Occupational Therapy Pediatric Evaluation
Learn about the process of pediatric occupational therapy evaluation. Download Carepatron's free PDF example to assist in understanding and conducting assessments for children.


What is pediatric occupational therapy?
Pediatric occupational therapy is a versatile intervention that addresses a spectrum of challenges children may face in their development. This specialized therapy is adept at addressing issues related to fine and gross motor skills, sensory processing, and overall functional abilities.
Children encountering difficulties in tasks requiring hand-eye coordination, such as writing, tying shoelaces, or using utensils, can benefit significantly from pediatric occupational therapy. The therapy aims to refine fine motor skills, fostering improved precision and control.
Occupational therapy provides targeted interventions for children struggling with gross motor skills, which involve larger muscle groups and body movements. This can improve coordination, balance, and participation in running, jumping, or sports.
Pediatric occupational therapy is instrumental in addressing sensory processing challenges. Children who experience sensitivities or difficulties in processing sensory information may face challenges in daily activities. Occupational therapists work to create tailored interventions that help children regulate their responses to sensory stimuli, promoting a more comfortable and focused everyday experience.
Additionally, occupational therapy supports children in developing essential life skills necessary for independent living. This includes tasks related to self-care, such as dressing, grooming, and feeding. By focusing on enhancing these functional abilities, occupational therapists contribute to a child's overall autonomy and self-esteem.
What problems can pediatric occupational therapy address?
Pediatric occupational therapy is a comprehensive approach designed to address various challenges that children may encounter in their development. Tailored interventions by occupational therapists can effectively target and mitigate a range of issues, including:
- Fine motor skill delays: Pediatric occupational therapy assists children experiencing difficulties in tasks requiring precision and coordination, such as writing, drawing, or manipulating small objects.
- Gross motor skill delays: For children struggling with larger muscle group coordination and movement, occupational therapy interventions focus on improving balance, coordination, and participation in physical activities.
- Sensory processing issues: Occupational therapists specialize in addressing sensory processing challenges, helping children regulate responses to sensory stimuli, reducing sensitivities, and enhancing overall comfort through sensory processing measures.
- Develop self-care and adaptive behavior in daily activities: The therapy supports children in developing essential life skills, including dressing, grooming, and feeding, promoting independence in daily routines.
- Attention and concentration difficulties: Occupational therapy interventions benefit children facing attention and concentration challenges, providing activities to enhance focus and cognitive abilities.
- Social skills development: Occupational therapists play a key role in fostering social skills and helping children navigate social interactions and communication effectively.
- Behavioral challenges: Addressing behavioral challenges is a crucial aspect of pediatric occupational therapy, contributing to improved emotional regulation and coping mechanisms.
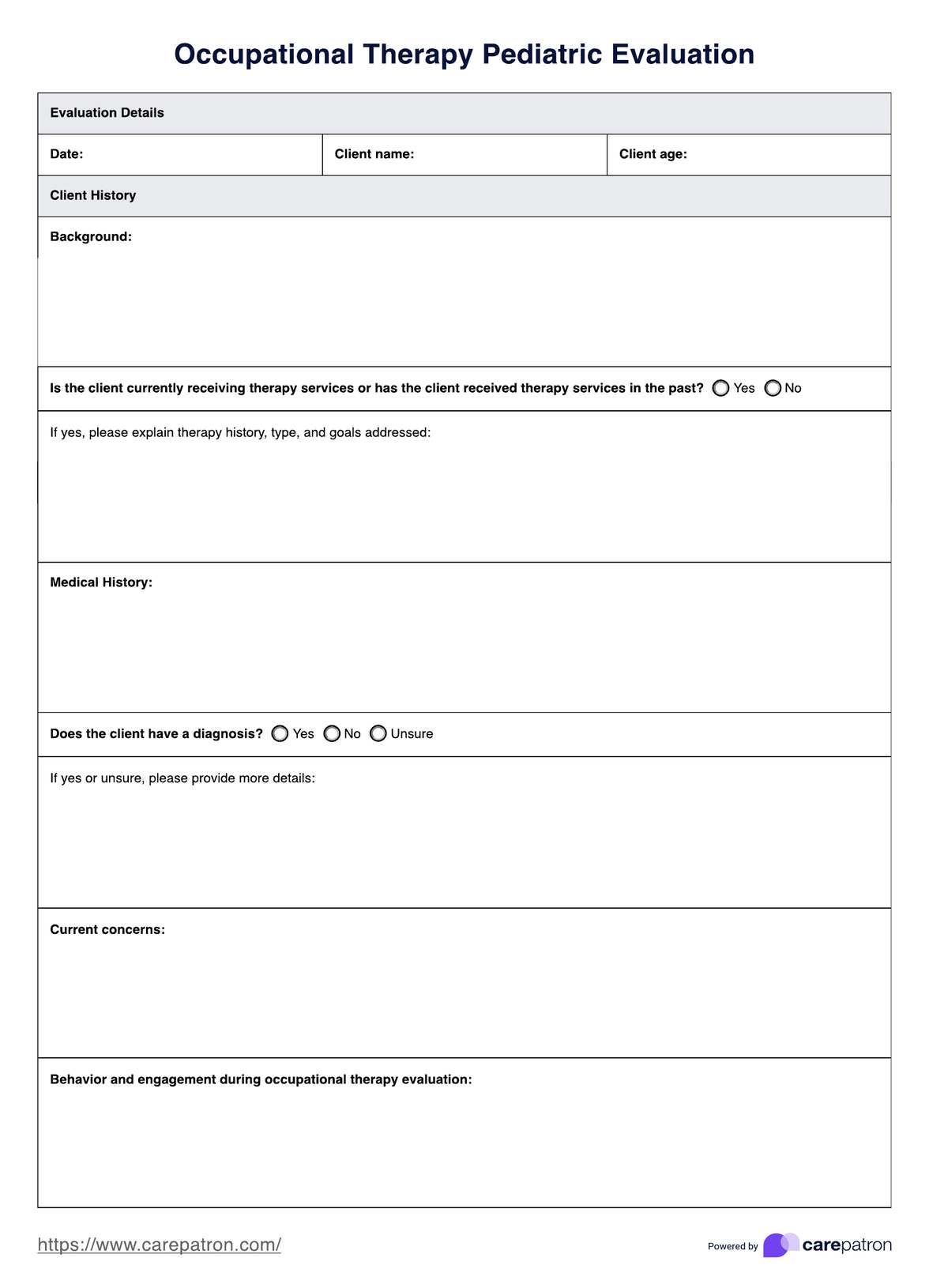
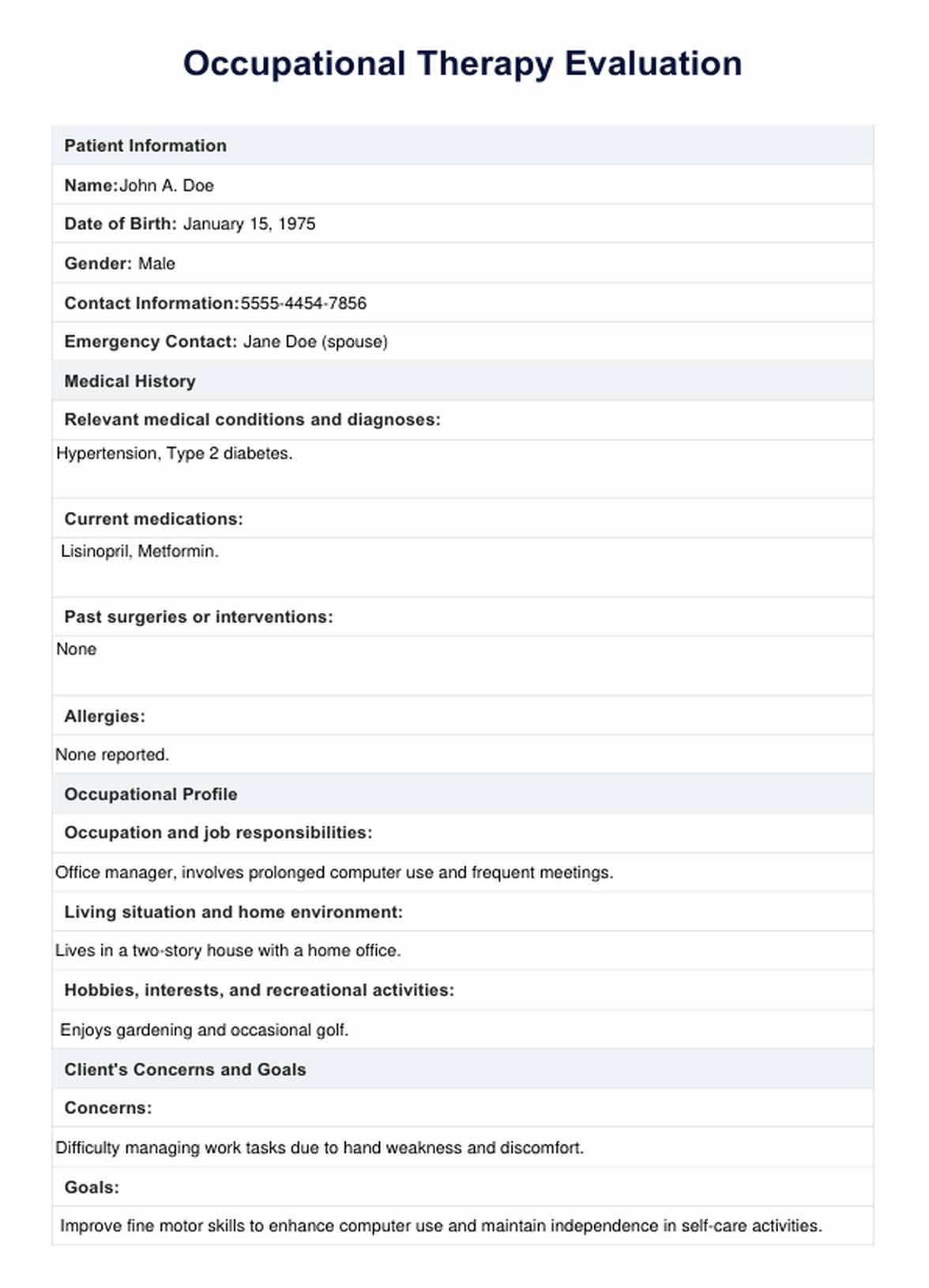
Occupational Therapy Pediatric Evaluation Template
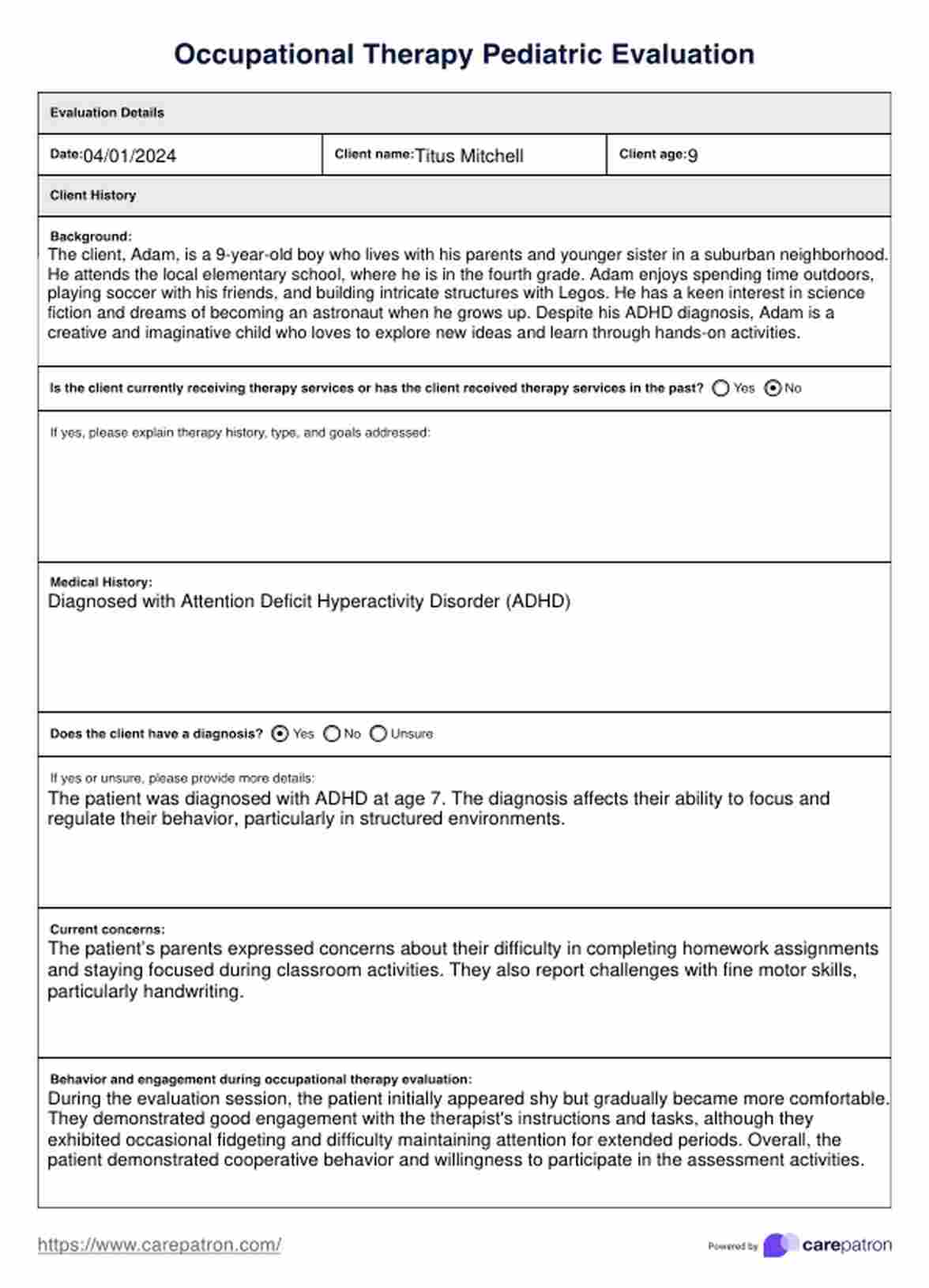
Occupational Therapy Pediatric Evaluation Example
What is an Occupational Therapy Pediatric Evaluation?
Pediatric occupational therapy evaluations are comprehensive assessments conducted by pediatric occupational therapists to gain insights into a child's development and functional abilities. These evaluations are essential for tailoring interventions that address specific needs and promote optimal growth.
Here are the critical components of an occupational therapy pediatric evaluation:
Visual motor integration
A critical evaluation component focuses on visual motor integration, assessing how well a child coordinates visual perception with motor skills. This examination is crucial for understanding a child's ability to interpret and respond to visual information effectively.
Developmental test of visual perception
Pediatric occupational therapists often use standardized assessment tools within the evaluation process, such as the Developmental Test of Visual Perception. This tool helps systematically evaluate a child's visual perception abilities, identifying strengths and areas that may require attention.
Visual perception
Assessing visual perception is integral to understanding how well a child interprets and processes visual information. Occupational therapists use specific tests and observations to evaluate a child's visual perceptual skills, helping to tailor interventions accordingly.
Next steps
After completing a thorough pediatric occupational therapy assessment, the next steps involve a strategic and individualized approach to address the specific needs identified. Let's break down the key steps:
Review and analyze assessment findings
The first crucial step is for the pediatric occupational therapist to review and analyze the assessment findings meticulously. This involves interpreting assessment results on motor proficiency, visual motor integration skills, and functional abilities.
Formulate individualized goals
Based on the assessment findings, the therapist develops individualized goals tailored to the child's needs. These goals serve as a roadmap for therapy sessions, addressing areas of concern and fostering overall development.
Develop a customized intervention plan
With the goals, the therapist creates a customized intervention plan incorporating evidence-based strategies and therapeutic activities. This plan is designed to enhance motor skills, improve visual motor integration, and promote the development of functional skills.
Select appropriate intervention strategies
Therapists carefully select intervention strategies based on the assessed needs of the child. This may include activities targeting fine and gross motor skills, sensory integration, and other relevant areas identified during the assessment.
Collaborate with caregivers and educational teams
Communication with caregivers and educational teams is essential. The therapist collaborates with parents, teachers, and other professionals involved in the child's care to ensure consistency in implementing therapeutic strategies at home and in educational settings.
Monitor progress and adjust interventions
Continuous monitoring of the child's progress is integral to the therapeutic process. Therapists regularly reassess the child's development, adjusting interventions to address emerging needs and celebrate achievements.
Provide ongoing support and education
Ongoing support and education are crucial for the child and their support network. Therapists guide caregivers on how to incorporate therapeutic activities into daily routines, empowering them to reinforce progress outside of therapy sessions.
Benefits of this evaluation
Occupational therapy pediatric evaluations offer a range of invaluable benefits, providing a comprehensive understanding of a child's development and guiding tailored interventions. Let's explore the specific advantages of these evaluations:
Early identification of developmental challenges
By conducting thorough assessments, occupational therapists can identify potential developmental challenges early on. This early detection allows for prompt intervention, maximizing the effectiveness of therapeutic strategies.
Tailored intervention plans
The evaluation process informs the creation of personalized intervention plans. Occupational therapists can design targeted activities and exercises that address the identified areas of concern, promoting optimal skill development.
Improved academic performance
For school-aged children, occupational therapy evaluations contribute to enhanced academic performance. By addressing fine motor skills, sensory processing, and other critical factors, interventions support a child's ability to engage effectively in the classroom.
Enhanced daily functioning
Pediatric evaluations facilitate a holistic understanding of a child's abilities in activities of daily living. Occupational therapists use this information to enhance a child's functional skills, promoting independence in self-care tasks and other daily activities.
Informed collaborative approach
The evaluation process fosters collaboration among parents, educators, and healthcare professionals. Informed by assessment results, a collaborative approach ensures that everyone involved is aligned in supporting the child's development.
Addressing behavioral challenges
Occupational therapy evaluations play a pivotal role in addressing behavioral challenges. By understanding the root causes of certain behaviors through assessments, therapists can tailor interventions that contribute to improved emotional regulation and coping mechanisms.
Support for sensory processing
Children with sensory processing challenges benefit significantly from occupational therapy evaluations. The assessments guide therapists in developing sensory-focused interventions that help children regulate responses to stimuli, contributing to improved attention and focus.
Commonly asked questions
A pediatric occupational therapy evaluation thoroughly assesses a child's fine and gross motor skills, sensory processing abilities, visual motor integration, and overall developmental milestones. The review may involve standardized evaluations, direct observations, and collaboration with parents and educators to understand the child's abilities comprehensively.
Pediatric occupational therapists utilize assessments tailored to the child's age and developmental stage. Common tools include the Peabody Developmental Motor Scales, Developmental Test of Visual Perception, and sensory processing checklists. These assessments provide valuable insights into specific areas of a child's functioning, guiding the formulation of targeted intervention plans.
A child may need an occupational therapy assessment if they exhibit challenges in fine and gross motor skills, sensory processing, self-care tasks, or school-related activities. The assessment helps identify specific areas of difficulty and informs the development of individualized interventions to support the child's overall development.

















-template.jpg)