C4 Complement Blood
Learn about the C4 Complement Blood Test and its significance! Download a free PDF guide on the C4 Complement Blood Test here.


What is a C4 Complement Blood Test?
A C4 Complement Blood Test, often called the C4 blood test, is a vital diagnostic tool in clinical immunology and pathology. This test plays a pivotal role in assessing the functionality of the complement system within the human immune system. The complement system is a complex network of proteins that plays a crucial role in immune responses, helping to combat infections and contributing to the removal of damaged cells and immune complexes from the body.
The C4 Complement Blood Test measures the levels of C4 proteins in a patient's bloodstream. C4A and C4B proteins are vital components of the complement system. Monitoring their levels can provide valuable insights into the functioning of this immune response mechanism.
The C4 Complement Blood Test results can offer significant diagnostic and prognostic information. Abnormal levels of C4, whether high or low, can serve as indicators of various medical conditions. Elevated levels suggest active inflammation or autoimmune diseases like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) or rheumatoid arthritis. Conversely, reduced levels can be associated with genetic deficiencies in complement components or other autoimmune disorders.
This resource, dedicated to C4 Complement Blood Tests, provides a comprehensive understanding of the test's purpose, the medical conditions it can help diagnose, and the factors affecting its results. It also offers a practical example of a C4 Complement Blood Test form, allowing patients and healthcare professionals to navigate the test efficiently.
Whether you are a healthcare provider seeking to interpret test results or an individual interested in understanding your immune system's health, this resource sheds light on the significance of C4 Complement Blood Tests and their role in maintaining overall well-being.
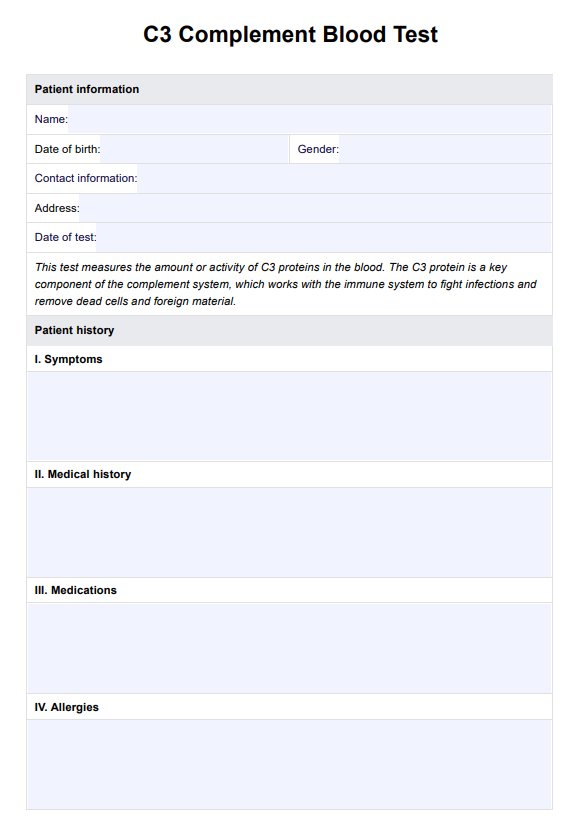
C4 Complement Blood Template
C4 Complement Blood Example
How does it work?
The C4 Complement Blood Test is a crucial diagnostic tool in assessing immune system function and identifying potential health issues related to complement component levels. Patients and healthcare professionals must understand how to use and fill out the accompanying form. Here's a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Obtain the Form
Begin by obtaining a printable C4 Complement Blood Test form, which may be provided by your healthcare provider or available for download from a reputable medical source.
Step 2: Patient Information
Start by filling out the patient information section, including your full name, date of birth, gender, contact details, and emergency contact information. Ensure accuracy to avoid any communication issues.
Step 3: Medical History
This section provides a detailed medical history, including any known autoimmune disorders, symptoms, previous diagnoses, or other relevant medical conditions. Honest and thorough information is vital for an accurate assessment.
Step 4: Medications
List all medications, supplements, and drugs you currently take, both prescription and over-the-counter. Include the medication name, dosage, frequency, and the reason for taking it. This information is crucial for assessing potential interactions.
Step 5: Laboratory Results
A healthcare professional completes the laboratory results section. It includes the actual C4 Complement Blood Test results, typically measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or grams per liter (g/L), and any other relevant findings from the test.
Step 6: Recommendations
Healthcare providers will use this section to provide recommendations based on the test results. It may include a diagnosis, treatment recommendations if necessary, and suggestions for additional tests or evaluations.
Step 7: Follow-up
The follow-up section outlines the next steps. It specifies whether a follow-up appointment is recommended, the date of the next appointment, and any additional instructions or comments from the healthcare provider.
Understanding these steps and accurately filling out the C4 Complement Blood Test form is essential for practical healthcare assessment and decision-making. Patients and healthcare professionals should collaborate closely to ensure all relevant information is provided and the form is completed correctly.
When Would You Use the C4 Complement Blood Test?
The C4 Complement Blood Test is a valuable diagnostic tool with various applications in clinical medicine. It is a critical resource for various healthcare practitioners to assess and monitor immune system function and detect specific medical conditions. Here are scenarios in which healthcare professionals may consider using the C4 Complement Blood Test:
Rheumatologists and Immunologists
Rheumatologists and immunologists often use the C4 Complement Blood Test to diagnose and monitor autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis. Abnormal C4 levels can indicate active disease activity and guide treatment decisions.
Nephrologists
Nephrologists specializing in kidney disorders may utilize the C4 Complement Blood Test to investigate kidney diseases associated with complement deficiencies. Low C4 levels can be linked to certain forms of kidney disease.
General Practitioners and Primary Care Physicians
General practitioners and primary care physicians can use the C4 Complement Blood Test to screen patients with symptoms suggestive of autoimmune disorders, such as joint pain, rash, and fatigue. Early detection can lead to timely referrals to specialists for further evaluation and management.
Hepatologists
Hepatologists focusing on liver disorders may consider the C4 Complement Blood Test in cases where chronic hepatitis is suspected. Abnormal complement levels can provide insights into the underlying immune response associated with liver diseases.
Clinical Immunologists
Clinical immunologists rely on the C4 Complement Blood Test as part of a broader immunological assessment. It aids in diagnosing complement component deficiencies and immune complex disorders.
Monitoring Disease Progression
For patients already diagnosed with autoimmune diseases or complement deficiencies, healthcare providers across specialties may use this test to monitor disease progression and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
Research and Clinical Trials
Researchers and clinicians involved in immunology research and clinical trials may incorporate the C4 Complement Blood Test to assess the impact of treatments on complement system function.
In summary, the C4 Complement Blood Test is a versatile resource used by a range of healthcare practitioners to aid in diagnosing, monitoring, and managing various medical conditions, particularly those related to autoimmune diseases and complement deficiencies. Its applicability extends across multiple specialties, making it an invaluable tool in clinical medicine.
What do the C4 Complement Blood Test Results Mean?
Interpreting the results of a C4 Complement Blood Test is a critical step in understanding an individual's immune system health and diagnosing certain medical conditions. The test provides insights into the levels of C4 proteins in the bloodstream, and these results can vary, indicating different health scenarios.
Here's what common C4 Complement Blood Test results typically mean:
Normal Range (16 to 48 mg/dL or 0.16 to 0.48 g/L)
A C4 level falling within the normal range is a positive sign. It suggests that the complement system, a part of the immune system, functions as it should. Normal results are often seen in healthy individuals without autoimmune disorders or complement deficiencies.
High C4 Levels
Elevated C4 levels can be indicative of active inflammation or immune system activation. Healthcare professionals may investigate further to determine the underlying cause. Elevated C4 levels are sometimes associated with autoimmune diseases like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
Low C4 Levels
Low C4 levels may signal a variety of medical conditions:
- Autoimmune Diseases: Reduced C4 levels, often accompanied by low C3 levels, are common in autoimmune diseases like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). These lower levels are due to the overconsumption of complement proteins in response to immune system activation.
- Complement Component Deficiencies: A deficiency in C4 levels, while other complement components are normal, can indicate an inherited complement component deficiency.
- Kidney Disease: Some forms of kidney disease may be associated with decreased C4 levels.
- Chronic Hepatitis: Low C4 levels can also be observed in chronic hepatitis, though this is less common.
Understanding these typical result interpretations is crucial for healthcare providers to make accurate diagnoses and treatment decisions. It's important to note that C4 Complement Blood Test results should always be considered alongside a patient's clinical history and other relevant tests to assess their immune system and overall health comprehensively.
For more detailed information on C4 Complement Blood Test results and their implications, refer to a free C4 Complement Blood Test resource, such as a downloadable PDF guide, which may offer additional insights.
Commonly asked questions
C4 Complement Blood Tests are typically requested by healthcare providers, including rheumatologists, immunologists, nephrologists, primary care physicians, and hepatologists. These tests are often ordered when evaluating patients with suspected autoimmune diseases, complement deficiencies, kidney diseases, or chronic hepatitis.
C4 Complement Blood Tests are used to assess the levels of C4 proteins in the bloodstream. The results are valuable for diagnosing and monitoring various medical conditions, including autoimmune diseases like lupus, complement component deficiencies, kidney diseases, and chronic hepatitis. They help healthcare providers make informed decisions about treatment and follow-up care.
The actual blood draw for a C4 Complement Blood Test typically takes just a few minutes, similar to a routine blood test. However, the total time for the entire process, including registration, blood collection, and waiting for results, can vary depending on the healthcare facility and the number of tests being conducted. Patients may spend 30 minutes to an hour or more at the healthcare facility for this test, including potential waiting time.
Results are usually available within a few days, but the exact turnaround time may vary by laboratory and location.






















-template.jpg)