Organ Maps
Download our Organ Map handout as a visual guide and educational resource for anatomy and physiology.


What is an Organ Map?
The human anatomy is an intricate network of interconnected systems working in harmony to support life. To help understand this better, an Organ Map is a comprehensive visual and conceptual representation of how and organ system and its organs are positioned and function within the human body.
Organ Maps are essential tools for understanding major internal organs and their interconnected relationships in human anatomy. They are usually used as a guide or educational resource to familiarize themselves with anatomy and physiology. Though commonly used by medical and nursing students in school, medical professionals can also use these maps to refresh their knowledge. Our Organ Map, in particular, isn't only for the aforementioned purposes. It also has a space to document notes, findings, and observations of an actual patient or write down insights while they are studying anatomy.
As a medical practitioner or student, you don't need a rundown of the organ systems, which you will find on an Organ Map. So, instead of enumerating the organs, you'll find our take on an Organ Map template. We'll provide you with instructions on how to download our template when to use it, and the benefits of using our template.
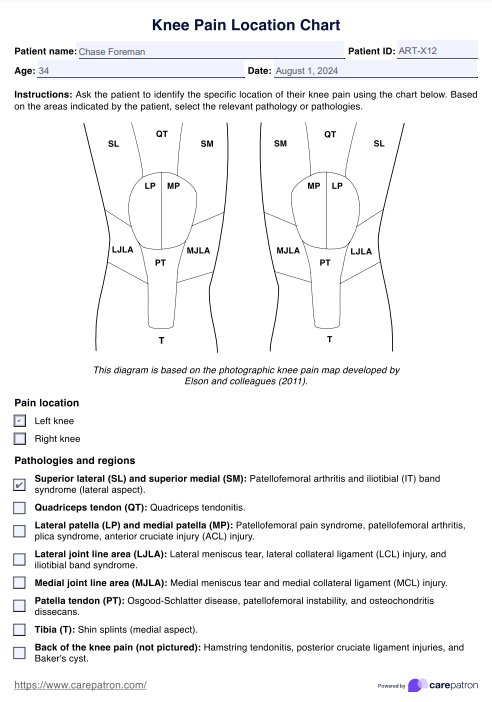
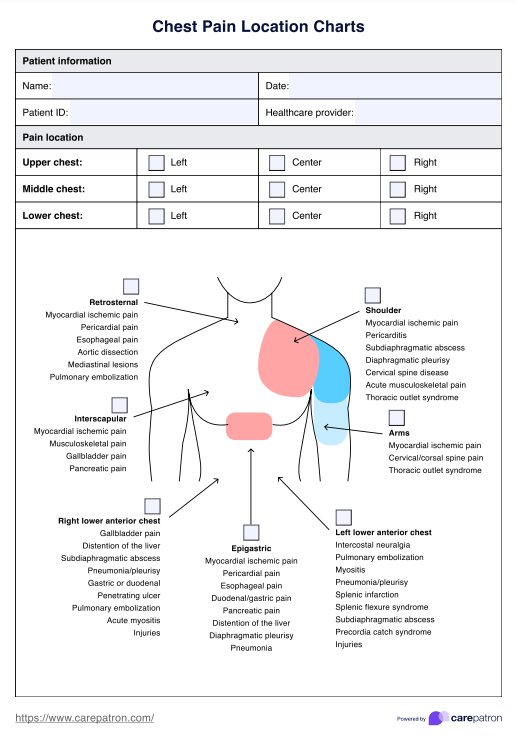
Organ Maps Template
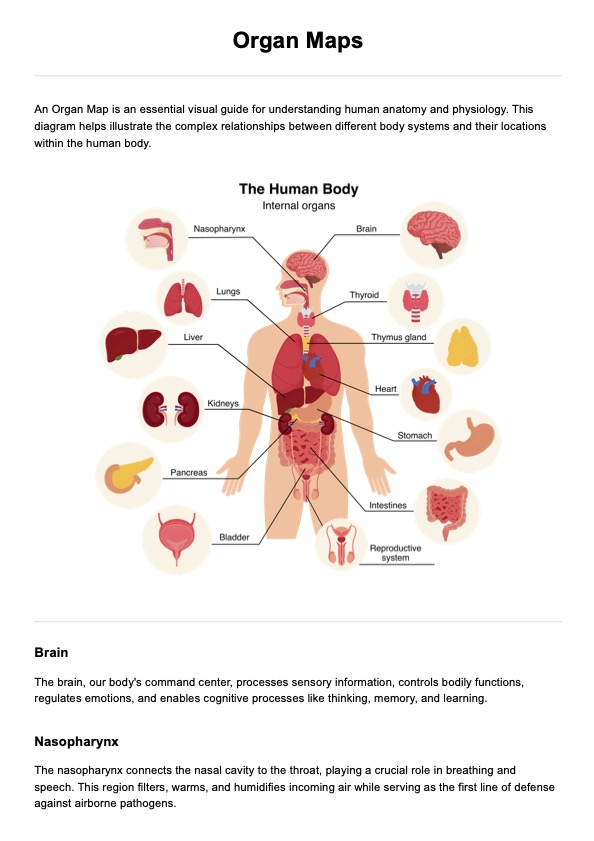
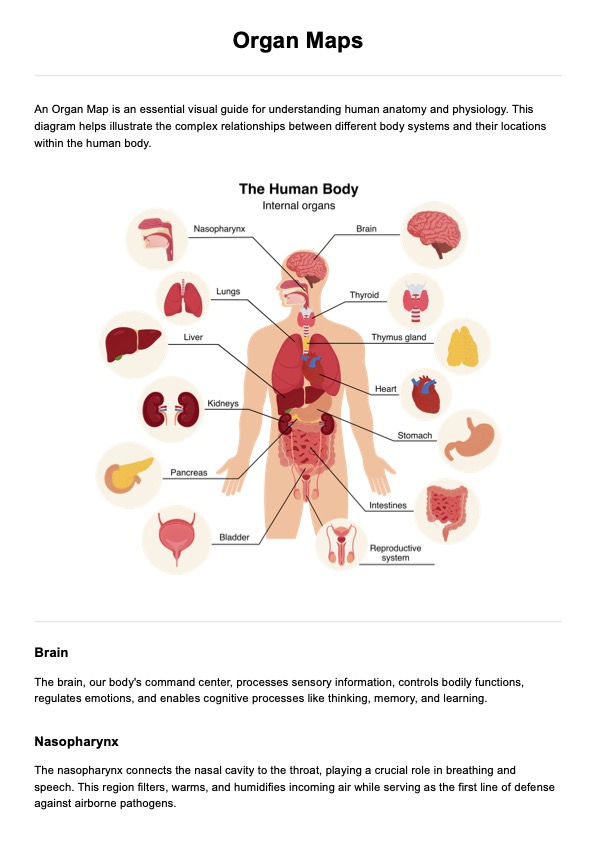
Organ Maps Example
How to use our Organ Maps template
Other systemic maps often provide specific and individual illustrations for each of the following:
- digestive system
- central nervous system
- human skeletal system
- reproductive system
- endocrine system
- circulatory system
- respiratory system
However, we have designed our Organ Map as an easy-to-understand overview of the major internal organs, such as the human brain, kidneys, and lungs. The following are steps on how to use this in clinical practice:
Step 1: Access and download the template
To access and download a digital and printable copy of the “Organ Map” template, you can click the “Use Template” button and access this within the Carepatron platform or select "Download" to get a fillable PDF copy.
Step 2: Use the map as a tool for general overview
Use the map as a general overview tool to identify basic organ positions and their relative locations to each other. For instance, noting how the liver sits in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, adjacent to the stomach, helps establish fundamental anatomical relationships.
Step 3: Map out connections
When using this handout in studying, you can use the Organ Map to trace organ systems and their connections. This involves following pathways such as the digestive tract from start to finish or examining how blood vessels connect different organs to understand their functional relationships.
Step 4: Keep it accessible
The map serves as a quick reference point during study sessions, clinical rotations, or when needing to refresh anatomical knowledge. Keep it accessible to complement detailed textbooks and clinical guides, using it to verify organ locations or explain basic concepts to others.
When would you use this Organ Map?
An Organ Map serves as an essential reference tool in various clinical and educational settings, providing a detailed visual and conceptual understanding of human anatomy. This can be useful in the following scenarios:
Clinical assessment
Organ Maps help identify precise anatomical locations and potential areas of concern during physical examinations and diagnostic procedures. They also provide reference points for documenting findings and planning further investigations.
Procedural planning
Organ Maps are essential in preparing for medical procedures, from routine examinations to complex interventions. They assist in visualizing anatomical relationships and planning appropriate approaches, particularly when considering the proximity of vital structures.
Patient education
These maps serve as effective visual aids during patient consultations, helping explain anatomical concepts, medical conditions, and planned procedures. They facilitate a better understanding of organ functions and relationships, enabling more informed discussions about health conditions and treatment options.
Medical education and training
Organ Maps provide a foundational tool for learning anatomy, physiology, and pathology in educational settings. They support the development of spatial awareness and understanding of organ relationships, which is essential for medical students and practicing healthcare professionals to maintain their anatomical knowledge.
Benefits of using our Organ Maps handout
Using our map of body organs handout can also offer the following benefits:
Enhanced anatomical understanding
Organ Maps present complex anatomical relationships in an accessible format, allowing for quick reference and detailed study. The visual organization helps reinforce spatial relationships between organs and systems, leading to better retention of anatomical knowledge and more accurate clinical assessments.
Improved clinical decision-making
Access to detailed Organ Maps supports more informed clinical decisions by providing clear reference points for physical examinations and diagnostic procedures. The ability to quickly visualize organ locations and their relationships to surrounding structures helps in developing more accurate differential diagnoses and treatment plans.
Enhanced patient communication
Organ Maps are effective educational tools during patient consultations, facilitating clearer explanations of medical conditions and procedures. The visual format helps bridge communication gaps, enabling patients to better understand their health conditions and proposed treatments.
Time-efficient learning
The organized visual format of Organ Maps allows for rapid information access and review, saving valuable time in both clinical and educational settings. Rather than searching through extensive texts, practitioners can quickly reference this tool.
Commonly asked questions
The human body consists of 12 major organs: the brain, heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, stomach, intestines, pancreas, spleen, gallbladder, skin, and bladder. These organs play a vital role in maintaining bodily functions and overall health.
There are 11 organ systems in humans: the integumentary system, skeletal system, muscular system, nervous system, endocrine system, cardiovascular system, lymphatic system, respiratory system, digestive system, urinary system, and reproductive system (which includes both male and female reproductive systems). These systems work together to perform complex functions necessary for survival and homeostasis.
The easiest organ to live without is typically the spleen. While the spleen filters blood and supports the immune system, individuals can lead normal lives without it as other organs and systems can compensate for its absence.

















-template.jpg)