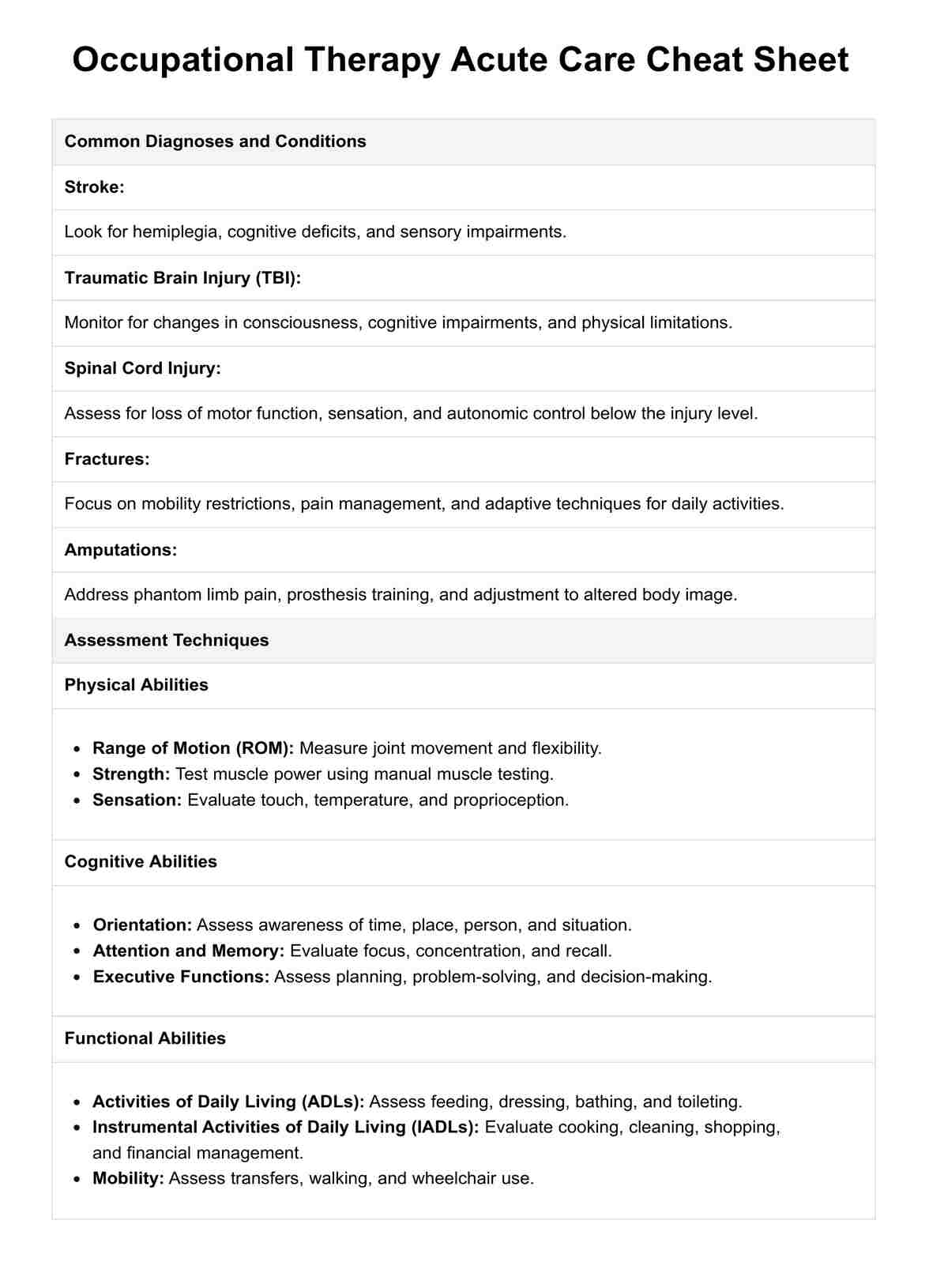
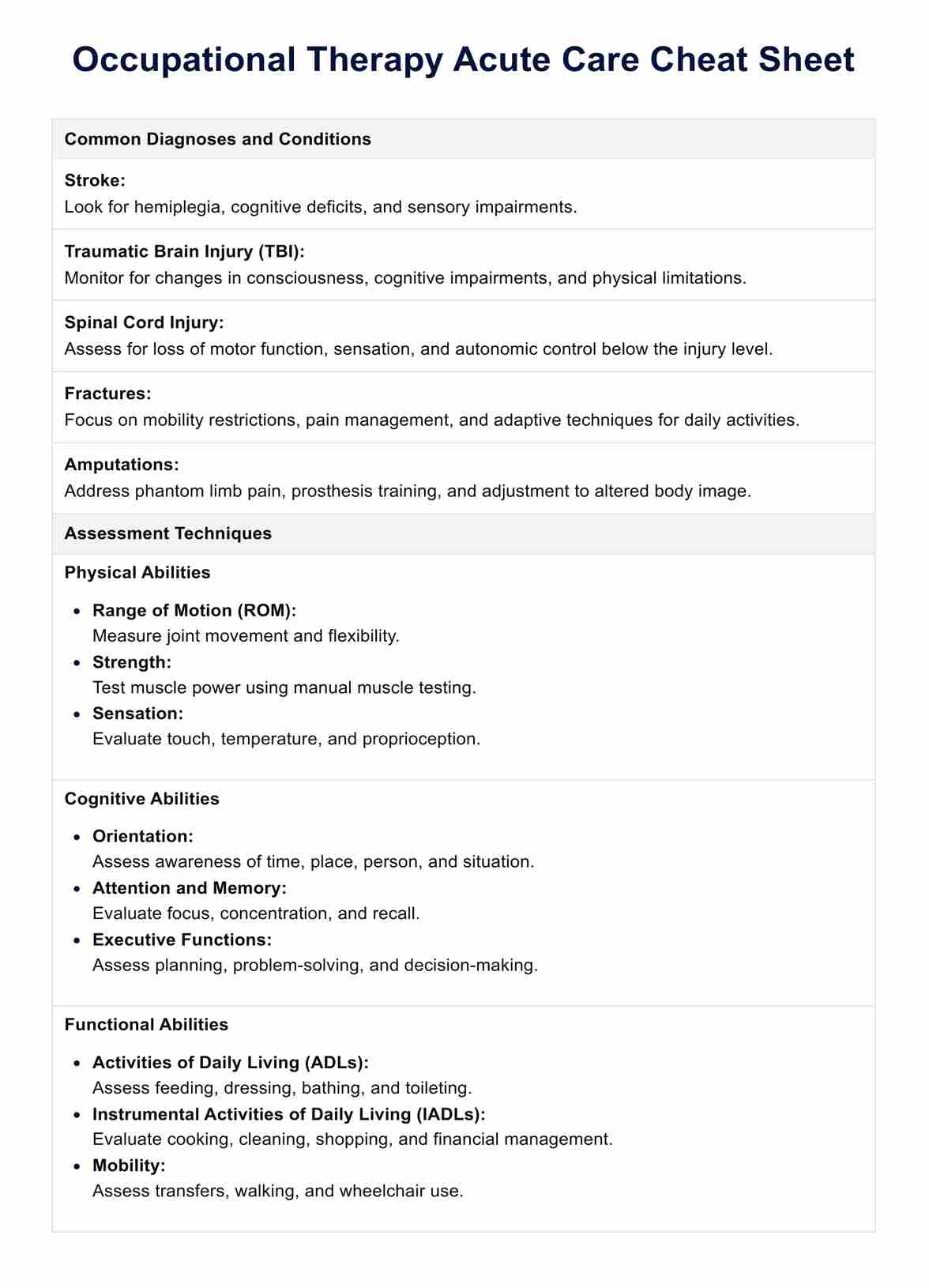
Occupational Therapy Acute Care Cheat Sheet
Streamline patient recovery with key strategies for enhancing independence in acute settings. Download our free Occupational Therapy Acute Care Cheat Sheet.


What is acute care?
Acute care refers to the branch of healthcare specifically designed to provide short-term treatment for patients with severe illness, injury, or medical conditions that require immediate care. This type of care is typically provided in a hospital setting or skilled nursing facility and focuses on rapid diagnosis and intervention to prevent death or long-term disability.
Acute care also encompasses various clinical healthcare functions, including emergency medicine, trauma care, pre-hospital emergency care, acute care surgery, critical care, urgent care, and short-term inpatient stabilization.
Occupational Therapy Acute Care Cheat Sheet Template
Occupational Therapy Acute Care Cheat Sheet Example
Types of patients in acute care setting
Acute care settings cater to a diverse group of patients, each presenting with different medical needs. Some of the common types of patients in acute care include:
- Emergency patients: Individuals who require immediate medical attention due to accidents, injuries, or sudden illness. This includes cases like heart attacks, strokes, severe bleeding, or respiratory distress.
- Surgical patients: Patients undergoing surgery for various reasons, ranging from elective surgeries to emergency operations due to trauma or acute conditions that cannot be treated through medication alone.
- Critical care patients: Those who are critically ill and need intensive care. This group includes patients with life-threatening conditions requiring constant monitoring and advanced medical support, often in an intensive care unit (ICU).
- Trauma patients: Individuals who have suffered severe injuries, such as from car accidents, falls, or violence. These patients require immediate and specialized care to address multiple, often life-threatening, injuries.
- Acute medical patients: Patients with sudden exacerbations of chronic conditions or the rapid onset of symptoms due to new acute illnesses such as pneumonia, asthma attacks, or acute kidney failure that necessitate hospitalization for stabilization and treatment.
- Postoperative patients: Those recovering from surgery and requiring short-term hospital care to manage pain, prevent infection, and monitor for any complications arising from the surgical procedure.
- Infectious disease patients: Individuals with severe infections that require isolation and specialized medical treatment to manage symptoms and prevent the spread of disease, such as severe cases of influenza, COVID-19, or other contagious diseases.
Each type of patient in an acute care setting presents unique challenges and requires specialized care tailored to their specific medical needs, ensuring the best possible outcomes.
Purpose of occupation therapy in the acute setting
In the acute care setting, the primary purpose of occupational therapy (OT) is to facilitate early mobilization, prevent functional decline, and start the rehabilitation process for patients facing sudden health changes due to illness, surgery, or injury. An occupational therapist aims to:
- Assess and enhance functional ability: Quickly assess patients' functional status and capacity to perform daily activities, and implement interventions to maintain or improve their level of independence.
- Promote early mobilization: Encourage and assist patients in engaging in early mobilization activities to prevent the complications associated with prolonged bed rest, such as muscle weakness and decreased endurance.
- Prevent secondary complications: Implement strategies to prevent secondary complications, such as pressure ulcers, contractures, or falls, which can arise from acute medical conditions or hospitalization.
- Facilitate discharge planning: Collaborate with the healthcare team to plan safe discharges, ensuring that patients have the necessary support and adaptations to return home or transition to another level of care.
- Educate patients and families: Provide education and training to patients and their families on coping strategies, the use of adaptive equipment, and modifications to activities of daily living (ADLs) to enhance safety and independence.
Occupational therapists' interventions in acute care
Occupational therapists in acute care settings employ a variety of interventions tailored to meet the immediate needs of patients, examples including:
- Functional assessments: Conduct comprehensive evaluations of patients' abilities to perform ADLs, such as bathing, dressing, and eating, to determine the impact of their acute condition on daily functioning.
- Early mobilization: Guide and support patients in participating in mobility and strengthening exercises to maintain muscle tone and prevent deconditioning.
- Cognitive and perceptual assessments: Evaluate and address any cognitive or perceptual deficits affecting a patient's safety and ability to perform tasks independently.
- Adaptive equipment and assistive technology: Recommend and train patients to use adaptive equipment and assistive technologies to facilitate independence in ADLs despite limitations.
- Environmental modifications: Advise on modifications to the patient's environment, both in the hospital and at home, to enhance safety, accessibility, and functional independence.
- Discharge planning and coordination: Work closely with the healthcare team to develop comprehensive discharge plans that address the patient's needs, including home modifications, outpatient therapy referrals, and community resources.
- Patient and caregiver education: Educate patients and their caregivers on strategies to manage daily activities safely and effectively, including energy conservation techniques and instructions on using adaptive equipment.
Through these interventions, occupational therapists play a critical role in acute care settings by helping patients regain function, promoting independence, and ensuring a smooth transition to the next stage of recovery or care.
How to use this template
The Occupational Therapy Acute Care Cheat Sheet is designed as a comprehensive resource for therapists working in acute care settings, providing a structured overview of essential aspects of patient care. Here's how to effectively utilize this template:
Step 1: Access the template
Begin by accessing the Occupational Therapy Acute Care Cheat Sheet from our platform. Available in PDF format, it supports both digital and print use to suit your clinical preferences. Ensure your device or system is compatible for digital edits if needed.
Step 2: Collaborate and educate
Use the cheat sheet as a foundation for team collaboration. Demonstrating its contents can help your multidisciplinary team understand how to apply it effectively, streamlining patient assessments, pinpointing vital interventions, and facilitating efficient care planning. This encourages a unified approach to patient care across different specialties.
Step 4: Embed in clinical workflow
Integrate the cheat sheet into your daily clinical activities. Its detailed format makes it an indispensable reference tool during patient evaluations, team meetings, and when crafting individualized care plans. Regular usage will solidify its role as a key component of your clinical practice, aiding in swift decision-making and maintaining high-quality patient care.
Additional acute care resources
Additional resources can be invaluable for occupational therapists and healthcare professionals seeking to deepen their understanding and enhance their practice while on the job. Whether you're looking for comprehensive guides on specific therapeutic approaches or customizable templates to streamline patient care, the following links offer a wealth of information:
- Explore the guide on acute care physical therapy for insights into effective strategies and interventions that can significantly impact patient recovery and rehabilitation.
This resource provides valuable information and practical tools to support high-quality care delivery in acute care settings, helping healthcare professionals meet the complex needs of their patients efficiently and effectively.
Commonly asked questions
Occupational therapy in acute care settings is crucial as it helps patients regain independence and functionality after a sudden illness or injury. By focusing on daily activities and adaptive techniques, occupational therapy supports patients in their recovery process, promoting faster discharge and reducing the risk of hospital readmission.
The role of occupational therapy in acute care involves assessing patients' functional needs, providing therapeutic interventions to enhance their ability to perform daily activities, and devising personalized rehabilitation plans. Occupational therapists collaborate with other practitioners as a multidisciplinary team to ensure holistic patient care, addressing physical, cognitive, and emotional challenges to improve overall quality of life.
To create cheat sheets in Carepatron, log into your account and navigate to the "Resources" or "Templates" section. Choose "Create New" and select the type of cheat sheet you want to make, such as client information, therapy protocols, or billing codes. Customize it by adding relevant fields and content. Save your cheat sheet for easy access and use it to streamline your workflow and enhance care delivery.

















-template.jpg)