A Healthy Eating Plan is a structured approach to choosing various nutrient-rich foods in appropriate portions to support overall health, maintain a healthy weight, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. It includes balanced meals with fresh fruit, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy protein sources while limiting saturated fat and added sugars.
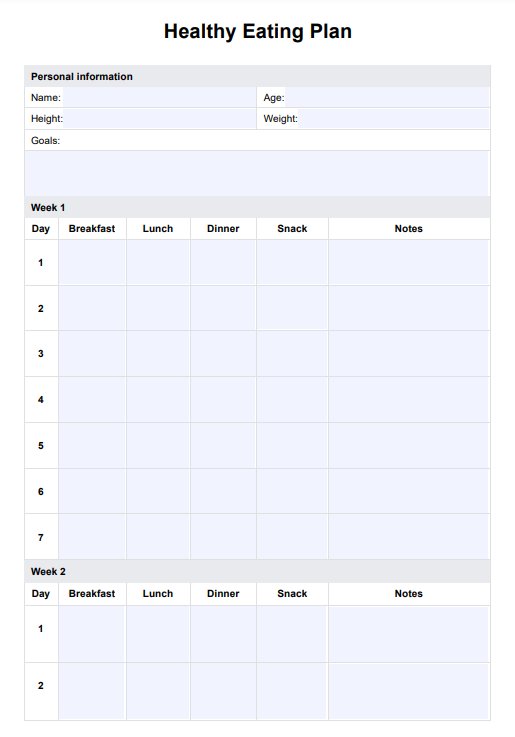
Healthy Eating Plan
Download our Healthy Eating Plan PDF for a comprehensive guide to creating balanced meals.
Use Template
Healthy Eating Plan Template
Commonly asked questions
Yes, but focus on consuming unsaturated fats in nuts, seeds, and avocados to support heart health.
Implementing nutrition policies promoting balanced diets rich in nutrients like potassium can aid in preventing and managing chronic diseases.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











