Vegan Keto Meal Plan
Explore expert-crafted Vegan Keto Meal Plans designed for healthcare professionals. Nutrient-dense, plant-based recipes for optimal health.


What is a Vegan Keto Meal Plan?
A Vegan Keto Meal Plan combines the vegan diet—which excludes animal products—with the keto diet, a low-carb, high-fat regimen. It focuses on healthy fats such as coconut oil, avocado oil, full-fat coconut milk, and vegan butter while minimizing carb intake from starchy vegetables and grains.
Key components of a vegan keto diet include vegan protein sources like hemp seeds, pumpkin seeds, and almond butter. Fortified foods and nutritional yeast help meet essential nutrient needs, and non-starchy vegetables such as leafy greens and cauliflower support low-net carb consumption. Creative swaps like cauliflower rice and zucchini noodles replace traditional carbs.
By entering nutritional ketosis, the body burns fat for energy, promoting weight loss and improving blood sugar control. However, healthcare professionals should monitor for potential nutritional deficiencies in vegan keto dieters and recommend fortified foods and a well-structured meal plan to ensure adequate intake of essential vitamins and amino acids.
Vegan Keto Meal Plan Template
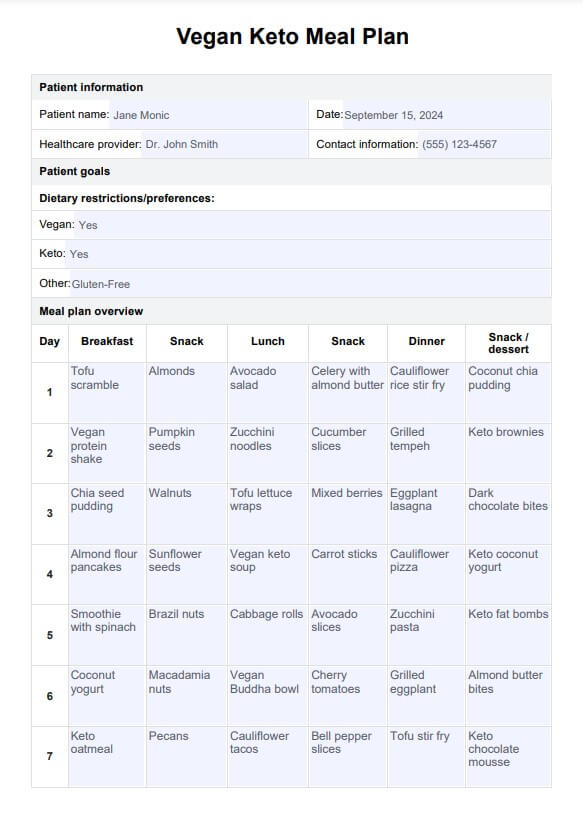
Vegan Keto Meal Plan Example
Vegan Keto Meal Plan template
The Vegan Keto Meal Plan template provides a structured guide to adopting a ketogenic vegan diet. It helps clients combine the benefit of a vegan diet with the principles of the ketogenic diet. It's a blank template that healthcare professionals can use to formulate balanced vegan keto diet meal plans, focusing on healthy fats such as olive oil, coconut oil, and full-fat coconut milk while minimizing carb intake from starchy vegetables.
This 7-day Vegan Keto Meal Plan template also helps healthcare professionals emphasize nutrient-dense foods like leafy greens, chia seeds, pumpkin seeds, and vegan protein sources to ensure adequate essential nutrients and amino acids.
By using this template, professionals can help clients adopt low-carb vegan diets that support weight loss, fat metabolism, and improved blood sugar control through a balance of plant-based foods and low-carbohydrate diets.
Key staple foods in a Vegan Keto Meal Plan
A well-structured Vegan Keto Meal Plan includes various nutrient-dense staples that provide essential nutrients while maintaining the low-carb, high-fat principles of both the vegan and ketogenic diets. Here are some of these foods:
Low-carb vegetables
Leafy greens like spinach, kale, arugula, and cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli and cauliflower are foundational in a vegan keto meal. These vegetables offer essential vitamins and minerals while keeping carb intake minimal.
Plant-based proteins
Sources like tofu, tempeh, edamame, and legumes such as black soybeans and Lupini beans are also key components of vegan keto diets. Additionally, plant-based protein powders from peas, hemp, and soy can help meet protein needs in vegan and ketogenic diets.
Nuts and seeds
Almonds, walnuts, macadamia nuts, pumpkin seeds, chia seeds, and hemp seeds are rich in healthy fats and protein. They can be incorporated into various vegan keto meal plans, serving as snacks, toppings, or recipe ingredients.
Plant-based oils
Coconut oil, olive oil, avocado oil, and MCT oil are essential sources of healthy fats that support ketosis and promote the health benefits of keto-vegan diets.
Non-dairy alternatives
Unsweetened almond milk, coconut milk, and coconut cream are widely used in vegan keto meal preparation. They add texture and flavor while maintaining low net carbs.
Low-carb fruits
Avocados, rich in healthy fats and low in carbohydrates, are a staple in many vegan keto diets. They are often used in salads, smoothies, and as toppings in various dishes.
Low-carb flours and alternatives
Coconut flour, almond flour, and flaxseed meal are versatile options for vegan keto foods, enabling the preparation of low-carb bread, pancakes, and other baked goods in a keto meal plan.
Plant-based dairy alternatives
Vegan cheese, coconut milk yogurt, and nut-based cheeses are commonly used substitutes for traditional dairy, offering texture and flavor to vegan keto meals.
These staples ensure that a 7-day vegan keto meal plan remains rich in essential nutrients while supporting weight loss and the overall health benefits of vegan and ketogenic diets.
Optimizing nutrient intake on a vegan keto diet
Maintaining adequate intake of essential vitamins and minerals on a vegan keto diet requires strategic planning and careful selection of plant-based foods. Here are key considerations to ensure proper nutrition for those following vegan ketogenic diets:
- Diverse vegetable intake: Incorporating a range of low-carb vegetables like leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, bell peppers, and mushrooms is essential for providing a broad spectrum of vitamins and minerals while keeping net carbs low. These nutrient-dense foods offer crucial nutrients, including vitamins like A, C, and K.
- Fortified foods: Many vegan foods and packaged foods, such as plant-based dairy alternatives and meat substitutes, are fortified with nutrients like vitamin B12, vitamin D, calcium, and iron. Vegan keto dieters should review labels to ensure they're consuming fortified foods to meet their nutritional needs, particularly for nutrients commonly found in animal foods.
- Nutritional yeast: This vegan-friendly food is an excellent source of vitamin B12, critical for neurological health and red blood cell production. It also adds a savory flavor to vegan keto meals, such as vegan cauliflower mac and chia seed pudding.
- Omega-3-rich foods: Flaxseeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, and walnuts provide alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a plant-based omega-3 fatty acid that supports heart health and reduces inflammation. These high-fat options are ideal for a keto meal plan.
- Supplementation: Given the exclusion of animal products in a vegan ketogenic diet, supplementation may be necessary for nutrients like B12, iron, and vitamin D. Healthcare professionals should assess individual nutrient needs and recommend appropriate supplements.
- Tracking intake: Utilizing a food diary or nutrition tracking tool can help monitor daily intake of essential nutrients, ensuring that the moderate protein diet remains balanced and deficient-free. This approach helps in minimizing carb intake while maintaining overall health.
By incorporating various unprocessed foods, fortified foods, and plant-based protein sources, vegan keto dieters can ensure they receive sufficient vitamins and minerals while supporting overall health and promoting fat metabolism and weight loss.
Benefits of a vegan keto diet vs. traditional diets
The vegan keto diet offers unique advantages when compared to other vegan or ketogenic diets, particularly for individuals looking to lose weight and improve metabolic health:
1. Weight loss
Combining the low-carb focus of the keto diet with the plant-based benefits of vegan diets promotes effective fat loss by encouraging the body to use body fat for fuel, reducing fat mass. Including unprocessed foods and high-fat options like avocados and nuts supports satiety and aids in weight management.
2. Blood sugar control
The vegan ketogenic diet stabilizes blood sugar levels by minimizing carb intake. This can be particularly helpful for those with diabetes or insulin resistance. The reduced reliance on carbohydrates helps maintain steady glucose levels.
3. Nutrient-dense, plant-based focus
A vegan keto diet emphasizes unprocessed foods such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and chia seed pudding, offering a higher intake of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants than a traditional keto diet that relies heavily on animal products.
4. Heart health
This dietary approach can improve heart health by reducing the intake of saturated fats common in traditional keto diets and increasing the consumption of heart-healthy fats from plant sources like olive oil, nuts, and seeds. The focus on plant-based fats reduces the risk of cardiovascular issues linked to a high intake of animal fats.
5. Environmental impact
A vegan ketogenic diet reduces reliance on animal foods, leading to a lower carbon footprint. This diet promotes sustainability and reduces environmental impact by focusing on plant-based foods.
Combining low-carb principles with a plant-based focus allows for a balanced approach to weight management, improved metabolic health, and a lower environmental footprint.
Risks of long-term adherence to a vegan keto diet
While a vegan keto diet can provide various health benefits, there are potential risks and challenges to consider, particularly when following this low-carb diet over the long term:
Nutrient deficiencies
Eliminating animal products and certain starchy vegetables can increase the risk of deficiencies in essential nutrients like vitamin B12, iron, calcium, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamin D (Neufingerl & Eilander, 2021). Eating fortified foods such as vegan butter, vegan cheese, and almond butter, as well as incorporating full-fat coconut milk and fortified plant-based foods, can help mitigate these risks. Careful planning and supplementation may be necessary for those adhering to a long-term vegan keto diet meal plan.
Limited food variety
The restrictive nature of a vegan keto diet limits the range of foods that can be consumed, potentially reducing dietary variety. Relying on staple vegan keto foods can make maintaining diversity and interest in meals challenging, making long-term adherence difficult. Utilizing a 7-day Vegan Keto Meal Plan with diverse recipes can help sustain motivation.
Risk of disordered eating
Strict adherence to diets like a keto-vegan diet may lead to an unhealthy focus on food choices and portion control (Alcorta et al., 2021), potentially increasing the risk of disordered eating behaviors like orthorexia. Healthcare professionals should encourage a balanced approach, prioritizing nutrient-dense foods over rigid dietary restrictions.
Digestive issues
The shift to a low-carb diet may result in digestive discomfort, such as constipation or bloating, especially if fiber intake is not adequately managed. Including fiber-rich foods like leafy greens and chia seed pudding can help alleviate these issues. Staying hydrated and ensuring a balanced intake of plant-based foods is essential for digestive health.
Cholesterol concerns
While the vegan keto diet can improve cholesterol levels for some, others may experience an increase in LDL cholesterol due to the higher intake of saturated fats from sources like coconut oil and coconut cream. Regularly monitoring cholesterol levels and adjusting dietary fats, such as using olive instead of coconut oil, may be necessary.
Social and practical challenges
Maintaining a vegan ketogenic diet in social situations, while dining out, or when traveling can be difficult due to limited food options. Advanced planning, clear communication of dietary needs, and flexibility are crucial to navigating these situations successfully.
Healthcare tips for supporting a vegan keto diet
Healthcare professionals play a critical role in supporting individuals following a vegan keto diet. Effective patient counseling, continuous monitoring, and individualized management can help ensure the diet is nutritionally adequate and sustainable. Here are key tips for healthcare professionals:
Patient counseling
Educate patients on the importance of a well-balanced vegan keto diet by emphasizing the need for nutrient-dense foods like leafy greens, hemp seeds, and almond butter. Encourage using fortified foods (e.g., vegan cheese and coconut milk yogurt) to prevent common nutrient deficiencies, such as B12, iron, and vitamin D. Offer guidance on structuring meals, avoiding over-restriction, and maintaining variety to support long-term adherence.
Monitoring nutrient intake
Monitor key biomarkers, including vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and cholesterol levels, regularly, particularly in individuals following the diet long-term. Regular blood tests can help detect potential nutrient deficiencies or imbalances. Use this data to adjust the patient's meal plan, adding supplements if necessary to meet their specific needs.
Customizing the diet
Tailor the vegan keto diet to each patient's status and goals, such as weight loss, blood sugar management, or cardiovascular health. For example, patients with high cholesterol may need to reduce their intake of saturated fats from sources like coconut oil and increase olive oil. Likewise, those struggling with digestive issues may require adjustments in fiber-rich foods like chia seed pudding to support gut health.
Addressing potential risks
Discuss the importance of flexibility and balance in the diet to proactively address risks like disordered eating. For patients struggling with food restrictions, offer strategies to manage low-carb diet requirements without becoming overly rigid. Encourage patients to focus on overall well-being rather than solely on weight loss.
References
Alcorta, A., Porta, A., Tárrega, A., Alvarez, M. D., & Vaquero, M. P. (2021). Foods for plant-based diets: Challenges and innovations. Foods, 10(2), 293. NCBI. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020293
Neufingerl, N., & Eilander, A. (2021). Nutrient intake and status in adults consuming plant-based diets compared to meat-eaters: A systematic review. Nutrients, 14(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010029
Commonly asked questions
Yes, the Vegan keto diet is possible. It combines the principles of the vegan diet with the low-carb, high-fat focus of the keto diet, relying on plant-based sources of fats and proteins like avocados, nuts, and seeds.
The vegan ketogenic diet may promote more effective weight loss due to its ability to increase fat metabolism and reduce carb intake. However, individual results vary based on adherence and overall nutrition.
Good vegan keto protein options include tofu, tempeh, hemp seeds, almond butter, and plant-based protein powders like pea or hemp protein. These are low in carbs and high in protein, supporting the needs of a vegan keto meal plan.


















-template.jpg)