Neurological assessments are typically performed by healthcare professionals with specialized training in neurology, such as neurologists, neurosurgeons, and specialized nurses. However, other healthcare providers, including primary care physicians, emergency medicine physicians, rehabilitation specialists, and advanced practice providers, may also perform neurological assessments as part of their clinical practice.
Neurological Assessment
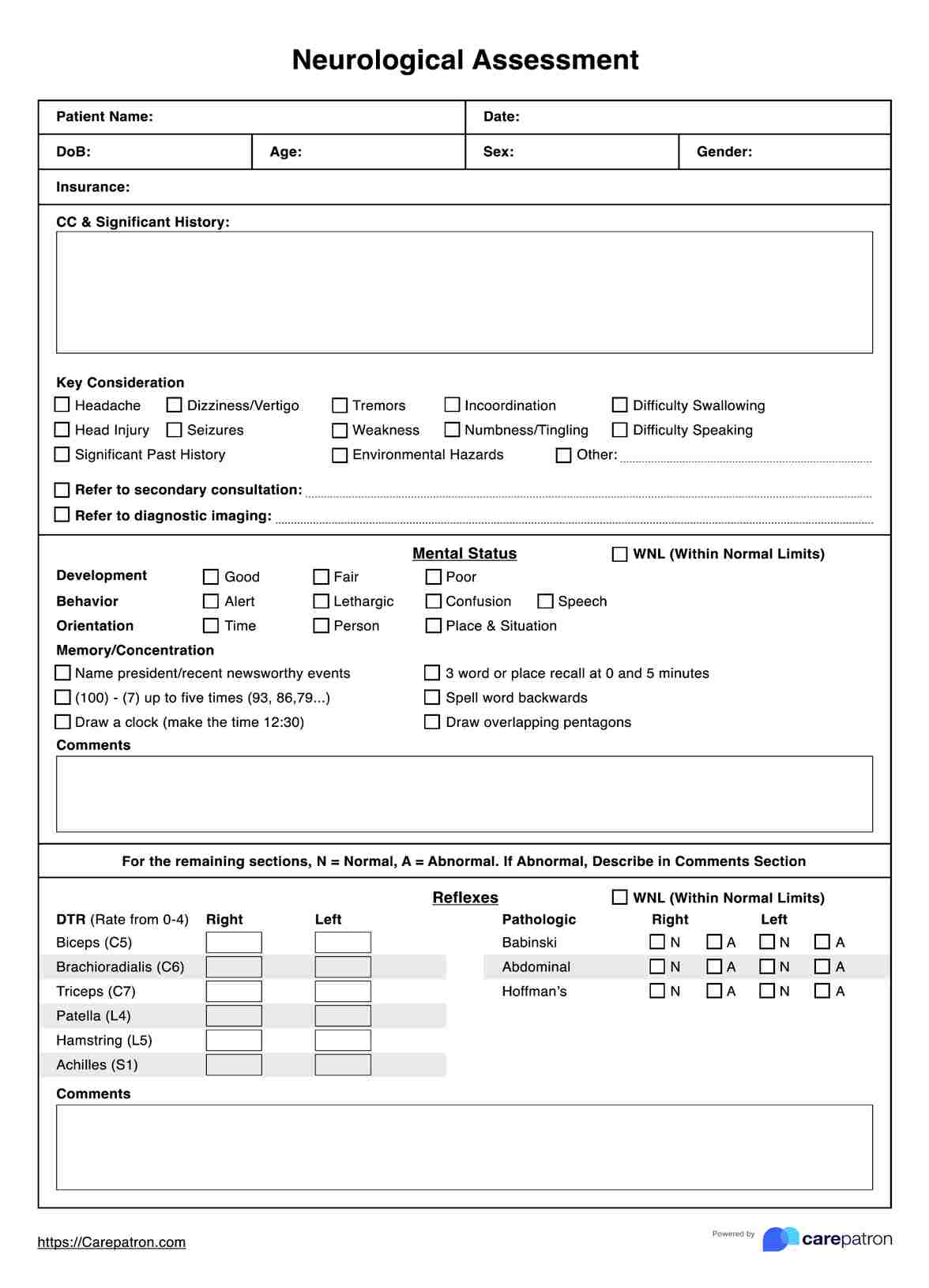
Neurological assessment is a medical evaluation that tests the function of the nervous system. It helps diagnose conditions like strokes and seizures.
Neurological Assessment Template
Commonly asked questions
Standard tools used in a neurological assessment include reflex hammers, tuning forks, visual acuity charts, pinprick or touch sensation tests, muscle strength testing equipment, coordination tests (such as finger-to-nose or heel-to-shin), and cognitive screening tools (such as the Mini-Mental State Examination).
The duration of a neurological assessment can vary depending on the complexity of the patient's condition, the specific tests conducted, and the thoroughness of the evaluation. It can range from a few minutes for a focused assessment to more than an hour for a comprehensive review.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











