MRNI
Explore the Male Role Norms Inventory (MRNI), a tool for assessing masculinity ideologies, health behaviors, and gender role attitudes in research.


What is the Male Role Norms Inventory (MRNI)?
Male role norms are societal expectations and beliefs about how men should think, behave, and present themselves in various aspects of life. These norms often emphasize traits such as emotional stoicism, physical toughness, independence, dominance, and traditional views on sexuality. While these gender roles are deeply ingrained in many cultures, they can create pressure on men to conform to rigid standards, which may impact their mental health, relationships, and overall well-being.
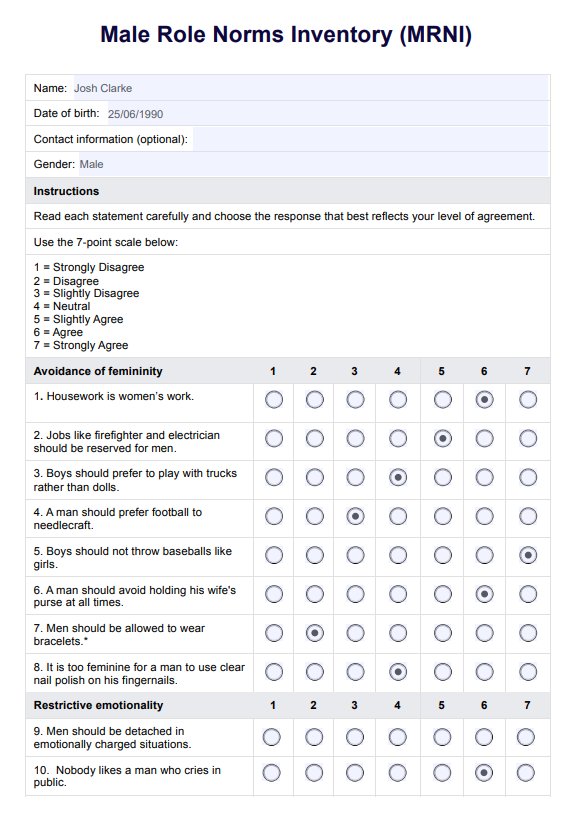
The Male Role Norms Inventory (MRNI) is a 58-item self-report measure assessing beliefs about traditional male gender norms across seven subscales (Levant et al., 1992):
- Avoidance of femininity: Measures rejection of traits seen as feminine, like emotional expressiveness and passivity.
- Restrictive emotionality: Assesses suppression of emotions, particularly vulnerability and sadness.
- Aggression: Evaluates beliefs in aggression, dominance, and competitiveness as key masculine traits.
- Achievement/Status: Reflects pressure on men to achieve success, financial stability, and recognition.
- Self-reliance: Measures belief in independence and avoiding help-seeking behavior.
- Homophobia: Assesses negative attitudes toward homosexuality linked to traditional masculinity.
- Attitudes toward sex: Reflects views on male dominance in sexuality and promiscuity.
The MRNI helps identify how adherence to traditional masculinity may influence mental health, relationships, and social behavior. High scores on certain subscales can be linked to issues like emotional repression, aggression, and social isolation. It is used in clinical, educational, and research settings to explore and address the impact of rigid gender norms.
MRNI Template
MRNI Example
How to use our MRNI template
The Male Role Norms Inventory is valuable for assessing beliefs about traditional male gender norms. Follow this step-by-step guide to use our MRNI template effectively:
Step 1: Access and download the MRNI template
You can access the MRNI template directly from this guide. Click "Use template" to open it with Carepatron for customization to meet your practice's needs. Alternatively, click "Download" to obtain a fillable PDF version for manual use.
Step 2: Administer the MRNI questionnaire
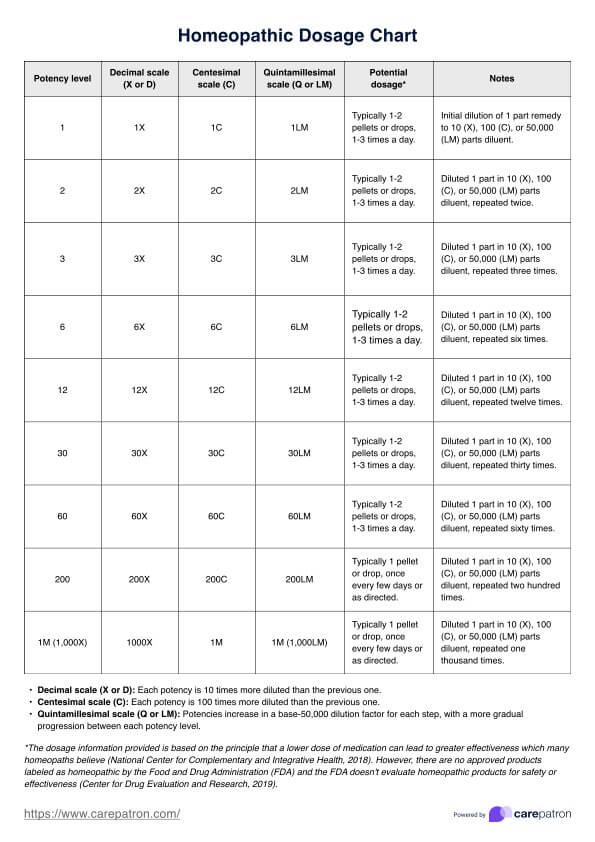
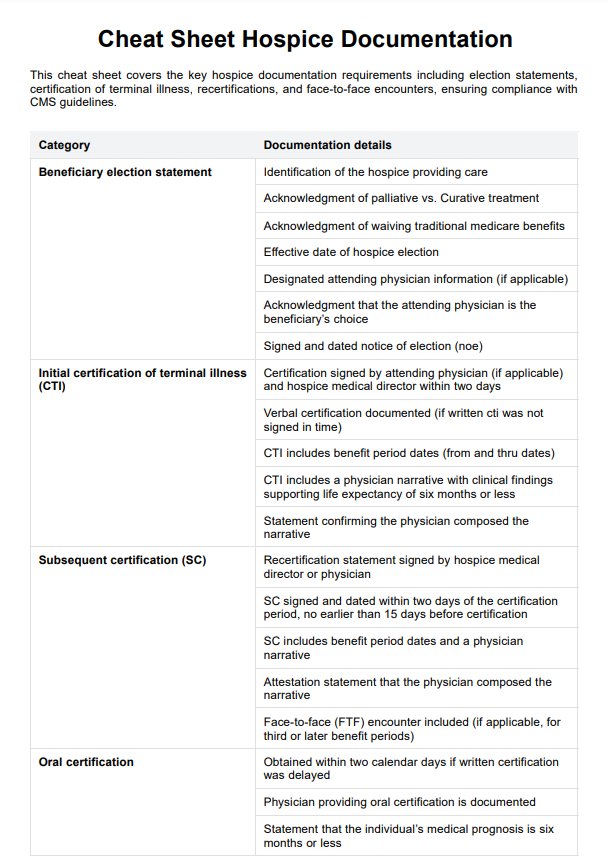
Provide participants with the MRNI questionnaire and clear instructions. The MRNI consists of 58 items and uses a 7-point Likert scale, where 1 represents "Strongly Disagree" and 7 represents "Strongly Agree." Make sure participants understand the scale and encourage honest responses.
Step 3: Collect responses to all items
Participants should rate all 58 statements on the questionnaire. These statements are grouped into seven subscales: Avoidance of Femininity, Restrictive Emotionality, Aggression, Achievement/Status, Self-Reliance, Homophobia, and Attitudes Toward Sex. Make sure to review completed forms for completeness.
Step 5: Score the MRNI
After collecting the questionnaires, calculate scores for each subscale and the total MRNI score. Reverse-code specific items as indicated in the instructions (e.g., reverse 1 to 7, 2 to 6, etc.). Subscale scores provide insights into specific dimensions, while the total score reflects overall adherence to traditional male role norms.
Step 6: Analyze and interpret results
Review the scores to determine participants' adherence to traditional male role norms. Higher scores indicate stronger endorsement of these norms, while lower scores suggest more egalitarian beliefs. Use contextual factors, such as cultural or demographic information, to guide interpretation.
Step 7: Store completed forms securely
Ensure that all completed MRNI forms are stored securely to maintain participant confidentiality. For digital forms, save them in a secure, encrypted system. For physical forms, store them in a locked and restricted-access location.
Interpretation of the results
Participants rate items on a 7-point Likert scale (1 = Strongly Disagree, 7 = Strongly Agree), with some items reverse-coded for accuracy. Scores for each subscale and a total score indicate adherence to male role norms. Scores are interpreted at both the subscale and total levels:
- Subscale scores: These reflect adherence to specific dimensions of male role norms, such as Avoidance of Femininity, Restrictive emotionality, or Achievement/Status. For example, a high score in Restrictive emotionality indicates strong beliefs in emotional suppression as a male norm. In contrast, a low score in Homophobia suggests less adherence to traditional gender expectations regarding homosexuality.
- Total score: This represents an overall measure of adherence to traditional male role norms. Higher scores indicate stronger endorsement of these norms, reflecting traditional beliefs about masculinity, such as dominance, independence, and emotional stoicism. Lower scores suggest more flexible, egalitarian views of gender roles.
Results can vary based on cultural, demographic, and personal factors. Researchers or practitioners should contextualize scores to account for societal influences or specific study objectives, recognizing that rigid adherence to traditional norms may correlate with negative outcomes such as stress or reduced interpersonal satisfaction.
Benefits of using Carepatron's template
Carepatron’s masculine norms inventory template is designed to streamline the assessment process for healthcare professionals, offering a user-friendly and efficient tool for evaluating traditional male role norms. By using this template, professionals gain access to several key benefits:
- Ease of use: The template provides a clear, standardized format, ensuring that participants can complete the questionnaire with minimal confusion. The 7-point Likert scale and subscale organization make data collection straightforward.
- Time efficiency: The ready-to-use structure saves time, eliminating the need for manual formatting or creating questionnaires from scratch. This allows more focus on interpretation and patient care.
- Customization options: You can also tailor the template to suit specific study or organizational needs, ensuring relevance to diverse healthcare settings or research objectives.
- Secure data management: With digital and printable options, the template supports secure handling of sensitive data, complying with confidentiality standards for patient and participant information.
Reference
Levant, R. F., Hirsch, L. S., Celentano, E., Cozza, T. M., et al. (1992). The male role: An investigation of contemporary norms. Journal of Mental Health Counseling, 14(3), 325–337.
Questions fréquemment posées
The Male Role Norms Inventory (MRNI) is a psychometric tool designed to assess adherence to masculine norms, including traits such as physical toughness, self-reliance, and the avoidance of behaviors seen as feminine. It evaluates masculine ideologies across various domains, including emotional expression, health behaviors, and societal expectations related to mechanical skills and leadership roles. The MRNI is widely utilized in research on men's health and mental health, helping to highlight the influence of gender role strain. By measuring general and specific masculinity factors, the inventory sheds light on how traditional norms contribute to health risk behaviors and the challenges men face in aligning with societal expectations, offering valuable insights into the relationship between masculine norms and gender role conflict.
Male society norms refer to the societal expectations and behaviors that define what it means to be a man in a given culture. These norms are often tied to traditional masculinity ideology, which emphasizes traits such as emotional stoicism, dominance, self-reliance, aggression, and avoidance of femininity. Such norms can lead to gender role conflict, as men may feel pressure to conform to these ideals, even if they are not aligned with their true identities or well-being.
Masculine norms are specific beliefs and expectations about how men should behave, often rooted in traditional gender roles. These norms typically promote traits such as strength, independence, and control while discouraging vulnerability, emotional expressiveness, and help-seeking behavior. Adherence to these norms can encourage risk-taking, as men may feel pressure to prove their masculinity through dangerous or high-stakes actions. The belief in these norms can also lead to gender role conflict, where men experience stress or discomfort when they are unable to meet these societal expectations, potentially impacting their mental health and well-being.














-template.jpg)