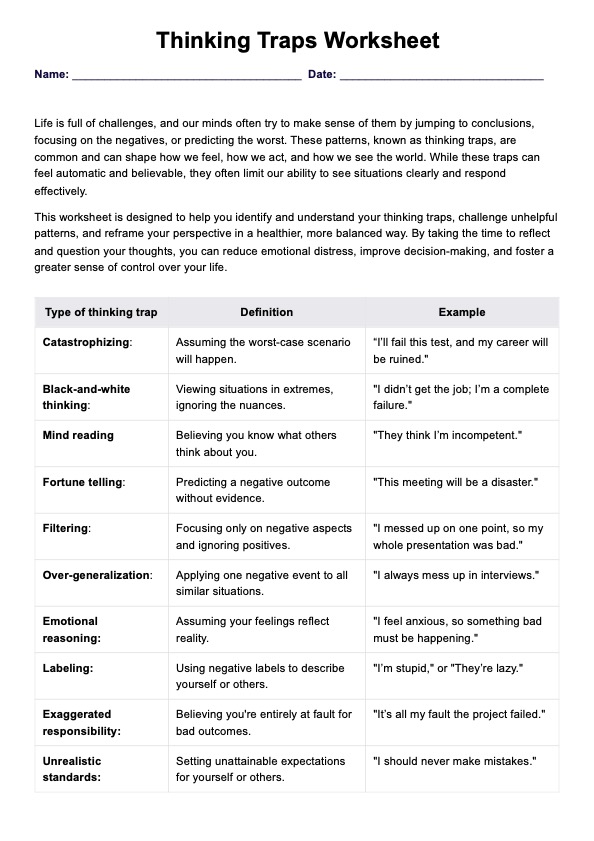
The Thinking Traps Worksheet is a tool designed to help individuals identify and challenge cognitive distortions, such as all-or-nothing thinking or mind reading. It provides structured prompts for recognizing automatic negative thoughts and reframing them into balanced, positive perspectives. This worksheet is particularly helpful in cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) to address negative thought patterns and improve emotional resilience in daily life.
Thinking Traps Worksheet
Unlock a healthier mindset with our Thinking Traps Worksheet, designed to identify and correct cognitive distortions. Download your free example today.
Thinking Traps Worksheet Template
Commonly asked questions
The worksheet focuses on common cognitive distortions, such as fortune telling, emotional reasoning, and the mental filter. Guiding individuals to identify and challenge their distorted thinking patterns encourages them to analyze their beliefs, examine evidence, and replace unhelpful thoughts with more balanced and realistic ones. This process, called cognitive restructuring, is a significant first step toward reducing stress and improving confidence.
Yes, the Thinking Traps Worksheet can be adapted for children and kids to help them identify and manage negative thoughts. Children can recognize irrational thoughts, like imagining the worst possible scenario, by using age-appropriate examples, such as addressing worries about school or social life, and reframe them into helpful and constructive perspectives. Teaching these skills early can help them build confidence and better handle frustration and challenges.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











