Cognitive Ability Test
Explore Cognitive Ability Tests to assess reasoning, problem-solving, memory, and more with Carepatron. Ideal for predicting job performance and cognitive function.


What is a Cognitive Ability Test?
A Cognitive Ability Test is a standardized assessment that measures different aspects of an individual's mental capabilities. Cognitive testing evaluates a person's capacity to process information, solve problems, and apply knowledge across different domains. It provides valuable insights into cognitive functions that are crucial for learning, decision-making, and everyday tasks.
These cognitive tests typically assess skills such as:
- Verbal reasoning
- Numerical reasoning
- Abstract reasoning
- Spatial reasoning
- Problem-solving
- Critical thinking
- Language comprehension
These assessments are used in various settings, including educational institutions, workplaces, and healthcare environments. In educational contexts, they help identify students' strengths and areas for improvement. In occupational settings, they assist in predicting job performance and potential for success in specific roles.
For healthcare practitioners, these tests can be invaluable tools for diagnosing cognitive impairments, tracking progress in neurological conditions, and developing targeted interventions.
Cognitive Ability Test Template
Cognitive Ability Test Example
Types of Cognitive Ability Tests
Cognitive Ability Tests come in various forms, each designed to assess different aspects of mental functioning. Understanding these different types can help select the most appropriate test for a given situation or patient. Here are some of the most commonly used Cognitive Ability Tests:
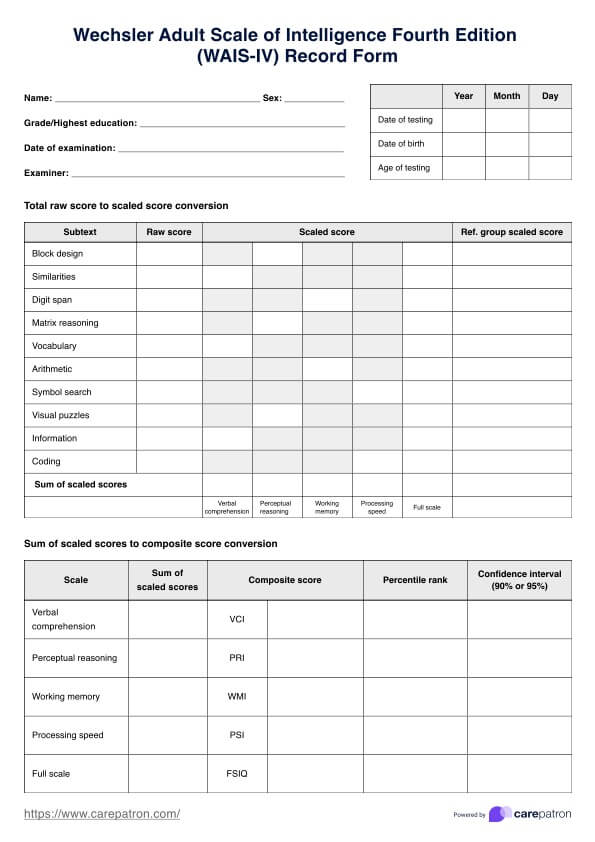
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)
The WAIS is one of the most widely used comprehensive Cognitive Ability Tests. It assesses various aspects of cognitive function, including verbal comprehension, perceptual reasoning, working memory, and processing speed.
Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scales
The Stanford-Binet Intelligence Test measures five cognitive abilities: fluid reasoning, knowledge, quantitative reasoning, visual-spatial processing, and working memory. It's often used to assess children and adults and can help identify intellectual giftedness or cognitive delays.
Raven's Progressive Matrices
This non-verbal test focuses on abstract reasoning and problem-solving abilities. It's particularly useful for assessing individuals from different cultural backgrounds or those with language difficulties, as it doesn't rely on verbal skills.
Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA)
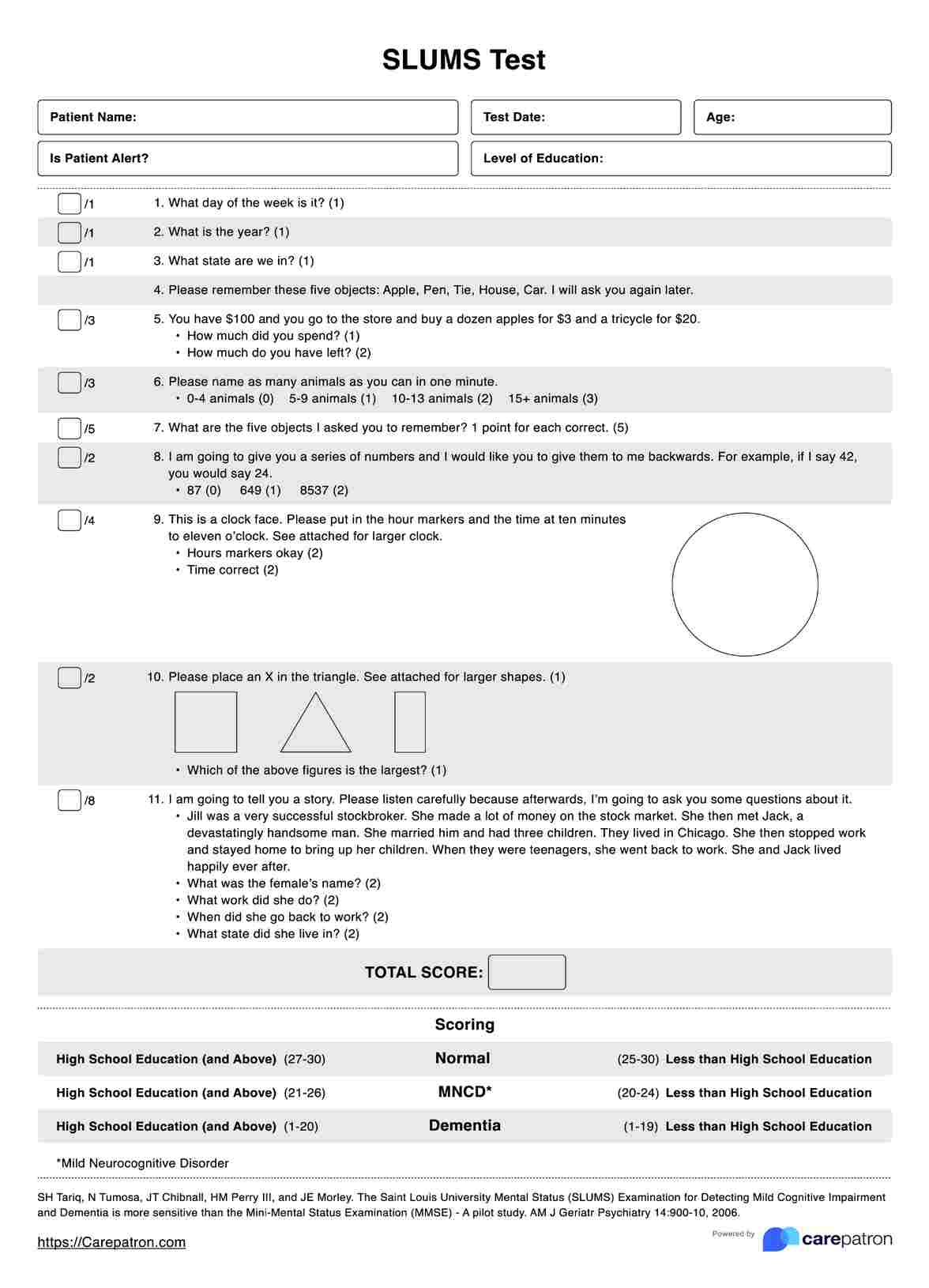
The MoCA is a rapid screening instrument for mild cognitive dysfunction. It assesses different cognitive domains, including attention, concentration, executive functions, memory, language, and orientation. It's particularly useful in detecting mild cognitive impairment and early-stage dementia.
Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE)
The MMSE is a widely used test for screening cognitive function. It briefly measures orientation to time and place, attention, recall, language, and visual construction. While it's not as sensitive as some other tests for detecting mild impairment, it's quick and easy to administer (Folstein et al., 1975).
Cognitive Abilities Test (CogAT)
The CogAT is primarily used in educational settings. It measures reasoning abilities in three areas: verbal, quantitative, and nonverbal. It's often used to identify gifted students or those needing additional support.
Criteria Cognitive Aptitude Test (CCAT)
Often used in employment settings, the CCAT assesses an individual's ability to solve problems, digest and apply information, learn new skills, and think critically. It's designed to predict job performance and learning potential. A CCAT practice test available online can help aspiring applicants train themselves on how to pass the test.
How to use this Cognitive Ability Test
Cognitive Ability Tests are methodically structured assessments that systematically measure an individual's mental capabilities. Here's a detailed look at how you can use this test in your practice:
Step 1: Gather client information and background
Begin by collecting essential client details, including personal information, presenting concerns, and relevant medical, educational, and occupational history. This context is crucial for accurately interpreting test results and tailoring recommendations to the individual's situation.
Step 2: Administer the cognitive assessment
Conduct the assessment across seven key cognitive domains. Each domain includes specific cognitive test questions and tasks designed to evaluate that particular aspect of cognitive function. Ensure consistent administration and accurate recording of results for each task.
Step 3: Record observations and interpret results
While administering the test, note any general observations about the client's behavior, engagement, or factors that might influence performance. After completing all tasks, interpret the results by comparing the client's performance to normative data or their own baseline.
Step 4: Develop recommendations and complete the report
Based on the interpretation, formulate tailored recommendations for the client. These might include further assessments, interventions, or strategies to support cognitive function. Complete the report by summarizing the findings, interpretation, and recommendations.
What do the results mean?
Interpreting the results of cognitive assessments involves critical thinking skills and clinical judgment in analyzing performance across seven key cognitive domains. Each area provides unique insights into the individual's cognitive functioning, helping to build a comprehensive picture of their strengths and potential areas for improvement.
- Memory: The test evaluates both short-term and long-term memory. Being able to answer correctly indicates how many words the individual can recall after brief and extended delays. This information can highlight any discrepancies between immediate and delayed recall, which may be significant for certain cognitive conditions.
- Attention and concentration: Performance on this task reveals the individual's ability to focus and respond to specific stimuli within a given timeframe. Lower scores might suggest difficulties with sustained attention or distractibility.
- Problem-solving and logical reasoning: This section assesses the ability to solve puzzles or riddles under time constraints. Results can indicate strengths or weaknesses in analytical thinking and cognitive flexibility.
- Verbal abilities: Tasks such as word definitions and verbal analogies provide insights into language comprehension and expression. This can be particularly relevant when considering conditions that affect language processing.
- Visual-spatial abilities: Performance in interpreting visual information, patterns, or shapes can reveal strengths or difficulties in spatial reasoning and visual processing.
- Processing speed: The time taken to complete simple tasks under timed conditions indicates cognitive efficiency and information processing speed.
- Working memory: This assesses the ability to manipulate and recall information within short periods, which is crucial for many cognitive tasks.
Commonly asked questions
Cognitive Ability Tests are standardized assessments designed to measure various aspects of a person's cognitive functioning, such as reasoning, problem-solving, memory, processing speed, and verbal and nonverbal skills. These tests aim to evaluate an individual's cognitive strengths and weaknesses objectively.
Cognitive tests typically include various question types and tasks that assess different cognitive domains. Common components of cognitive tests include verbal reasoning, numerical reasoning, abstract reasoning, spatial awareness, memory, and processing speed. The specific content and format of the test can vary depending on the purpose and target population.
One simple cognitive test often used for older adults is the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE). The MMSE is a 30-point questionnaire that evaluates an individual's orientation, memory, attention, language, and visual-spatial skills.

.jpg)














-template.jpg)