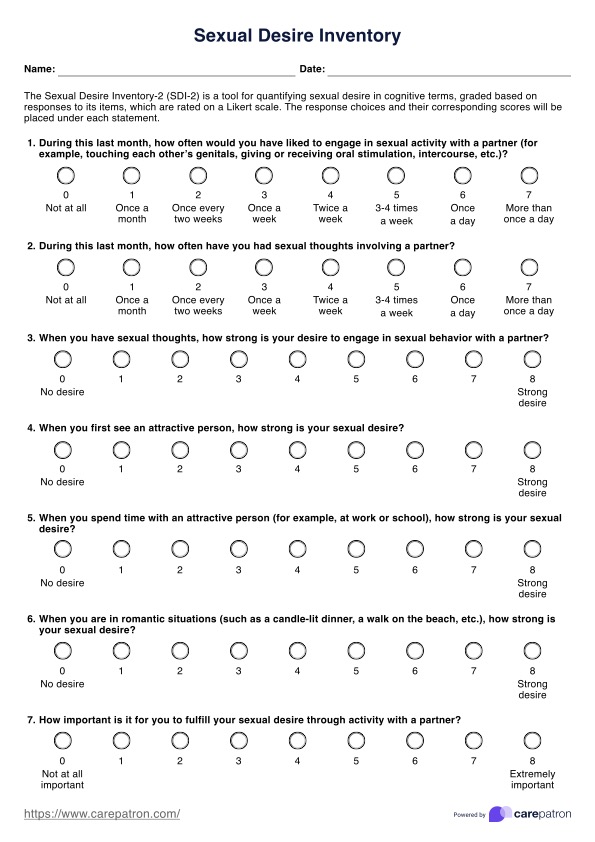
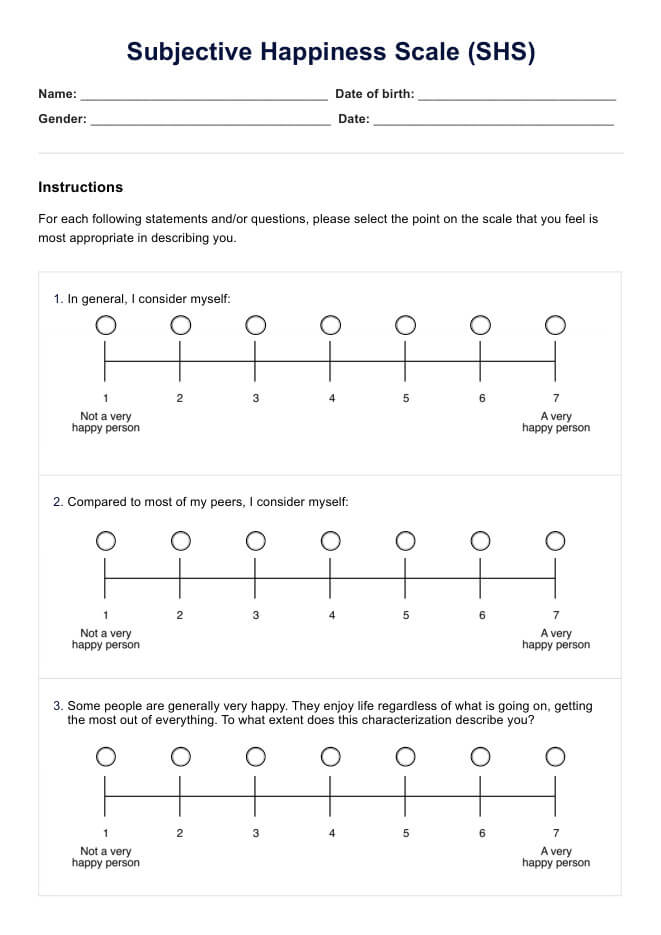
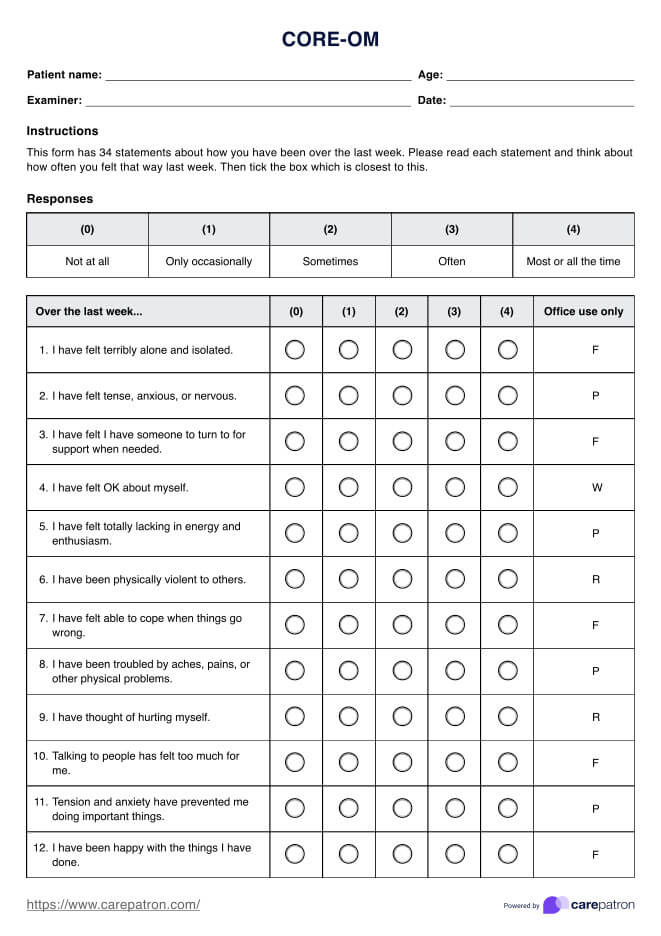
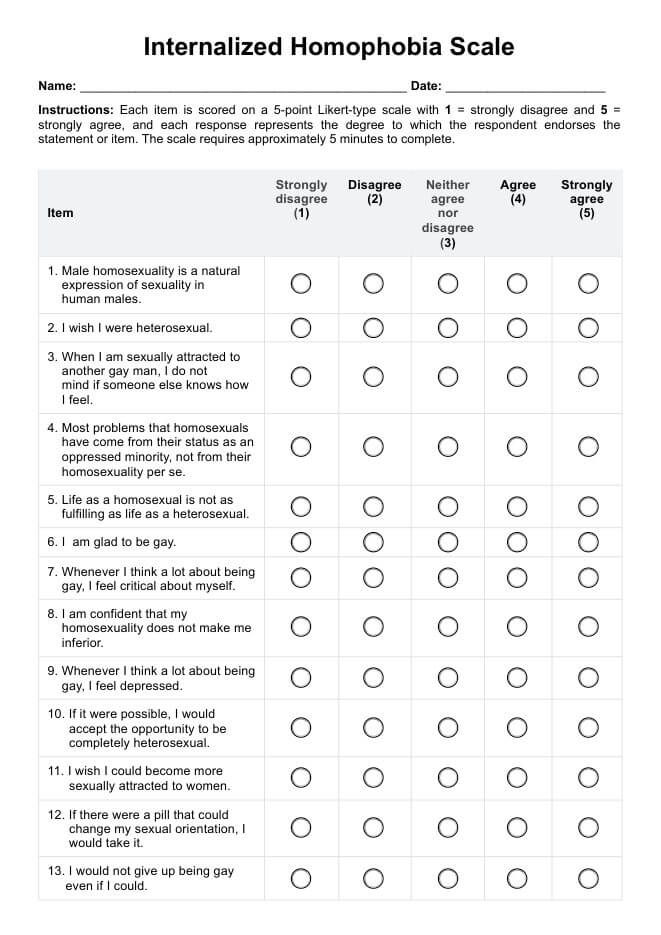
Dementia Worksheets PDF
Download our PDF dementia worksheets for adequate cognitive support and caregiver assistance in managing the challenges of dementia.


What is dementia?
Dementia is a broad term encompassing a set of symptoms that affect cognitive functions such as memory, reasoning, and communication. Alzheimer's disease, a specific type of dementia, is the most prevalent form and accounts for a significant portion of dementia cases. It is characterized by the gradual decline of cognitive abilities, impacting a person's memory, thinking, and behavior. Older adults and seniors are particularly susceptible to dementia, with its prevalence increasing with age.
Cognitive function refers to the mental processes of acquiring, processing, and utilizing information. In dementia, these functions progressively deteriorate, affecting a person's ability to perform daily activities independently. Working memory, a crucial aspect of cognitive function, is particularly vulnerable in dementia. This type of memory is responsible for temporarily holding and manipulating information needed for tasks such as problem-solving and decision-making. As dementia advances, working memory impairment can significantly hinder an individual's capacity to navigate daily challenges.
Understanding dementia is crucial for both individuals experiencing it and their caregivers. Early detection and intervention can help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. Providing support for older adults and seniors with dementia involves a multifaceted approach, including cognitive exercises, emotional support, and specialized care strategies tailored to individual needs.
Dementia Worksheets PDF Template
Dementia Worksheets PDF Example
What are the stages of dementia?
Dementia is a progressive condition that typically advances through different stages. It's important to note that the progression can vary among individuals, and not everyone will experience the same stages or at the same rate. However, a common framework for understanding the stages of dementia includes:
Early stage (mild cognitive impairment):
- Mild cognitive decline becomes apparent.
- Individuals may experience forgetfulness, difficulty finding words, and subtle behavioral changes.
- Daily functioning is generally preserved, but complex tasks may have challenges.
Middle stage (moderate cognitive decline):
- Clearer signs of dementia emerge.
- Memory loss and cognitive decline become more noticeable, affecting daily activities.
- Individuals may struggle with communication, exhibit mood swings, and have difficulty recognizing familiar faces.
Late stage (severe cognitive decline):
- Substantial cognitive decline is evident, impacting basic activities of daily living.
- Memory loss is severe, and individuals may lose awareness of their surroundings and identity.
- Communication becomes extremely limited, and there is a decline in physical abilities.
End stage (terminal decline):
- This is the final stage, marked by a severe loss of cognitive and physical function.
- Individuals may become bedridden, lose the ability to communicate, and require full-time care.
- Individuals in this stage are vulnerable to infections and other health complications.
What problems can dementia cause when it progresses?
Here are some issues that can lead to dementia when it progresses:
- Dementia can impede the ability to perform routine activities of daily living (ADLs), such as dressing, bathing, and meal preparation.
- Individuals may struggle with once-familiar tasks, leading to increased dependence on caregivers.
- Progressive damage to the brain is a hallmark of dementia, affecting areas responsible for memory, reasoning, and problem-solving.
- Structural and chemical changes in the brain contribute to the decline in cognitive abilities.
- Dementia can impact language skills, leading to difficulty finding and using words.
- Individuals may experience a decline in vocabulary and struggle with communication, making it challenging to express thoughts and needs.
- As dementia advances, comprehension abilities may decline, making it difficult for individuals to understand spoken or written information.
- Challenges in understanding and processing information can hinder effective communication and decision-making.
- Cognitive function encompasses a range of mental processes, including memory, attention, and problem-solving.
- Dementia progressively impairs cognitive function, affecting an individual's ability to think, reason, and make sound judgments.
How can dementia worksheets help a person with dementia?
Dementia worksheets play a crucial role in supporting individuals coping with the challenges of dementia. These tailored worksheets stimulate cognitive functions, promote memory recall, and engage individuals in meaningful activities. For someone with dementia, these worksheets provide structured exercises focusing on various cognitive domains, such as memory, language, and problem-solving. Engaging with these worksheets can serve as mental stimulation, helping to slow cognitive decline and maintain existing abilities.
Additionally, the structured nature of the worksheets can provide a sense of routine and familiarity, offering comfort to individuals navigating the complexities of dementia. Caregivers can use these resources to create purposeful and enjoyable interactions, fostering a positive environment for those with dementia.
Overall, dementia worksheets contribute to a holistic approach to managing the condition, enhancing the well-being and quality of life of individuals with dementia.
What are examples of helpful dementia worksheets?
- Memory recall worksheets: These worksheets typically include prompts and exercises aimed at stimulating memory recall. Activities may involve matching pictures to names, reminiscing about past experiences, or completing sentences related to personal memories.
- Cognitive stimulation puzzles: Specially designed puzzles can enhance cognitive function and problem-solving skills. Crossword puzzles, Sudoku, and word search games adapted for individuals with dementia provide mental challenges that are both enjoyable and beneficial.
- Life story worksheets: Life story worksheets focus on capturing and documenting personal histories. They include sections for detailing key life events, family members, and preferences. These worksheets help individuals reminisce, share their life stories, and maintain a sense of identity.
- Visual recognition worksheets: Activities involving visual recognition can be beneficial. Worksheets like matching shapes, identifying familiar objects, or categorizing pictures help stimulate visual perception and recognition skills.
- Conversation starter cards: These cards often feature open-ended questions or prompts that serve as conversation starters. They encourage communication, social engagement, and sharing thoughts and feelings, promoting a sense of connection and mental stimulation.
How does this Dementia Worksheet PDF work?
This Dementia Worksheet PDF is designed to be a user-friendly tool that supports individuals affected by dementia. The activity focuses on engaging the user in a structured and accessible manner. The user-friendly format ensures ease of use for individuals with dementia and their caregivers. The worksheet likely includes clear instructions and visually appealing elements to enhance engagement. Activities within the worksheet are likely designed to stimulate various cognitive functions, such as memory, problem-solving, or language skills.
The goal is to provide a meaningful and enjoyable experience that contributes to mental stimulation and the individual's overall well-being. Users can expect a thoughtful approach to addressing the unique needs of those with dementia, making the worksheet an effective and supportive resource in managing the challenges associated with the condition.
What are the benefits of using dementia worksheets?
Using dementia worksheets offers several benefits for individuals with dementia as well as their caregivers:
- Cognitive stimulation: Dementia worksheets are designed to engage various cognitive functions, providing mental stimulation. Activities that challenge memory, problem-solving, and language skills can help slow cognitive decline and maintain existing abilities.
- Memory enhancement: Memory recall exercises in worksheets can strengthen memory pathways. Revisiting familiar information or engaging in reminiscence activities helps individuals with dementia retain and recall important details.
- Promoting independence: Worksheets often focus on activities of daily living, promoting independence. By encouraging individuals to complete tasks independently, the worksheets contribute to a sense of accomplishment and self-efficacy.
- Communication and social interaction: Worksheets with conversation prompts or group activities facilitate communication and social interaction. These interactions are vital for maintaining connections, reducing feelings of isolation, and promoting emotional well-being.
- Routine and structure: Dementia worksheets can provide a sense of routine and structure in the daily lives of individuals with dementia. Consistent engagement with worksheets may offer comfort, familiarity, and a predictable element in their environment.
- Caregiver support: Caregivers benefit from the use of worksheets as well. The structured activities provide caregivers with tools to create purposeful interactions, reducing the stress associated with providing care and enhancing the quality of the caregiving experience.
- Emotional well-being: Engaging in enjoyable and meaningful activities through worksheets can contribute to a positive emotional state. It provides individuals with dementia a sense of purpose and satisfaction, contributing to overall emotional well-being.
- Documentation and monitoring: Some worksheets, such as life stories or daily activity logs, can be documentation tools. Caregivers can use these to monitor changes in behavior, preferences, and cognitive abilities, aiding in care planning and communication with healthcare professionals.
What are examples of dementia treatment?
Dementia treatment focuses on managing symptoms, slowing progression, and improving the quality of life for individuals affected. While there is no cure for most types of dementia, various interventions and strategies can be employed by nurses or other healthcare practitioners. Here are examples of dementia treatment:
- Cholinesterase inhibitors: Drugs like donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine may be prescribed to manage symptoms and slow cognitive decline.
- Memantine: This medication may be used in moderate to severe cases of Alzheimer's disease to regulate glutamate activity and improve cognitive function.
- Cognitive stimulation therapy (CST): Group activities and exercises designed to stimulate cognitive function, enhance memory, and promote social interaction.
- Reality orientation therapy: Orienting time, place, and person to improve awareness and reduce confusion.
- Occupational therapy: Tailored activities and exercises that help individuals maintain independence in daily tasks, adapt to challenges, and improve overall quality of life.
- Speech and language therapy: For individuals with dementia experiencing language difficulties, speech therapy can help maintain communication skills, enhance understanding, and improve verbal expression.
- Physical exercise: Regular physical activity has been linked to cognitive benefits. Exercise can improve overall health, reduce behavioral symptoms, and enhance mood in individuals with dementia.
- Music and art therapy: Engaging individuals in activities like listening to music or creating art can have therapeutic effects, stimulating emotions and memories.
- Technology-based interventions: Apps and technologies designed for cognitive training, reminiscence therapy, and virtual reality experiences tailored to individuals with dementia.
Why use Carepatron as your psychiatry software?
Choosing Carepatron as your psychiatry software allows you to opt for a comprehensive and efficient solution that enhances every aspect of mental health care. The platform excels in practice management, providing clinical tools that streamline daily operations. With features like online booking and reminders, appointment scheduling becomes a hassle-free process for both practitioners and clients, ensuring efficient time management.
Securely storing and managing client records, including detailed notes, progress reports, and treatment plans, contribute to an organized and centralized system. This centralized approach enhances the overall quality of care by enabling practitioners to access crucial information easily, ultimately benefiting the client's treatment journey.
Carepatron's billing and invoicing tools simplify financial processes, allowing for seamless invoice generation, online payment acceptance, and efficient management of insurance claims. This saves time and ensures accuracy and transparency in financial transactions.
The platform goes beyond traditional in-person consultations by facilitating telehealth services. Secure video consultations enhance accessibility and flexibility in mental health care delivery, enabling practitioners to connect with clients remotely.

Commonly asked questions
Dementia is a cognitive disorder involving memory loss and impaired reasoning, significantly impacting daily functioning and communication.
Dementia worksheets, designed for memory recall and cognitive stimulation, offer individuals with dementia enjoyable activities to maintain cognitive abilities.
Yes, dementia worksheets can be adapted to different stages, addressing cognitive abilities and preferences specific to each individual's stage of dementia.













-template.jpg)