Cardiac Diabetic Diet Food
Discover our Cardiac Diabetic Food List, an essential resource for diabetes-friendly foods.


What is a Cardiac Diabetic Diet Food List?
A cardiac diabetic diet combines heart-healthy and diabetes-friendly foods to manage cardiovascular and blood sugar health. Some diets are similar to a Mediterranean diet, which focuses more on heart-healthy eating. Additionally, the diet enlists heart-healthy foods low in saturated fats, trans fats, salt, and added sugars while high in fiber to control cholesterol and lower blood pressure and blood sugar levels. This includes certain fish, nuts, and seeds that support heart health through anti-inflammatory benefits, which are crucial to managing diabetes and heart conditions and promoting overall cardiovascular health.
The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet is often referenced in the context of a diabetic cardiac diet. Developed initially to help control high blood pressure, the DASH diet has proven beneficial for heart health and diabetes management. It focuses on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy while limiting processed foods high in saturated fat, trans fat, and sodium. This heart and diabetic diet aligns well with the needs of cardiac diabetic patients, as it supports the maintenance of healthy blood pressure and weight, both of which are crucial for managing diabetes and reducing heart disease risk.
A Cardiac Diabetic Diet Food List is a guide that offers a selection of beneficial foods for heart health and blood sugar control. This list aims to simplify meal planning and grocery shopping, making it easier for individuals to adhere to a diet that supports their cardiac and diabetic health.
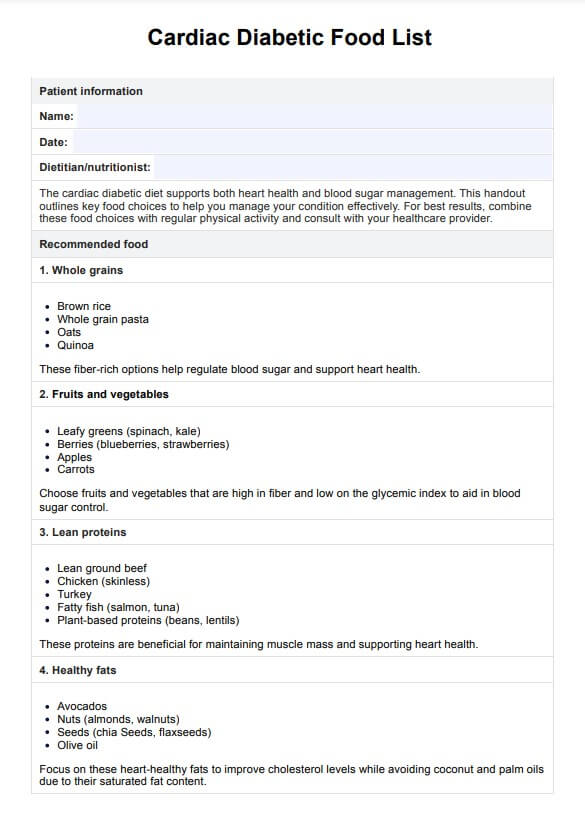
Cardiac Diabetic Diet Food Template
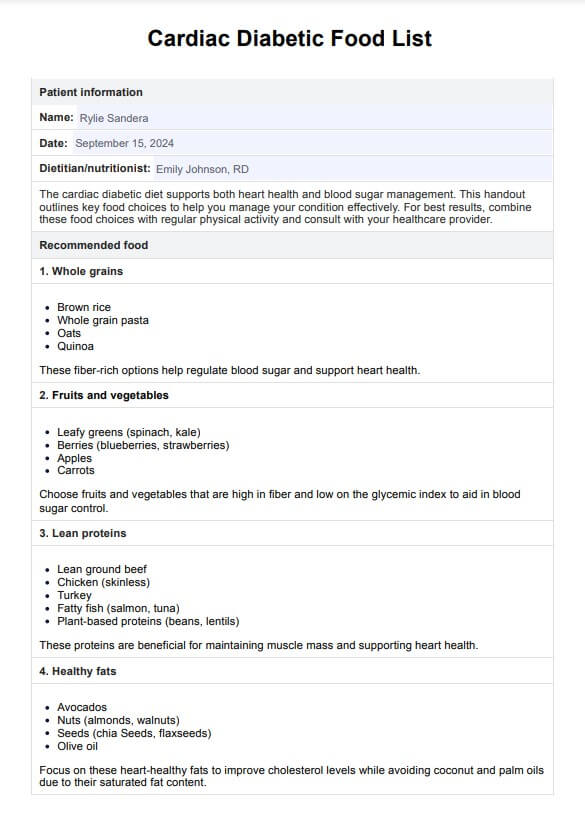
Cardiac Diabetic Diet Food Example
How to use the printable Cardiac Diabetic Food List?
To maximize the benefits of this tool, we've developed a detailed step-by-step guide on how to use our printable food list for a heart-healthy diabetic diet PDF:
Step 1: Download the list
You can access the list by clicking the link on our page. The document will open in your default PDF reader and be ready for digital use. Print it out for a tangible reference.
Step 2: Familiarize with the food categories
Examine the list to understand the different categories, such as lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Note the variety of food in a healthy heart diabetic diet, focusing on fiber-rich, low-sodium, and low-sugar options.
Step 3: Discuss the list with patients
Discuss the resource with patients. For instance, you can work with them and use the food list to help plan their daily meals. Ensure each meal includes a balance of nutrients essential for managing cardiac and diabetic health. They can also create a grocery shopping list and use the food list as a guide to highlight the items they need.
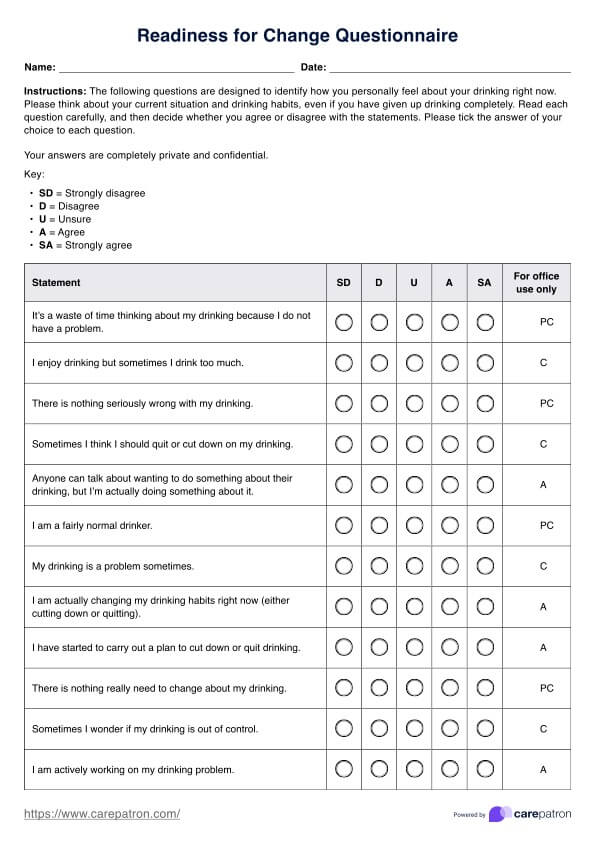
Cardiac Diabetic Diet Food List
The cardiac diabetic diet is designed to support heart health and blood sugar management. Our detailed Cardiac Diabetic Diet Food List PDF provides comprehensive guidance on food choices. Here's an overview of what the list includes:
- Whole grain: Choices like brown rice, whole grain pasta, oats, and quinoa are emphasized for their fiber content, aiding blood sugar regulation and heart health.
- Fruits and vegetables: A diverse range of fruits and vegetables, particularly those high in fiber and low in glycemic index, are included. Examples are leafy green vegetables, berries, apples, and carrots, which provide essential nutrients and help with blood sugar control.
- Lean proteins: Lean meats such as lean ground beef, chicken, turkey, and fish, especially fatty fish like salmon, are recommended. Plant-based proteins, including beans and lentils, are also highlighted for their beneficial effects on heart health and diabetes management.
- Healthy fats: The list prioritizes sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, known for their heart-healthy fats and ability to improve cholesterol levels. Refrain from using coconut and palm oils, which have high saturated fat.
- Low-fat dairy products: Options like low-fat yogurt and skim milk offer protein and calcium without excess saturated fat, aligning with cardiac and diabetic diet needs.
- Limited sodium and sugar: The diet stresses the importance of minimizing salt and added sugars to manage blood pressure and blood sugar levels effectively. Also recommend that patients avoid processed foods.
What else to keep in mind?
While this free Cardiac Diabetic Diet Food List is an excellent tool for managing a heart healthy diet, there are additional vital aspects to consider for optimal health when implementing a cardiac diabetic diet. These factors work in tandem with dietary choices to enhance overall well-being:
Hydration
Adequate water intake is crucial for overall health, especially for managing diabetes and heart conditions. Recommend that patients limit sugary or caffeinated beverages to support hydration, and help control blood sugar levels.
Portion control
Even with healthy foods, portion size is critical for managing blood sugar and weight. Suggest using measuring tools or visual cues can help maintain appropriate portion sizes so they can avoid overeating.
Regular exercise
Physical activity is essential for managing cardiac and diabetic health by controlling blood sugar, reducing blood pressure, strengthening the heart, and managing weight. Encourage patients to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity weekly exercise for optimal health benefits.
Monitoring blood sugar levels
You can also recommend regularly checking blood sugar levels. This is vital for understanding their fluctuations based on diet and activities, enabling effective diabetes management.
Stress management
Techniques like mindfulness, meditation, or breathing exercises can mitigate chronic stress, which can adversely affect heart health and blood sugar levels. You can suggest that patients explore these techniques and find what works well for them.
Regular check-ups
Encourage patients to be present in their regular check-ups. Routine healthcare visits are crucial for monitoring heart and diabetic health progress, providing insights into the effectiveness of management strategies.
Commonly asked questions
Cardiac Diabetic Diet Food Lists are helpful because they provide a structured guide to eating for individuals managing both heart health and blood sugar levels. These lists simplify the prong foods that benefit both conditions, reducing the risk of complications. They help identify foods high in fiber, low in unhealthy fats, sodium, and sugars, and rich in nutrients essential for heart and diabetic health.
Cardiac diabetic diets are primarily used by individuals who have been diagnosed with heart conditions, diabetes, or both. They are also helpful for those at risk of these conditions or anyone interested in adopting a healthier eating pattern. Healthcare providers might recommend these lists post-diagnosis of diabetes or heart disease or as a preventive measure to lower the risk of these conditions.
These food lists are used as a guide for daily meal planning and grocery shopping. Individuals can refer to the list to choose foods suitable for their dietary needs, ensuring a balance of nutrients necessary for managing heart and diabetic health. The lists typically categorize foods into groups (like whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables) and suggest which foods to include and which to limit or avoid.