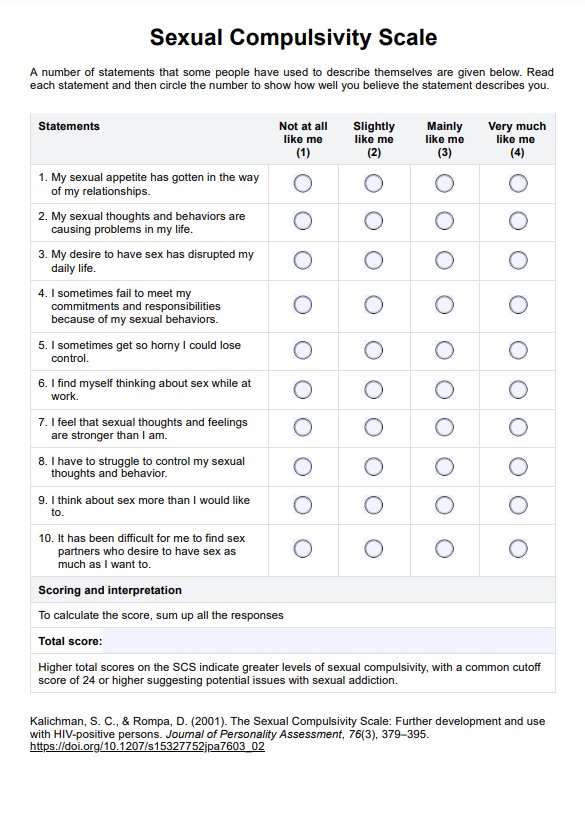
Sleeping Heart Rate Chart
Monitor patient heart health with a Sleeping Heart Rate Chart. Understand the importance of keeping heart rate at normal levels.


What is a Sleeping Heart Rate Chart?
A Sleeping Heart Rate Chart is a valuable health reference tool designed to provide typical heart rate values during awake states alongside specific information about sleeping heart rates for both children and adults. This chart offers a practical guide to understanding how heart rate varies between active and resting states, reflecting the body’s cardiovascular response throughout different phases of the day.
Our chart includes these key components:
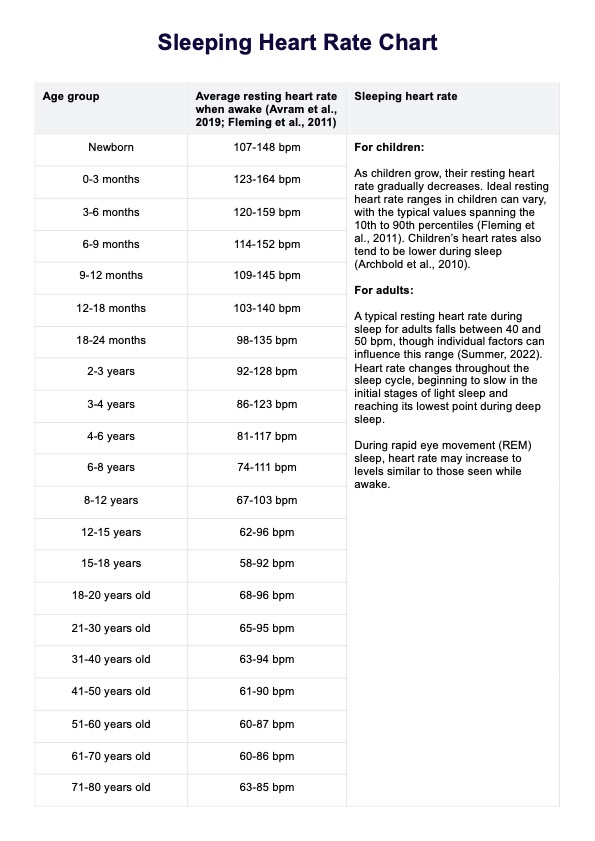
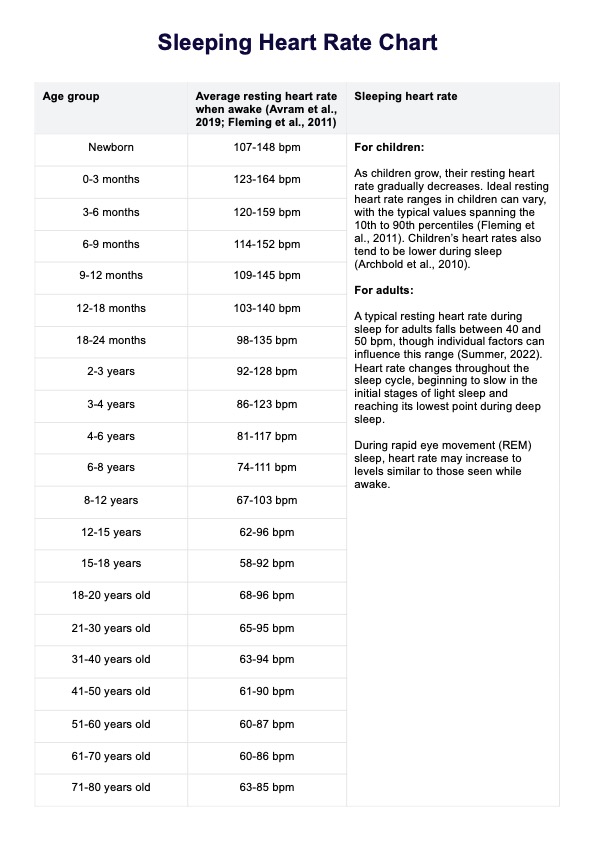
- Awake resting heart rates: Normal resting heart rate values in our chart represent baseline heart rate ranges measured in beats per minute (bpm) and are categorized by age group. These daytime resting heart rate values are based on the works of Avram et al. (2019) and Fleming et al.( 2011)
- Sleep heart rate information: Our chart also includes general information about normal sleeping heart rates for both children and adults. Sleeping heart rates tend to be lower than awake rates, reflecting the body’s reduced energy needs during rest. When the body is in a relaxed state, the heart rate slows as the body enters stages of deep sleep, facilitating physical and mental recovery.
Sleeping Heart Rate Chart Template
Sleeping Heart Rate Chart Example
How does it work?
Here's how to use our Sleeping Heart Rate Chart:
Step 1: Access the chart
Access the chart by clicking "Use template", allowing you to edit its content via the Carepatron app. For a PDF copy, click "Download."
Step 2: Understand the chart
Familiarize yourself with the components of the chart, including the awake resting heart rates and sleep heart rate information. Review the age-specific categories to find the relevant heart rate ranges for both children and adults. This understanding will help you interpret the data effectively and assess heart rate patterns accurately.
Step 3: Use as a reference
Utilize the chart as a reference guide to understand typical heart rate values during awake and sleeping states. While the chart itself does not include fields for recording personal data, you can refer to it when monitoring your patient's heart rate using a separate device, such as a heart rate monitor.
When should you use this chart?
The Sleeping Heart Rate Chart is a crucial tool for healthcare professionals to monitor patients’ cardiovascular health during sleep. Here are some key situations where this chart can be beneficial:
Monitoring for sleep disorders like sleep apnea
A stable, low sleeping heart rate is typical for healthy adults. However, fluctuations or consistently elevated rates can indicate sleep disorders such as sleep apnea. For example, individuals with sleep apnea may experience sudden increases in heart rate due to repeated interruptions in breathing, which places stress on the cardiovascular system.
Assessing physical fitness and average resting heart rate
For individuals who exercise regularly, the Sleeping Heart Rate Chart can also be a helpful tool to monitor heart health improvements. Regular physical fitness is often associated with a lower average resting heart rate, as a well-conditioned heart can pump blood more efficiently. Tracking these trends over time allows both individuals and healthcare professionals to assess improvements in cardiovascular health and fitness levels, using reduced sleeping heart rate as an indicator of physical fitness and overall health.
Identifying underlying health conditions
A consistently elevated or irregular sleeping heart rate can be a sign of underlying health conditions that might otherwise go unnoticed, such as thyroid issues or chronic stress. By comparing an individual’s sleeping heart rate to the normal ranges shown in the chart, healthcare professionals can detect early warning signs of health issues, prompting further investigation and treatment if necessary.
Factors affecting sleeping heart rate
A typical resting heart rate during sleep for adults falls between 40 and 50 bpm, though individual factors can influence this range (Summer, 2022). For children, normal sleeping heart rate also tends to be lower during sleep (Archbold et al., 2010). Here are some factors that affect these rates:
Physical activity levels
Individuals who engage in regular physical activity often have a lower average resting heart rate, which extends to their normal sleeping heart rate as well. This is due to improved cardiovascular efficiency, allowing the heart to pump blood more effectively. As a result, individuals with higher fitness levels tend to have lower sleeping heart rates, indicating better cardiovascular health and recovery during sleep.
Sleep stages
Heart rate varies across the different sleep stages. During deep sleep (slow-wave sleep), the heart rate typically reaches its lowest point, reflecting a calm and restorative state. However, in REM sleep, where vivid dreaming occurs, heart rate may briefly increase. The transition through these sleep stages naturally influences heart rate patterns, contributing to an average resting heart rate that changes throughout the night.
Presence of a sleep disorder
Sleep disorders like sleep apnea can disrupt normal sleeping heart rates by causing sudden spikes due to breathing interruptions. These disturbances prevent the heart from maintaining a steady rate, resulting in fluctuations that can stress the cardiovascular system. Tracking heart rate in individuals with sleep disorders can reveal patterns that might warrant further evaluation and treatment.
Age and health status
Age and general health status can also affect normal sleeping heart rates. While children naturally have slightly higher heart rates, their rates lower during sleep due to their rapid growth and metabolic activity. For adults, age-related health conditions, such as high-blood pressure, cardiovascular disease/heart disease or metabolic disorders, can lead to higher sleeping heart rates compared to younger, healthier individuals.
Stress and lifestyle factors
Stress, caffeine intake, and other lifestyle factors can influence heart rate during sleep. Chronic stress, for instance, can lead to higher-than-normal sleeping heart rates as the body remains in a heightened state of alert, even during rest. Limiting stimulants and adopting relaxation techniques before bed can help lower heart rate and improve sleep quality.
Research & Evidence
The importance of monitoring sleeping heart rate is underscored by various research studies, highlighting its role in assessing sleep quality and identifying potential health issues. Here's a summary of some fundamental research in this area:
- WiFi-Based Real-Time Breathing and Heart Rate Monitoring during Sleep (Gu, Zhang, Liu, & Ren, 2019): This study introduces a low-cost, continuous, and contactless method for monitoring vital signs, including heart rate, using WiFi-based technology. It emphasizes the accuracy of this method in detecting heart rate in different sleeping postures, showcasing the advancements in non-invasive sleep monitoring technologies.
- Vision-Based Heart and Respiratory Rate Monitoring During Sleep – A Validation Study for the Population at Risk of Sleep Apnea (Zhu, Li, Akbarian, Hafezi, Yadollahi, & Taati, 2019): This research validates an algorithm for tracking respiratory and heart rate using infrared video recordings. It highlights the potential of non-contact methods for monitoring vital signs during sleep, particularly for individuals at risk of sleep apnea.
- Sleep Diagnostics for Home Monitoring of Sleep Apnea Patients (Huysmans, Borzée, Buyse, Testelmans, Huffel, & Varon, 2021): The study focuses on developing a sleep-wake classifier for estimating sleep time in obstructive sleep apnea patients. It underscores the importance of monitoring heart rate and respiratory signals for practical sleep analysis.
- Smart Mandibular Advancement Device for Intraoral Monitoring of Cardiorespiratory Parameters and Sleeping Postures (Nabavi & Bhadra, 2021): This paper proposes a smart device for monitoring cardiorespiratory parameters and sleeping postures, highlighting the integration of technology in sleep health. It demonstrates the device's accuracy in estimating heart rate and other vital signs.
These studies collectively demonstrate the evolving landscape of sleep health monitoring, emphasizing the critical role of heart rate monitoring in diagnosing and managing sleep-related disorders.
References
Archbold, K. H., Johnson, N. L., Goodwin, J. L., Rosen, C. L., & Quan, S. F. (2010). Normative heart rate parameters during sleep for children aged 6 to 11 years. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine : JCSM : Official Publication of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, 6(1), 47–50. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20191937/
Avram, R., Tison, G. H., Aschbacher, K., Kuhar, P., Vittinghoff, E., Butzner, M., Runge, R., Wu, N., Pletcher, M. J., Marcus, G. M., & Olgin, J. (2019). Real-world heart rate norms in the Health eHeart study. Npj Digital Medicine, 2(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-019-0134-9
Fleming, S., Thompson, M., Stevens, R., Heneghan, C., Plüddemann, A., Maconochie, I., Tarassenko, L., & Mant, D. (2011). Normal ranges of heart rate and respiratory rate in children from birth to 18 years of age: a systematic review of observational studies. The Lancet, 377(9770), 1011–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(10)62226-x
Summer, J. (2022, March 25). What is a normal sleeping heart rate? Sleep Foundation. https://www.sleepfoundation.org/physical-health/sleeping-heart-rate
Commonly asked questions
A good sleeping heart rate can vary significantly by age, reflecting the natural changes in cardiovascular function throughout the lifespan.
An unsafe heart rate while sleeping is generally considered to be significantly higher or lower than the normal range for a given age group.
The best average sleeping heart rate typically falls within the range of 40 to 50 bpm for healthy adults.












-template.jpg)