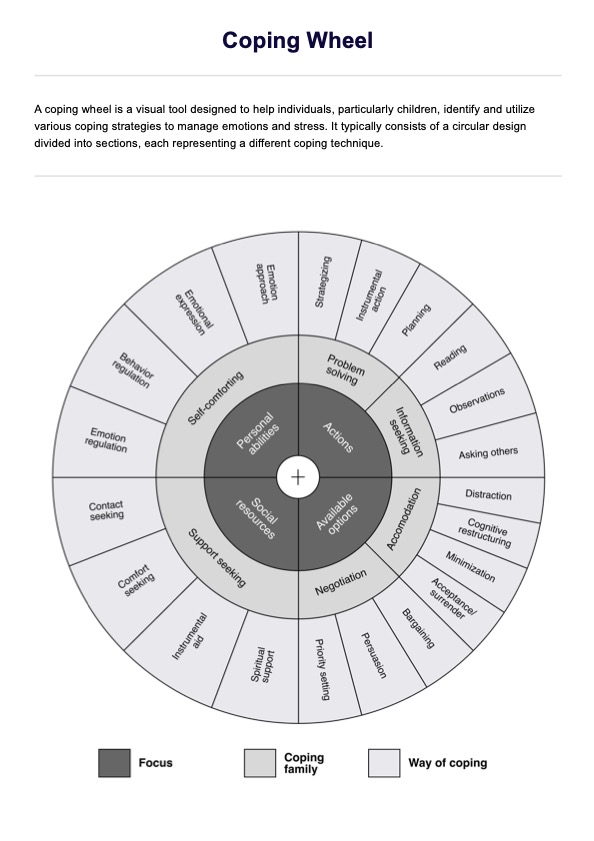
Vitamin B Test Reports
Access a free Vitamin B Test Report template to record patient results thoroughly. Use the example to gather insights and make informed decisions.


What is a vitamin B test?
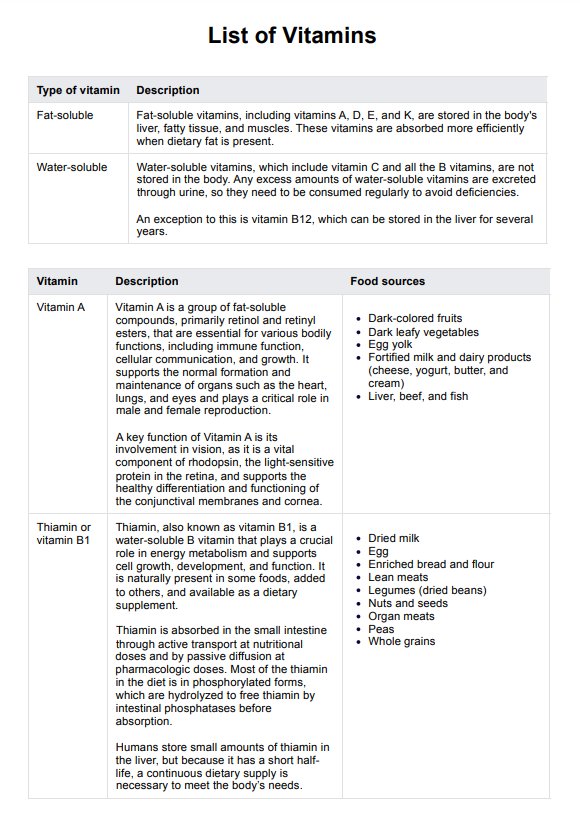
A vitamin B test, also known as a vitamin B panel or profile, is a diagnostic blood test designed to measure levels of eight essential B vitamins in the body. These vitamins include:
- Thiamine (B1): Vitamin B1 supports carbohydrate metabolism and nerve function.
- Riboflavin (B2): Vital for energy production and cell health.
- Niacin (B3): Niacin is crucial for DNA repair, metabolism, and maintaining healthy skin.
- Pantothenic acid (B5): A key component in synthesizing coenzyme A, necessary for fatty acid metabolism.
- Pyridoxine (B6): This plays an important role in neurotransmitter synthesis and red blood cell production.
- Biotin (B7): B7 promotes healthy skin, nails, and metabolism.
- Folic acid (B9): This is essential for DNA synthesis and vital during pregnancy to support fetal development.
- Cobalamin (B12): Vitamin B12 is important for maintaining neurological health and producing red blood cells.
These vitamins are essential for energy production, immune system function, and nervous system health. Vitamin B deficiencies may result from inadequate dietary intake, malabsorption disorders (e.g., celiac disease, Crohn’s disease), or lifestyle factors such as chronic alcohol use. Symptoms of deficiency often include fatigue, anemia, irritability, numbness, tingling, or difficulty concentrating.
How is the test performed?
A vitamin B test involves drawing blood from the patient, usually from the arm. The sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis, and patients may need to prepare beforehand by fasting or temporarily stopping medications that could affect results.
The test results will identify whether Vitamin B levels are within the normal range, below normal (deficient), or above normal (excessive). Based on these findings, healthcare providers can recommend appropriate interventions, such as dietary adjustments or supplementation, or conduct further investigations if necessary.
Vitamin B Test Reports Template
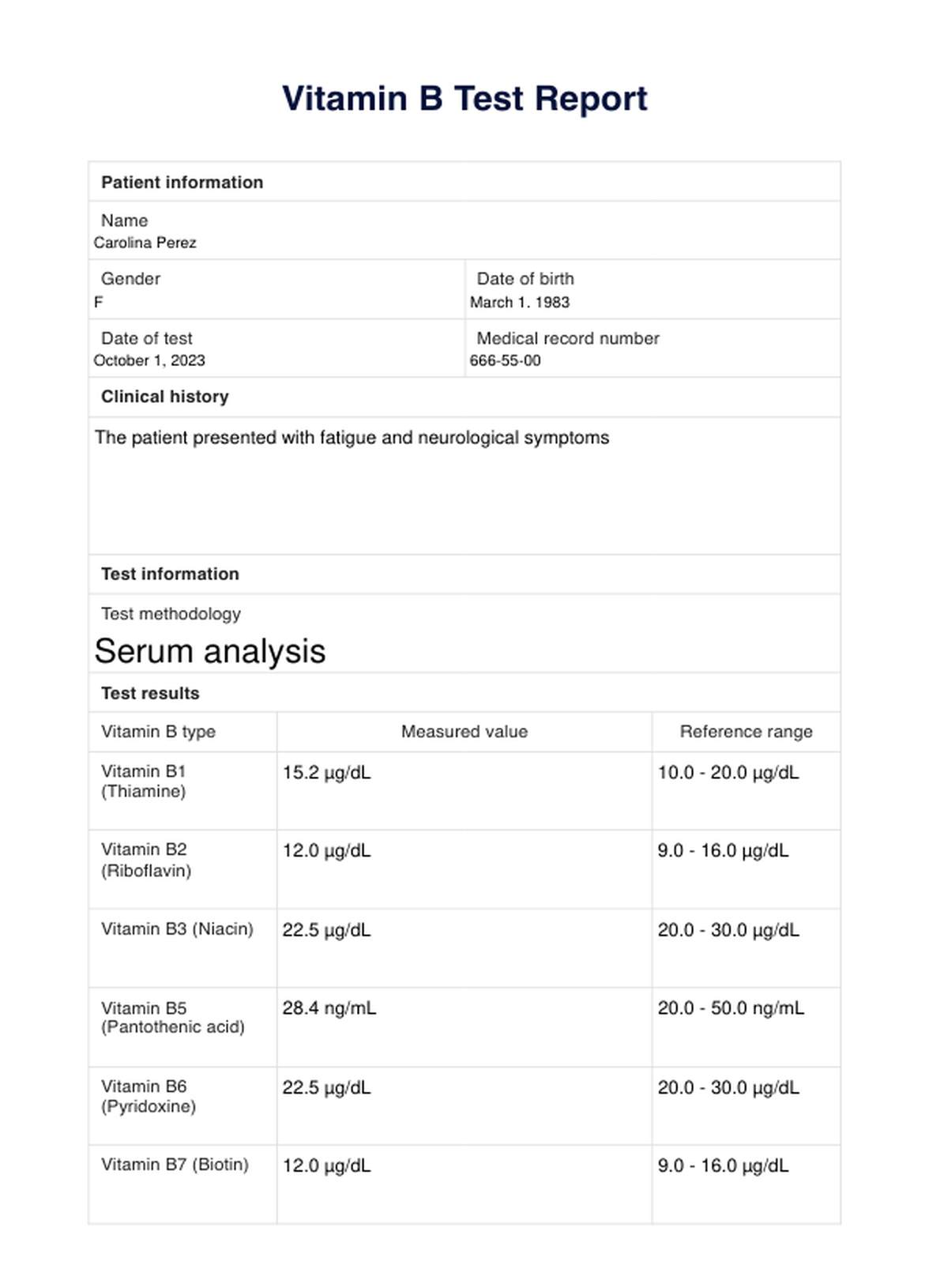
Vitamin B Test Reports Example
Why use a Vitamin B Test Report template?
The Vitamin B Test Report template is designed to simplify the process of documenting and interpreting test results. It ensures consistency, clarity, and accessibility for both healthcare providers and patients. The template includes sections for patient information, detailed test results, and actionable recommendations, promoting better outcomes through structured documentation.
How does it work?
Our free Vitamin B Test Report template makes it easy to document and track Vitamin B levels for your patients. Its intuitive design allows for seamless data entry and result interpretation. Follow these simple steps to get started:
Step 1: Download the template
Access the printable Vitamin B Test Report template from our website, practice management solution app, or the Carepatron resources library.
Step 2: Input patient information
Fill in the patient’s details, including their name, date of birth, gender, and relevant medical history, in the designated fields. This ensures all critical information is captured for a complete report.
Step 3: Record test results
Using the lab report, document the levels of each type of Vitamin B in the corresponding section. The template also includes space for notes or comments, allowing you to highlight abnormalities or trends.
Step 4: Interpret the results
Compare the recorded values against standard reference ranges to identify any deficiencies or excesses. Use these insights to recommend dietary changes, prescribe supplements, or investigate underlying conditions further.
Step 5: Share or save the report
Once completed, print the report or share it electronically with the patient and other healthcare providers as needed. You can also store it in the patient’s electronic health record for future reference, ensuring continuity of care.
By using this template, healthcare providers can simplify patient management, improve the accuracy of documentation, and collaborate effectively with colleagues to deliver high-quality care.
When would you use this test report?
The Vitamin B Test Report template is a valuable tool for various clinical scenarios. It can be utilized when a patient exhibits symptoms suggestive of a Vitamin B deficiency, such as fatigue, irritability, or neuropathy, or during routine check-ups to assess their overall nutritional status. Additionally, this report serves several important functions:
Guide treatment plans
The report helps identify potential deficiencies by providing a clear overview of Vitamin B test results. This information supports healthcare professionals in developing targeted treatment plans, such as recommending dietary changes or supplements, and facilitates early intervention to prevent further health complications.
Monitor progress over time
Regular use of the template allows healthcare providers to track a patient’s progress over time. By comparing test results across visits, practitioners can assess the effectiveness of interventions like dietary modifications or supplementation and adjust treatment strategies as needed.
Educate patients on their nutritional health
With its clear layout, the report can also be used as an educational resource. Patients gain a better understanding of their nutritional status and the importance of maintaining adequate Vitamin B levels, empowering them to make informed decisions about their diet and health.
Facilitate collaboration among healthcare providers
The report can be printed or shared electronically with other healthcare providers involved in the patient’s care. This ensures a coordinated approach to addressing any deficiencies, optimizing patient outcomes through collaborative care.
Interpreting Vitamin B Test results
The results of a Vitamin B Test provide critical insights into a patient’s nutritional status and overall health. These results indicate whether levels of B vitamins are adequate, deficient, or elevated, guiding appropriate clinical interventions.
Normal range
When results fall within the normal range, it indicates that the patient has sufficient levels of B vitamins to support essential physiological functions such as energy metabolism, red blood cell production, and nerve function. Maintaining these levels typically requires a balanced diet that includes B vitamin-rich foods like leafy greens, whole grains, eggs, lean meats, and fortified products. Routine monitoring may be necessary for individuals at greater risk of deficiency, such as those with dietary restrictions, digestive disorders, or chronic health conditions.
Below normal range
Results below the normal range suggest a Vitamin B deficiency, which, if unaddressed, can lead to significant health issues. Common contributing factors include:
- Inadequate dietary intake, particularly in patients with restrictive diets or limited access to nutritious foods.
- Impaired nutrient absorption due to digestive system disorders such as celiac disease or Crohn’s disease.
- Conditions such as low stomach acid or a lack of intrinsic factor, which are often associated with pernicious anemia.
- Certain medications or lifestyle factors, including alcohol use.
Symptoms of deficiency may include fatigue, irritability, neuropathy, memory problems, or vitamin deficiency anemia. Addressing these deficiencies may involve recommending dietary modifications, oral supplements, or, in severe cases, intramuscular injections. Additional tests, such as a cobalamin test or folate test, may help determine the specific deficiency and identify underlying causes.
Above normal range
Elevated levels of B vitamins are less common and may result from excessive supplement use or certain medical conditions. For example:
- High serum folate levels could indicate excessive folic acid supplementation or metabolic issues.
- Elevated B6 levels, if persistent, may lead to neuropathy or other complications.
- High B12 levels may point to underlying conditions such as liver disease or kidney dysfunction.
In these cases, reviewing the patient’s dietary intake and supplement use is essential. Further investigations, such as a random urine test or additional bloodwork, may be required to confirm the cause and guide treatment.
Commonly asked questions
A Vitamin B Test measures the levels of various B vitamins in the body, such as folic acid and cobalamin (B12). These vitamins are essential for producing healthy blood cells, supporting nerve function, and maintaining energy metabolism. The test typically involves a blood sample drawn from a vein, although in some cases, a urine sample may be used. Vitamin B testing is crucial for detecting deficiencies or excesses that can lead to conditions like folate deficiency, vitamin deficiency anemia, or other health issues.
Vitamin B testing is often recommended for individuals experiencing common symptoms of deficiency, such as fatigue, weakness, irritability, memory problems, or tingling sensations. It is also valuable for those at higher risk, including older adults, who may have reduced nutrient absorption, individuals with dietary restrictions, people recovering from surgeries, and people with underlying medical conditions like autoimmune disorders.
The test is usually conducted in a health office or testing laboratory. A blood sample is drawn using a test tube, typically from a vein in the arm. In some cases, a urine sample may be collected for additional analysis. The process is quick and minimally invasive, taking only a few minutes. Results are sent to the ordering healthcare provider, who evaluates the findings and provides a diagnosis or treatment plan.





















-template.jpg)