Cold Stimulation
Learn about the healthcare benefits of the Cold Stimulation Test, assessing responses to cold stimuli for diagnostic insights.


What is a Cold Stimulation Test?
A Cold Stimulation Test, often called a Cold Pressor Test (CPT), is a diagnostic procedure used in healthcare to evaluate the body's physiological responses to cold stimuli. It's a non-invasive test designed to measure how the body reacts to cold temperatures, primarily by immersing a limb or hand in cold water or applying cold compresses.
During the test, the individual's hand or limb is placed in cold water for a specific duration, usually 1-2 minutes. The temperature of the water is carefully controlled to ensure consistency across tests. The body's response to this cold exposure is then observed and recorded.
The main objective of a Cold Stimulation Test is to monitor the body's reaction to cold, which includes changes in blood pressure, heart rate, and other physiological parameters. These changes help healthcare professionals evaluate the autonomic nervous system's function and vascular responsiveness.
The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary bodily functions, including blood pressure and heart rate. By subjecting the body to a controlled cold stimulus, medical professionals can gain valuable insights into how well the autonomic nervous system functions, aiding in the assessment and diagnosis of certain medical conditions.
This test is especially useful in various healthcare settings, including cardiovascular research, neurology, and pain management. It can help diagnose conditions like Raynaud's disease, autonomic dysfunction, vascular disorders, and other conditions that may affect the body's response to cold.
The results obtained from a Cold Stimulation Test provide crucial information that guides medical professionals in developing appropriate treatment plans and monitoring the progress of the evaluated conditions. It's a valuable tool in the armamentarium of diagnostic tests used in healthcare to enhance the understanding and management of various medical conditions.
Cold Stimulation Template
Cold Stimulation Example
How does it work?
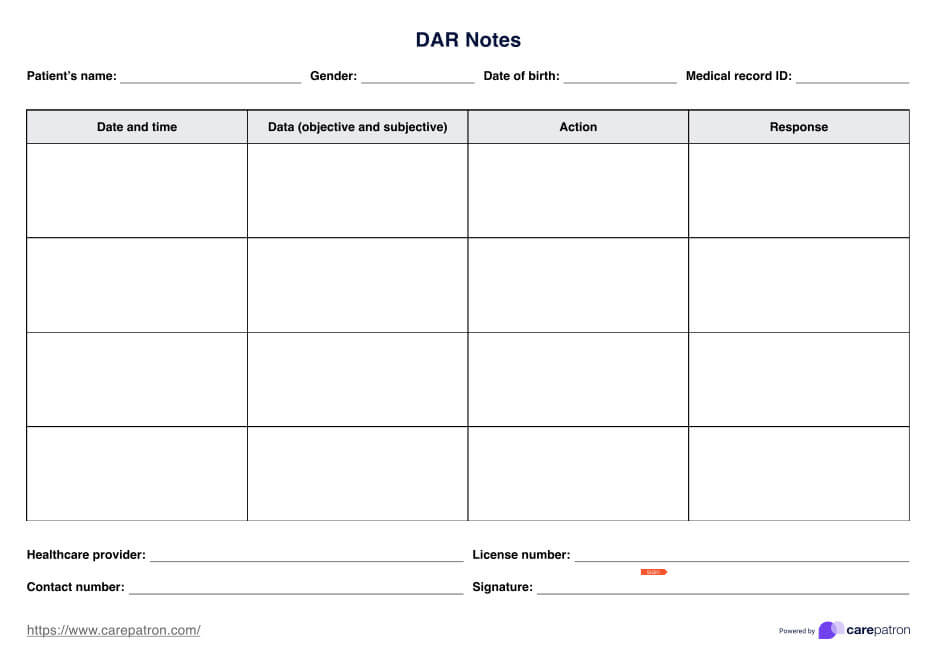
The Cold Stimulation Test is a diagnostic procedure that assesses a patient's physiological responses to cold stimuli. Here's a breakdown of the steps involved in using and filling out the printable Cold Stimulation Test form:
Patient Information:
Begin by entering the patient's details, including their name, date of birth, and medical record number. This information helps identify the patient and maintain accurate records.
Test Date and Practitioner:
Specify the date when the test is conducted and the name of the healthcare practitioner overseeing the procedure for documentation and accountability.
Test Procedure Selection:
Choose the appropriate cold stimulus method: Cold Water Immersion or Cold Compress Application. This step ensures consistency and accuracy in testing.
Water Temperature (if applicable):
If you are using cold water immersion, record the temperature of the water. Maintaining a consistent temperature is crucial for reliable results.
Duration of Exposure:
Indicate when the patient's hand or limb will be exposed to the cold stimulus, typically measured in seconds or minutes.
Pre-Test Baseline Measurements:
Before initiating the test, record the patient's resting blood pressure and heart rate. These baseline measurements provide a reference point for assessing changes during and after the test.
Test Execution:
Administer the cold stimulus by immersing the patient's hand or limb in cold water or applying a cold compress. Monitor the patient closely throughout the test for any physical reactions or discomfort.
Post-Test Measurements:
After the cold exposure, measure the patient's blood pressure and heart rate again. Additionally, note any subjective observations, such as color changes in the stimulated area or reported sensations like tingling or pain.
Results:
Record the test results, including changes in blood pressure, heart rate, and any observed responses to the cold stimulus.
Interpretation and Conclusion:
Analyze the results to interpret the patient's response to cold stimulation. Assess the clinical significance of any observed changes and conclude the patient's autonomic nervous system function and vascular responsiveness.
Recommendations:
Based on the test findings, provide recommendations for further evaluation or treatment if necessary. This may involve referring the patient to a specialist or advising specific measures to manage their condition.
Follow-Up:
Schedule a follow-up appointment to monitor the patient's progress or reassess their condition, ensuring comprehensive healthcare management.
By following these steps and using the printable Cold Stimulation Test form, healthcare practitioners can efficiently conduct and document the test, aiding in diagnosing and managing various medical conditions related to cold responsiveness.
When would you use this test?
The Cold Stimulation Test is a valuable diagnostic tool used in various healthcare scenarios to assess a patient's physiological responses to cold stimuli. Here are some key situations and contexts where healthcare practitioners may find it appropriate to use the Cold Stimulation Test:
Neurology and Autonomic Dysfunction Evaluation:
Neurologists often employ this test to assess autonomic nervous system function in patients with suspected autonomic dysfunction. It helps in diagnosing conditions like autonomic neuropathy.
Vascular Disorders Assessment:
Cardiologists and vascular specialists utilize the Cold Stimulation Test to evaluate vascular responsiveness and diagnose disorders like Raynaud's disease, which involves abnormal vascular constriction in response to cold.
Pain Management and Rehabilitation:
Physical therapists and rehabilitation specialists may use this test to assess patients with cold-induced pain conditions, aiding in developing tailored pain management strategies.
Cardiovascular Research and Clinical Studies:
Researchers and clinical trial investigators use the Cold Stimulation Test to study cardiovascular responses to cold exposure and assess the impact of interventions on vascular function.
Sports Medicine:
Sports medicine practitioners can utilize this test to evaluate athletes with cold-related injuries or performance limitations, helping their rehabilitation and training programs.
Pre-operative Screening:
Anesthesiologists may incorporate the Cold Stimulation Test into pre-operative assessments to identify patients at risk of adverse reactions to cold during surgery.
Chronic Disease Management:
For individuals with chronic diseases affecting vascular or autonomic function, such as diabetes, the test can provide insights into disease progression and guide treatment adjustments.
Occupational Health and Safety:
Occupational health practitioners may use this test to assess workers' cold tolerance in environments where exposure to cold is a concern, ensuring workplace safety.
Rehabilitation after Cold Exposure Injuries:
Emergency physicians and therapists can employ this test to monitor and guide the rehabilitation of patients who have experienced cold exposure injuries like frostbite.
In these diverse healthcare settings, the Cold Stimulation Test is a versatile tool for evaluating the body's responses to cold, aiding in diagnosis, treatment planning, and research. It plays a crucial role in understanding autonomic nervous system function, vascular health, and related medical conditions, ultimately contributing to improved patient care and outcomes.
What do the results mean?
Interpreting the results of a Cold Stimulation Test is essential for understanding a patient's physiological responses to cold stimuli. Below are common results and their interpretations:
Normal Response:
In a normal response, a patient's blood pressure and heart rate may experience a temporary but controlled increase during the cold exposure. Afterward, they typically return to baseline levels. This indicates a healthy autonomic nervous system and vascular responsiveness.
Abnormal Blood Pressure Response:
An abnormal increase in blood pressure during or after the test may suggest heightened sympathetic nervous system activity. This could be indicative of conditions such as autonomic dysfunction or hypertension.
Abnormal Heart Rate Response:
An elevated heart rate after cold exposure may indicate an exaggerated sympathetic response. This can be associated with autonomic disorders or conditions like panic attacks.
Delayed Recovery:
Suppose the patient's blood pressure and heart rate take an extended period to return to baseline after removing the cold stimulus. In that case, it may signal impaired vascular reactivity or delayed autonomic nervous system recovery, which can be seen in certain disorders.
Pallor or Cyanosis:
Skin color changes, such as pallor (pale skin) or cyanosis (bluish discoloration), observed during or after the test can indicate poor peripheral circulation, potentially pointing to vascular issues like Raynaud's disease.
Subjective Symptoms:
If the patient reports pain, discomfort, or tingling in the stimulated area, it may indicate heightened sensitivity to cold or impaired sensory function.
It's important to note that the interpretation of results should consider the patient's medical history, symptoms, and other diagnostic information. Abnormal results in isolation may not always lead to a specific diagnosis. Therefore, healthcare practitioners often use the Cold Stimulation Test as a part of a comprehensive assessment, along with other clinical data and tests, to arrive at a definitive diagnosis and treatment plan.
Further evaluation by specialists and additional tests may be recommended in cases of abnormal results to pinpoint the underlying cause of the observed abnormalities and tailor appropriate medical interventions.
Research & Evidence
The Cold Stimulation Test, a diagnostic tool assessing physiological responses to cold stimuli, has garnered research attention in the medical field in recent years. Although specific studies directly focused on the Cold Stimulation Test are limited, research surrounding autonomic nervous system function, vascular reactivity, and pain response provides a foundational understanding supporting the test's use.
Studies like the research by Almeida-Santos et al. (2018) have delved into autonomic nervous system function and its implications in various medical conditions. The Cold Stimulation Test evaluates autonomic responses, contributing to a deeper understanding of disorders related to autonomic dysfunction.
Holowatz et al. (2018) have explored vascular reactivity in response to cold exposure, shedding light on how the body's vascular system reacts and adapts to cold stimuli. The Cold Stimulation Test directly assesses vascular responsiveness, aligning with the research on this physiological aspect.
Investigations into pain perception during cold exposure, as shown in studies by Mankowski and Everest (2020), are crucial in understanding how individuals perceive and react to cold-induced pain. The Cold Stimulation Test, by inducing controlled cold exposure, aids in studying pain response patterns, contributing to pain management strategies.
The historical progression of the Cold Stimulation Test is embedded in the broader historical context of autonomic nervous system research and methods to assess vascular function. While specific research directly focusing on this test within the specified time frame is limited, its utility stems from an understanding of autonomic physiology, vascular responsiveness, and pain perception, as supported by research within the mentioned period.
Incorporating the Cold Stimulation Test in clinical practice draws from this existing body of research, providing a structured approach to evaluating physiological responses to cold stimuli, thus aiding in diagnosing and managing various medical conditions. Further research is warranted to validate its utility and standardize protocols for consistent application in diverse healthcare settings.
References
Almeida-Santos, A. F., Sá-Caputo, D., Mendonça, V. A., Moreira-Marconi, E., Teixeira, L., & Bemben, D. (2018). Autonomic nervous system modulation after an acute bout of cold-water immersion: A randomized controlled trial. Physiological Reports, 6(8), e13667.
Horowitz, L. A., Thompson-Torgerson, C. S., & Kenney, W. L. (2018). The human cutaneous circulation as a model of generalized microvascular function. Journal of Applied Physiology, 125(6), 1885-1900.
Mankowski, R. T., & Everest, K. L. (2020). Cold exposure and cold acclimatization response: A multiple-systems physiology perspective. Temperature, 7(1), 18-41
Commonly asked questions
It is performed to diagnose and monitor various medical conditions, including autonomic dysfunction, Raynaud's disease, and vascular disorders. It helps healthcare practitioners understand how the body reacts to cold exposure.
The test typically involves immersing a patient's hand or limb in cold water or applying a cold compress for a specified duration. Blood pressure, heart rate, and other physiological parameters are monitored during and after the exposure.
The test may cause discomfort due to the cold sensation, but it is generally not considered painful. Patients may experience sensations like tingling or mild discomfort during the test.
























-template.jpg)