Common causes of shoulder pain
Understanding the common causes of shoulder problems is essential for better planning interventions to treat shoulder pain.
Rotator cuff tear and tendinitis
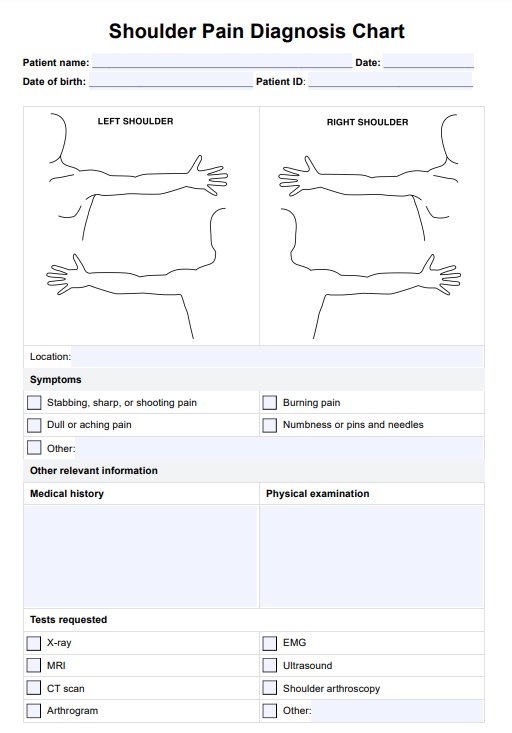
The rotator cuff is a group of four tendons that attach the shoulder muscles to the upper arm bone (humerus). Rotator cuff injuries can result from overuse, aging, or acute trauma, causing severe pain, weakness, and limited range of motion (Bigoni et al., 2019). Practitioners can use Shoulder Pain Diagnosis Charts like the Rotator Cuff Pain Location Diagram to diagnose shoulder pain in this area.
Shoulder impingement syndrome
Shoulder impingement syndrome occurs when the rotator cuff tendons become trapped and compressed against the shoulder blade, leading to inflammation and shoulder blade pain.
Frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis)
Frozen shoulder, or adhesive capsulitis, is a condition characterized by stiffness, pain, and limited shoulder joint mobility due to the joint capsule's thickening and tightening.
Shoulder bursitis
Bursitis is an inflammation of the fluid-filled sac (bursa) that cushions the shoulder joint, often caused by repetitive motions or injury.
Shoulder instability and dislocation
Shoulder instability or dislocation occurs when the upper arm bone (humerus) becomes wholly or partially displaced from the shoulder socket, often due to trauma or repetitive overhead activities.
Rotator cuff tendonitis
Rotator cuff tendinitis is a tendon inflammation that connects the rotator cuff muscles to the upper arm bone, typically caused by overuse or injury (Bigoni et al., 2009).
Shoulder separation or acromioclavicular (AC) joint injury
A shoulder separation or acromioclavicular (AC) joint injury involves the separation of the collarbone (clavicle) from the shoulder blade (scapula), commonly resulting from a fall or direct impact on the shoulder.
Clavicle fracture
The clavicle, or collarbone, is the most frequently broken bone. A clavicle injury can cause pain, swelling, and limited shoulder movement, often due to a motor vehicle accident or sports-related trauma.
Soft tissue injuries
Shoulder pain can also arise from injuries to the soft tissues surrounding the shoulder joint, such as the muscles, tendons, and ligaments. These injuries can result from trauma, overuse, or underlying conditions like rotator cuff tears or shoulder impingement syndrome.
Shoulder blade fractures
Fractures of the shoulder blade (scapula) are relatively uncommon but can occur due to high-energy trauma, such as motor vehicle accidents or falls from significant heights. These fractures in the shoulder blades can cause severe pain, swelling, and limited shoulder motion.
Muscle spasms and strains
Overuse, sudden movements, or underlying conditions like muscle weakness or imbalances can cause muscle spasms and muscle strains in the shoulder region. These issues can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced shoulder mobility.
Shoulder arthritis
Arthritis in the shoulder joint can be a source of chronic pain and stiffness. Different types of arthritis, such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or post-traumatic arthritis, can affect the shoulder joints and surrounding structures.
Referred pain
In some cases, shoulder pain may be referred from other areas of the human body, such as the neck (cervical spine), which causes nerve pain, chest (heart or lungs), or upper back (thoracic spine). This phenomenon, called referred pain, can make it challenging to identify the underlying cause of shoulder discomfort.
The most vulnerable parts of the shoulder to pain and injury are the four rotator cuff tendons, which are prone to conditions like rotator cuff injuries, tears, bursitis, and tendinitis. These structures play a crucial role in shoulder stability and movement, making them susceptible to overuse, trauma, and degeneration, leading to various painful conditions that can impact the function of the shoulder joint. It is then essential for patients to protect these shoulder bones and joints to prevent shoulder pain and shoulder injury.