Lung Cancer Genetic
Offer advanced genetic insights to your patients with Lung Cancer Genetic Tests for healthcare professionals.


What is a Lung Cancer Genetic Test?
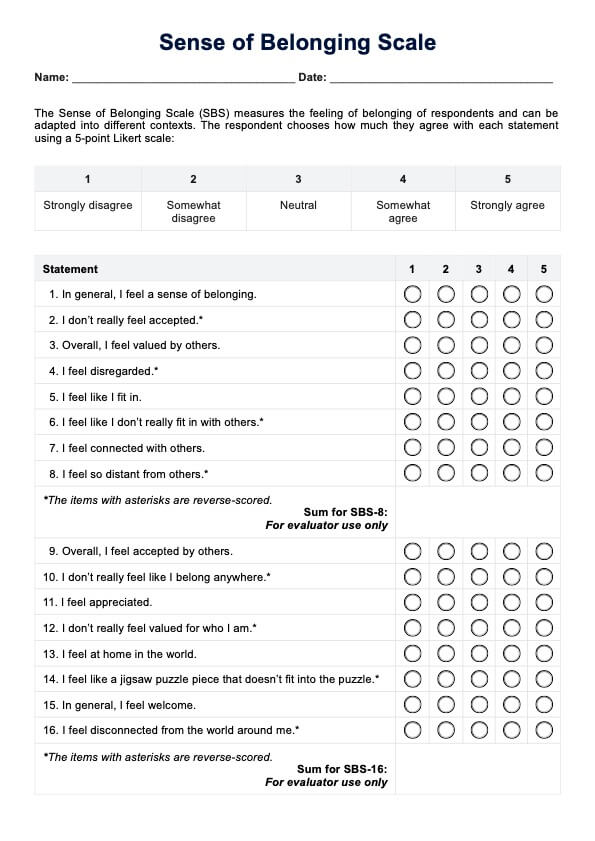
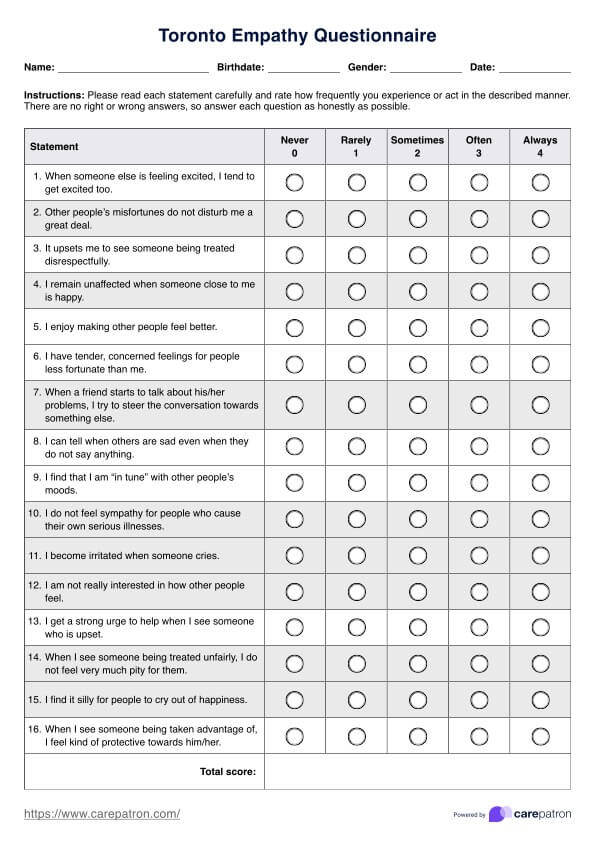
A Lung Cancer Genetic Test, a genetic screening or molecular profiling, is a diagnostic tool designed to identify specific genetic mutations and alterations within a patient's lung cancer cells. These tests are crucial in tailoring personalized treatment plans for lung cancer patients.
During the test, a sample of the patient's tumor tissue, typically obtained through a biopsy, is analyzed in a laboratory setting. Advanced techniques are used to examine the DNA or RNA within the cancer cells, searching for mutations and changes that drive the tumor's growth. Key genetic mutations commonly targeted include EGFR, ALK, ROS1, and KRAS.
The results of a Lung Cancer Genetic Test offer valuable insights into the tumor's molecular characteristics, helping oncologists determine the most suitable treatment options. This personalized approach is instrumental in selecting targeted therapies or immunotherapies that address the identified genetic alterations, potentially improving treatment efficacy and reducing side effects.
Lung Cancer Genetic Tests are a vital component of precision medicine in oncology, offering hope for more effective treatments and better outcomes for lung cancer patients by tailoring therapies to the unique genetic profile of each individual's tumor.
Lung Cancer Genetic Template
Lung Cancer Genetic Example
How Does it Work?
The Printable Lung Cancer Genetic Test is a diagnostic tool identifying specific genetic mutations in a patient's lung cancer cells. Here's how the test works:
Step 1: Sample Collection
The process begins with collecting a tumor tissue sample through a biopsy or surgery. This sample is crucial as it contains the cancer cells with genetic information necessary for analysis.
Step 2: Sample Preparation
Pathologists carefully prepare the collected tissue to isolate the cancer cells. The goal is to obtain a high-quality sample free from contaminants that could affect the test's accuracy.
Step 3: DNA Extraction
DNA or RNA is extracted from the isolated cancer cells. This genetic material carries the instructions that govern the growth and behavior of these cells, including any mutations responsible for driving the cancer.
Step 4: Genetic Analysis
Advanced laboratory techniques are employed to analyze the extracted DNA. Specialized equipment and software are used to search for specific genetic mutations and alterations associated with lung cancer, such as EGFR, ALK, ROS1, and KRAS.
Step 5: Interpretation
Trained geneticists and oncologists interpret the results. They determine the presence or absence of mutations and assess their clinical significance. This step guides the selection of the most appropriate treatments based on the identified mutations.
Step 6: Treatment Recommendations
Based on the genetic test results, physicians develop a personalized treatment plan for the patient. This may involve targeted therapies or immunotherapies addressing the specific genetic alterations in the cancer cells.
When Would You Use This Test?
Oncologists and healthcare practitioners employ the Lung Cancer Genetic Test in various critical scenarios to benefit patients.
Firstly, when a patient is diagnosed with lung cancer, this test plays a pivotal role in tailoring a precise treatment plan. It helps identify genetic mutations, such as EGFR, ALK, ROS1, and KRAS, determining the best therapeutic approach. Utilizing this test during diagnosis allows clinicians to make informed decisions, optimizing the chances of treatment success while minimizing side effects.
Secondly, the Lung Cancer Genetic Test is valuable for patients with advanced-stage or recurrent lung cancer. In these situations, the genetic landscape of the tumor may have evolved, necessitating a reevaluation of the treatment strategy. By conducting this test at such junctures, oncologists can adapt the treatment plan to target any new mutations, ensuring that therapy remains tailored to the patient's evolving condition.
Additionally, the genetic test can uncover alternative targeted therapies or immunotherapies for lung cancer patients who have not responded adequately to standard treatments. It is particularly relevant when patients require options beyond traditional chemotherapy or radiation.
Lastly, individuals with a family history of lung cancer, especially those with a known genetic predisposition, may benefit from proactive genetic testing. Identifying high-risk individuals early can aid in implementing preventive measures and regular screenings, potentially detecting lung cancer at an earlier, more treatable stage.
What do the Results Mean?
A Lung Cancer Genetic Test results provide crucial information that guides treatment decisions and offers hope to patients. Common results often fall into three categories, each with distinct implications.
A positive result indicates the presence of specific genetic mutations like EGFR, ALK, ROS1, or KRAS. For patients, this means a tailored treatment approach is possible. Targeted therapies or immunotherapies can attack the identified mutations, potentially leading to more effective and less invasive treatment.
A negative result means that the test did not detect these common mutations. In such cases, standard treatments like chemotherapy or radiation may be recommended. However, the absence of these mutations can also signify a potentially better prognosis.
Some results may be indeterminate or reveal complex genetic profiles. Further analysis or consultations with genetic specialists may be required in these instances. It's crucial to consider additional testing and clinical evaluation to determine the most appropriate treatment strategy. You can use this Clinical Evaluation template. It involves collecting and analyzing clinical data to demonstrate that the device meets regulatory requirements for its intended use.
A Free Lung Cancer Genetic Test can bring hope and precision to the treatment of lung cancer, ensuring that therapies align with the tumor's genetic makeup. Understanding these results empowers patients and their healthcare teams to make informed decisions, potentially improving treatment outcomes and quality of life.
Research & Evidence
The Lung Cancer Genetic Test has evolved due to significant research efforts over the past two decades, reshaping the landscape of lung cancer treatment. Its history traces back to the early 2000s when groundbreaking studies began identifying specific genetic mutations in lung cancer, notably EGFR and ALK. Researchers recognized that these mutations played a crucial role in driving tumor growth and offered potential targets for treatment. Subsequent studies and clinical trials expanded this understanding, revealing the effectiveness of targeted therapies in patients with these mutations.
One milestone in the history of this test was the IPASS trial (Iressa Pan-Asia Study), which demonstrated the superiority of the EGFR inhibitor gefitinib in EGFR-mutated lung cancer patients. This pivotal trial paved the way for personalized treatment of lung cancer. The discovery of ALK gene rearrangements and the development of ALK inhibitors, such as crizotinib, brought further evidence supporting genetic testing's significance in guiding treatment decisions.
Today, a wealth of research and clinical data supports using the Lung Cancer Genetic Test. It has become an essential tool for oncologists in tailoring treatment, leading to improved patient outcomes and quality of life. Research continues to explore new genetic targets and refine treatment strategies, promising further advancements in the field.
References
- Mok, T. S., Wu, Y. L., Thongprasert, S., Yang, C. H., Chu, D. T., Saijo, N., ... & Fukuoka, M. (2009). Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. New England Journal of Medicine, 361(10), 947-957.
- Shaw, A. T., Kim, D. W., Nakagawa, K., Seto, T., Crinó, L., Ahn, M. J., ... & Yang, J. C. (2013). Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. New England Journal of Medicine, 368(25), 2385-2394.
Commonly asked questions
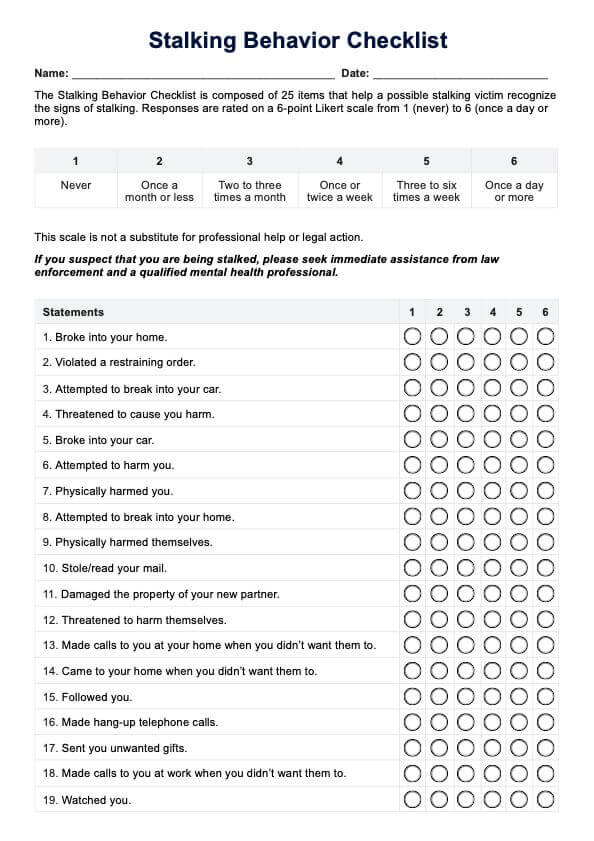
Doctors and sometimes patients request these tests when dealing with lung cancer, especially if they seek personalized treatment or have a family history of the disease.
These tests are used during diagnosis to guide treatment choices and can be repeated during treatment changes or when exploring different therapies.
These tests analyze tumor samples to find specific gene mutations. The results help decide the best treatment, like targeted therapies matched to a patient's genes.