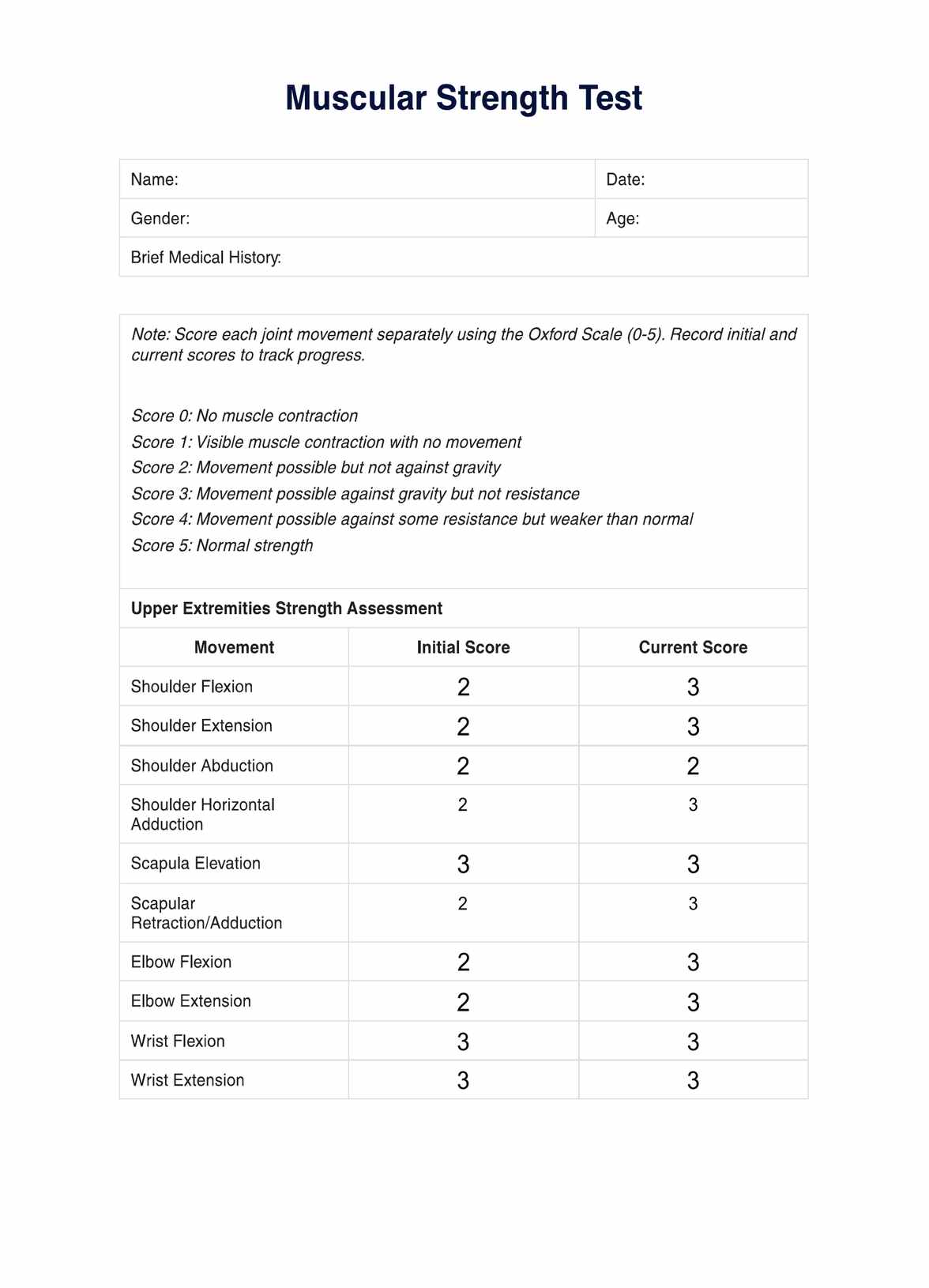
One of the most recognized methods for evaluating muscle strength is the Oxford Scale (the Medical Research Council Muscle Strength Grading System). This scale grades muscle strength from 0 to 5, with 0 indicating no muscle contraction and 5 representing normal muscle strength. The Oxford Scale is widely used for its simplicity and effectiveness in providing a quantitative measure of muscle strength that can be easily communicated and recorded.
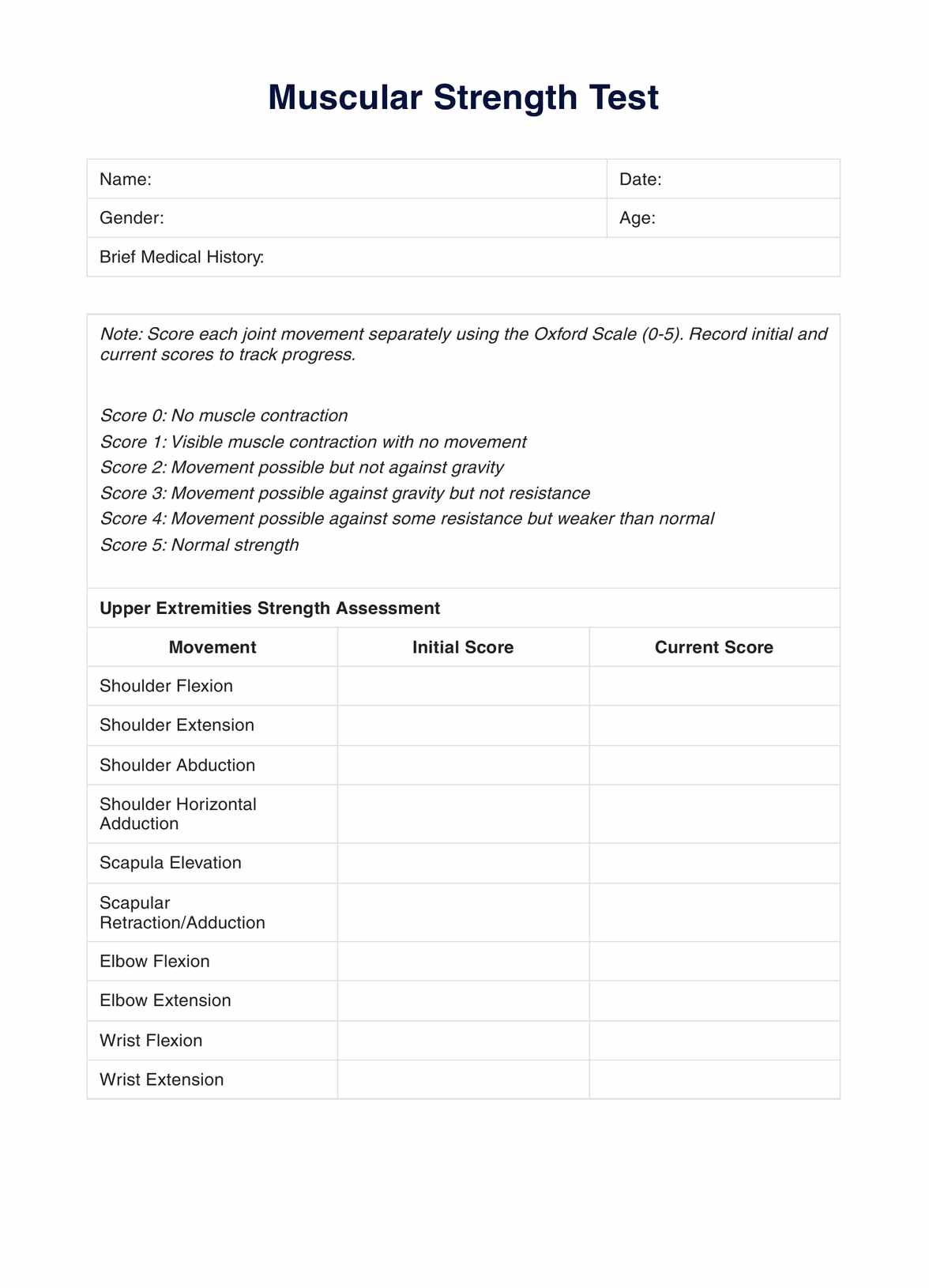
Muscular strength tests typically focus on upper and lower extremities, encompassing various muscle groups and joints. Tests may evaluate the strength of major muscle groups in the upper body, including the shoulder girdle and pelvic girdle, as well as specific movements such as shoulder flexion, elbow extension, knee flexion, and ankle dorsiflexion.
Healthcare professionals can comprehensively understand a patient's muscular health and physical capabilities by assessing these various elements.
Muscular Strength Test Template
Muscular Strength Test Example
Why take a Muscular Strength Test?
Undergoing a muscular strength test is fundamental for anyone looking to understand their physical capabilities and limitations. These tests, including manual muscle testing and utilizing grading systems like the Oxford Scale, serve multiple pivotal roles:
- Diagnostic insight: They offer insight into conditions affecting muscle strength, endurance, and overall functionality. By pinpointing muscle strength levels and essential spinal nerve roots to peripheral muscles across various upper and lower extremities, healthcare professionals can identify specific areas of muscle weakness or imbalance.
- Baseline establishment: Muscular strength tests provide a crucial baseline for individuals beginning a new fitness regimen or recovering from injury. This baseline is essential for crafting personalized exercise programs that target specific needs, ensuring safety and efficacy in strengthening and rehabilitation efforts.
- Progress monitoring: Regularly scheduled muscular strength tests allow progress monitoring over time. This is invaluable for adjusting rehabilitation or fitness strategies to ensure continuous improvement and to motivate by demonstrating tangible progress.
- Preventive measures: Identifying potential areas of vulnerability before they lead to injury is another critical benefit. For those with sedentary lifestyles or occupations requiring repetitive motions, these tests can highlight risks and inform preventive strategies to avoid future musculoskeletal issues.
Muscular strength tests are not just for athletes or those recovering from injuries. They are a critical component of health and wellness for anyone interested in maintaining or improving their physical health. By evaluating muscle strength, individuals and healthcare professionals can make informed decisions that enhance well-being, prevent injuries, and improve quality of life.
How does this Muscular Strength Test work?
Implementing the Muscular Strength Test in clinical or therapeutic settings involves structured steps. This ensures a comprehensive assessment of an individual's muscle strength across various body parts. Here’s a simplified guide tailored for healthcare professionals to effectively use the template:
Step 1: Access this template
Start by accessing the Muscular Strength Test Template, available through healthcare management platforms like Carepatron. This digital format allows for easy editing, sharing, and storage, facilitating seamless integration into patient care plans.
Step 2: Explain the template
Healthcare professionals should clearly explain the purpose and process of the test to patients. This includes discussing the Oxford Scale, the significance of testing different muscle groups, and what the patient can expect during the assessment.
Step 3: Conduct the test
Begin with tests for shoulder, elbow, wrist, and hand muscles, including a push-up test designed to assess upper body strength, evaluating flexion, extension, and abduction actions. Each movement is tested against resistance to gauge strength.
Proceed with assessing hip, knee, ankle, and foot muscles, including tiptoe tests (distal strength), covering movements like hip abduction, knee extension, and ankle dorsiflexion. Similar to upper extremities, resistance is applied to evaluate muscle strength.
Step 4: Record observations
Utilize the template to document findings for each muscle group tested. This includes noting each action's Oxford Scale rating (0-5), any observable weaknesses, and patient feedback during the test.
Step 5: Analyze results
Analyze the collected data to identify muscle weakness, strengths, or imbalance patterns. This analysis should consider the patient’s medical history, current condition, and specific complaints.
Step 6: Develop a treatment plan
Based on the test results, develop a personalized treatment plan. This might include targeted exercises, physical therapy interventions, or referrals to specialists for conditions identified during the test.
Step 7: Review and adjust
Regularly review the patient's progress through follow-up tests. Adjust the treatment plan as necessary to reflect improvements in strength or to address any new areas of concern.
This structured approach facilitates an accurate assessment of muscular strength and informs subsequent treatment strategies, ensuring that interventions are tailored to the patient’s specific needs and progress.
Interpreting Muscular Strength Test results
Interpreting the results of a Muscular Strength Test requires a thorough understanding of the Oxford Scale, which grades muscle strength on a scale from 0 to 5. Each score reflects a specific level of muscle function, from no muscle contraction to full strength with a full range of motion against gravity and resistance. Here's how healthcare professionals can interpret these scores and plan appropriate interventions:
- Score 0 (No visible muscle contraction): Indicates paralysis or extremely weak muscle strength. Immediate medical evaluation and possibly physiotherapy are recommended to determine the cause and to begin rehabilitation.
- Score 1 (Trace of contraction): Suggests a slight contraction with no movement at the joint. This may require electrical stimulation and passive exercises to prevent atrophy and stimulate muscle activity.
- Score 2 (Movement possible but not against gravity): The patient can move the limb horizontally but not lift it. Therapy may focus on gravity-eliminated exercises to gradually increase strength.
- Score 3 (Movement possible against gravity but not resistance): The patient can lift the limb against gravity. Strength training exercises, without resistance, are recommended to improve muscle strength.
- Score 4 (Movement possible against some resistance but not full strength): Indicates moderate strength. Therapeutic exercises should include resistance training to enhance muscle strength further.
- Score 5 (Normal muscle strength): Represents full muscle strength. Maintenance exercises and regular physical activity are advised to keep muscles strong and healthy.
For instance, if a patient scores a 2 in ankle inversion, it indicates that while they can perform the movement, they cannot do so against gravity. If a patient achieves a 2 in ankle inversion or demonstrates difficulty in hip abduction, it suggests pelvic girdle weakness, indicating that while they can perform the movement, they cannot do so against gravity.
Therapists should tailor their recommendations based on the patient's overall health, the presence of any medical conditions, and the specific weak muscles. Recommendations could range from targeted physical therapy sessions focusing on strengthening weak muscles utilizing assistive devices to improve mobility to prescribing a home exercise program that encourages continuous improvement. For best results, you may also use the Muscle Strength Scale.
Benefits of taking the Muscular Strength Test
The Muscular Strength Test offers invaluable insights for both healthcare professionals and patients. This test helps design precise and tailored rehabilitation or fitness programs by evaluating muscle strength across various body parts. Here are distinct benefits:
Tailored rehabilitation plans
The test outcomes allow therapists to develop rehabilitation programs tailored to the patient's muscular capabilities. Identifying weaker muscles or areas needing more focus ensures that the rehabilitation efforts are as efficient and effective as possible.
Baseline for progress tracking
Establishing a baseline is crucial for monitoring progress over time. The Muscular Strength Test provides a clear starting point, making it easier to set realistic goals and celebrate improvements, no matter how small.
Injury prevention
By identifying muscular imbalances or weaknesses, the test can play a significant role in preventing injuries. Strengthening weak muscles reduces the risk of strains and other injuries, especially in athletes or individuals with physically demanding jobs.
Enhanced physical performance
Understanding their muscular strengths and weaknesses is crucial for athletes or anyone looking to improve their physical capabilities. The test results can guide targeted strength training, focusing on both upper-body muscular endurance and lower-body strength, enhancing overall performance in sports and daily activities.
Improved functional mobility
Strength tests can highlight areas affecting a patient's functional mobility. Targeted interventions to improve strength in these areas can significantly improve the ability to perform daily tasks, enhancing independence and quality of life.
Increased motivation
Seeing tangible improvements in strength scores can be highly motivating for patients. This motivation can lead to increased adherence to physical therapy or exercise regimens, further accelerating progress.
The benefits of taking a Muscular Strength Test extend beyond mere measurement. They lie in the actionable insights derived from the results, paving the way for personalized care, injury prevention, and enhanced physical functionality.
You can enhance your practice by using the Home Exercise Program Template in conjunction with the Muscle Strength Scale Template and the Manual Muscle Testing Template. Together, these tools provide a thorough approach to assessing muscle strength, tracking progress, and creating effective exercise plans tailored to your clients’ needs.
Commonly asked questions
The test for muscle strength, often involving the Oxford Scale, assesses muscle power on a scale of 0 to 5, measuring how muscles perform against resistance.
You can test muscular strength at home using bodyweight exercises like push-ups, squats, and sit-ups, noting the maximum repetitions you can perform.
The best assessment of muscular strength combines manual muscle testing, functional movement assessments, and standardized tests like the Oxford Scale.



















-template.jpg)