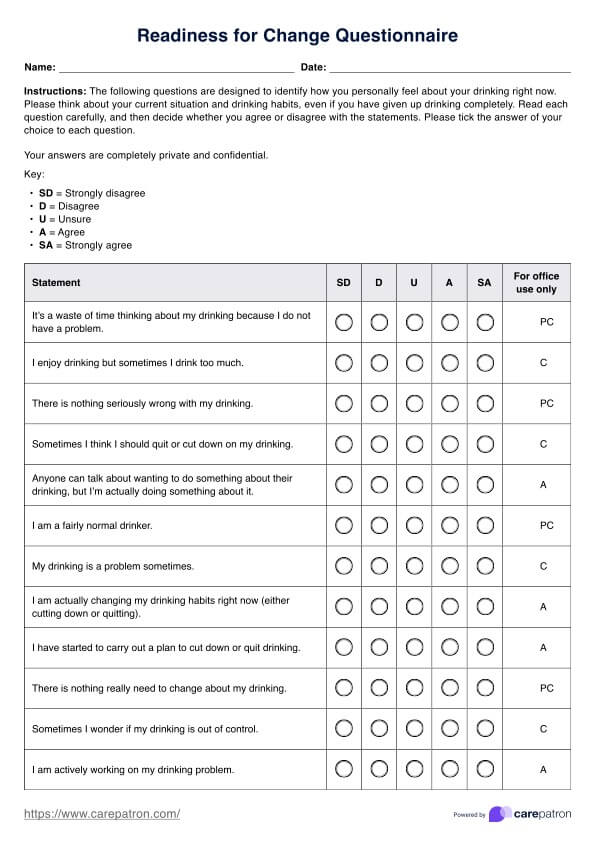
Duluth Models Guide
Promote healthy relationships through empowerment, accountability, and systemic change with the Duluth Model. Free PDF can be downloaded here.


What is a Duluth Model?
The Duluth Model is a gender-based cognitive-behavior approach to counseling and educating men who have committed domestic violence, aiming to change their violent and threatening behaviors.
It employs revolutionary approaches to addressing violence, such as shifting the blame from the victim to the offender, redirecting the responsibility of victim safety from the victim to the community and state, and highlighting restorative justice.
Anchored on feminist ideologies, it exposes gender mechanisms behind abuse and emphasizes the role of the community and state in addressing domestic violence. It challenges the societal conditions reinforcing men's use of tactics of power and control over women. However, it contends that male violence is a consequence of a patriarchal system that condones male violence while refraining from directly blaming individual men.
In crafting policies and procedures, it prioritizes the voices and experiences of women victimized by abusive behavior. It is a perspective that domestic violence involves a deliberate series of actions specifically designed to intentionally control an intimate partner.
The model is embedded in a larger system of interventions, including arrests for domestic violence, sanctions against non-compliance to court orders, safety planning and support for victims in family court, and referral to agencies with collaborative approaches. It highlights empathetic, progressive, and collaborative objectives in addressing abuse.
The power and control wheel
The Power and Control Wheel is a crucial tool in the Duluth Model. It visually represents tactics employed by abusers over their victims. For the context of the abusers or clients in the Duluth Model, this assists them in recognizing their negative behaviors. This recognition is vital in developing their sense of accountability.
Other educational resources used in the Duluth Model include equality, post-separation, abuse of children wheels, and others. These resources guide the client in transforming their violent behaviors into healthy ones.
Duluth Model is an empowering framework built on theoretical and empirical support. It is a genuinely transformative paradigm within the context of addressing intimate partner violence.
Duluth Models Guide Template
Duluth Models Guide Example
How does it work?
Duluth Model involves a structured approach to educating the clients about the dynamics of domestic violence, empowering them to recognize and change their abusive behaviors, and providing them with resources for domestic violence programs, support, and intervention. Here are the steps on how the Duluth Model works:
Step 1: Familiarize yourself with the framework
As a framework, the Duluth Model focuses on salient components vital to its applications. It is important to familiarize yourself with these components for effective implementation. Printable Duluth Models can be downloaded from the Carepatron website to aid you in this.
Step 2: Establish safety and rapport
Creating a safe and supportive environment before discussing sensitive topics is vital. Building rapport involves introducing yourself to the clients, ensuring privacy and confidentiality, and clearly explaining the purpose of the model.
Step 3: Introduction
Explain the framework's basic concepts, structure, and purpose to the clients. Introduce how it actively works and its components to the clients, highlighting the expected outcomes and the resources to be used in the implementation.
Step 4: Formal implementation
This step involves introducing the Power and Control Wheel to the client and explaining how this tool illustrates how abusers maintain control and power. Discuss each section to help the client recognize abusive behaviors. Encourage the client to reflect and explore. This step should highlight raising awareness and accountability. Other processes included in this step are safety planning, understanding perpetrator behavior, and providing resources for support.
Step 5: Goal-setting and behavioral change
Work with the client to set goals for behavioral change. Discuss strategies for communicating boundaries, seeking help, promoting non-violence, and seeking alternatives for abusive behaviors. Teaching skills in anger and stress management is essential.
Step 6: Follow-up and continued support
Ongoing support and guidance should be provided throughout the intervention process. Progress and changes should also be regularly assessed.
When would you use this template?
The Duluth Model is used in diverse settings to address domestic violence, foster healthy relationships, and make systemic transformation. Here are some of the critical scenarios where you can apply this framework:
- Intervention programs: The Duluth Model can serve as a guide in domestic abuse intervention program designed for individuals who have committed domestic violence. It aims to educate, promote accountability, and facilitate behavior change based on actual experiences.
- Counseling and therapy: The Duluth Model, designed for therapists and counselors addressing partner abuse, fosters understanding of abusive dynamics and promotes healthy relationships. It also guides support groups in processing experiences, sharing insights, and empowering participants with such a desire to change societal conditions related to partner abuse.
- Educational settings: The Duluth model can be used by educators in developing programs and educational workshops on healthy relationships, communicating boundaries, and preventing domestic abuse.
- Legal and social services: Legal professionals and social workers can apply the Duluth Model in domestic abuse cases, encouraging responsibility and accountability.
- Policy-making: The Duluth Model can be used to craft policies on addressing domestic violence, fostering non-violence, and systemic change.
- Awareness campaigns and youth programs: Advocates can leverage the Duluth Model, drawing from convened focus groups and the battered women's movement, to inform the public about domestic violence. This valuable tool facilitates community dialogues about domestic abuse. It can be adapted for youth programs, fostering education among adolescents on healthy relationships and non-violence, particularly within social work initiatives.
Elevate your practice and client outcomes with the help of these equality wheel and power and control wheel templates.
Benefits of the Duluth Model
The Duluth model offers numerous benefits in addressing domestic violence and can be applied in various settings. Here are some of the benefits of this framework:
- Adaptability and accessibility: It can be adapted to different settings to meet the unique needs of diverse populations. Moreover, the Duluth Model PDF templates are free resources that can be accessed by other individuals concerned with building cultures of peace.
- Comprehensive framework: The model provides a comprehensive and structured framework for understanding the motivating force behind men's violence that seeks to control women. It aims to shed light on the dynamics that contribute to abusive situations, especially for female victims, to promote a safer and more supportive environment.
- Trauma-informed approach: The model gives insights into the mechanisms behind most common abusive behaviors, power and control issues, and fostering non-violence. It delves into the tactics chosen in domestic violence situations to promote a better comprehension and facilitate efforts toward creating a safer environment.
- Research-based: The Duluth Model is grounded on theoretical and empirical evidence. It has been widely studied, offering evidence-based strategies for addressing domestic violence.
- Long-term impact: The long-term impact can be seen at micro and macro levels. It promotes behavior change at the individual level through educating, counseling, and raising accountability. At the same time, it leads to long-term systemic transformation by challenging the structural roots of domestic violence.
- Community collaboration: The model understands that domestic violence cannot be addressed by focusing only on the individual but by encouraging a coordinated community response involving different sectors and organizations.
Research & evidence
The Duluth Model, developed in 1981 in Duluth, Minnesota, was a revolutionary approach to addressing domestic violence. It emerged as a response to the need for a comprehensive approach to domestic abuse intervention and prevention. Scaffolded on feminist ideologies, the Duluth Model offered progressive insights that challenged the societal conditions that reinforce men's use of power and control over women. It exposed the structures that allowed men to get away from their committed crimes while blaming women for being victims.
Gondolf (2007) published an article in support of the model and highlighted its salient components. It discussed the theoretical and empirical support of the model, emphasizing its research-based foundations. The author dissected the model and offered valuable insights into the effectiveness of the model in contrast to its critics.
One of the salient tools of the Duluth Model is the Power and Control Wheel. Evidence has shown the significant contribution of this tool in helping both the perpetrators and the victims recognize the schemes employed by perpetrators to maintain their power and control over their victims. Meanwhile, another tool utilized in the Duluth Model is the Equality Wheel.
While the wheel exposes the nature of abuse, this tool allows women to recognize what a healthy relationship is supposed to look like. These tools have helped perpetrators and victims identify unhealthy behaviors and learn how to transform them into healthy ones.
The Duluth Model was adapted by different populations to address domestic violence. The power of this model lies in its ability to target the systemic and structural roots of domestic violence, urging accountability not only to abusers but also to the community and state in general.
References
The duluth model. Safe Haven. (2017, July 17). http://safehavenshelter.org/learn/educational-resources/domestic-violence/duluth-model/
Gondolf, E. W. (2007). Theoretical and research support for the Duluth Model: A reply to Dutton and corvo. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 12(6), 644–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2007.03.001
Taylor, B., & Sullivan, B. (2011). The Duluth Model, what it is and is not: Clarifying and correcting common misconceptions. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/43517465_The_Duluth_Model_what_it_is_and_is_not_Clarifying_and_correcting_common_misconceptions
Trading the power and Control Wheel for the equality wheel. Raft Cares. (2022, March 16). https://www.raftcares.org/resources/community-blog/trading-the-power-and-control-wheel-for-the-equality-wheel/#:~:text=That%20is%20why%20power%20and,identify%20abusive%20behavior%20more%20easily.
Commonly asked questions
The Duluth Model is utilized by various individuals, professionals, and organizations involved in addressing domestic violence and promoting healthy relationships, including counselors, social workers, psychologists, advocates, law enforcers, and many more.
The Duluth Model can be used in different scenarios, including counseling and therapies, intervention programs, educational settings, and many more. It is a versatile model tailored for different settings and uses.
Yes! The Duluth Model can be adapted and tailored to consider cultural and contextual factors to make it applicable and relevant in diverse communities.















-template.jpg)