AST
Learn about the AST test and its uses and interpretation. Get insights into AST test results and their significance.


What is an AST Test?
The , short for Aspartate Aminotransferase test, is a diagnostic blood test that measures the levels of the enzyme aspartate aminotransferase in the bloodstream. This test is primarily used to assess the health of the liver and heart. AST is an enzyme found within cells throughout the body, with exceptionally high concentrations in the liver, heart, muscles, and kidneys. When these organs are damaged or injured, they release AST into the bloodstream, leading to elevated enzyme levels in blood tests.
The test serves several vital purposes in clinical medicine. First and foremost, it helps doctors diagnose and monitor various medical conditions. Elevated AST levels often indicate liver diseases such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, or fatty liver disease. It can also help diagnose heart conditions, such as heart attack since AST is present in cardiac muscle. Monitoring AST levels over time can aid in assessing treatment progress or the severity of a medical condition.
Furthermore, the test is used alongside other liver function tests, such as ALT (Alanine Aminotransferase) and ALP (Alkaline Phosphatase), to provide a comprehensive picture of liver health. It is a crucial tool in evaluating and managing patients with liver or heart-related issues.
The test is simple and involves a healthcare professional drawing blood from a vein in the arm. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, and results are usually available within a few days.
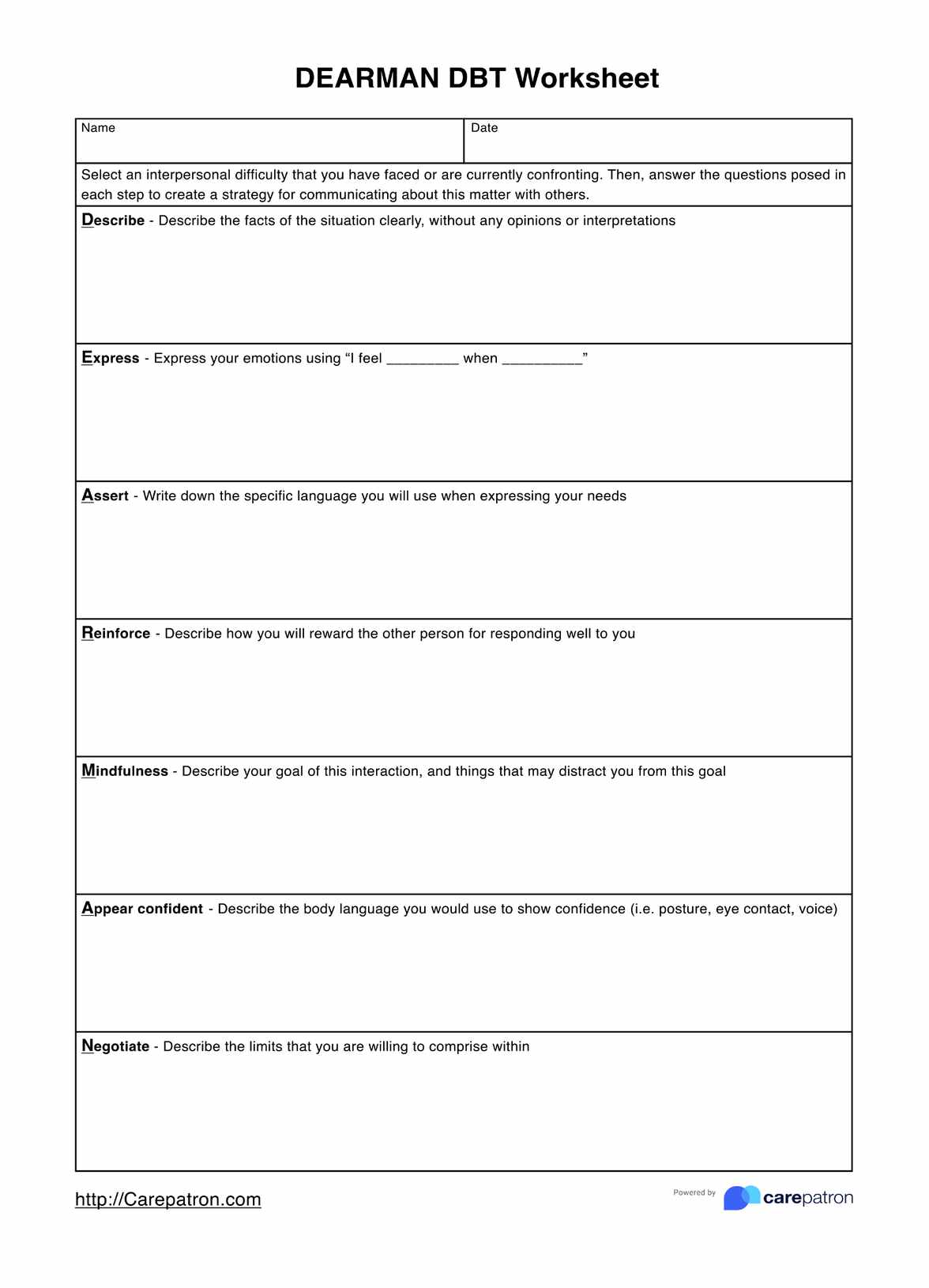
AST Template
AST Example
How Does It Work?
An AST (Aspartate Aminotransferase) test is a diagnostic blood test that measures the levels of the AST enzyme in the bloodstream. It helps assess the health of the liver and heart. Here's how the AST test works:
1. Patient Preparation
Patients typically need minimal preparation for an AST test. Fasting is not required, and there are no dietary restrictions.
2. Blood Sample Collection
A healthcare professional, usually a nurse or phlebotomist, collects a blood sample from the patient's vein, typically in the arm. They clean the area with an antiseptic and use a needle and collection tube to draw the blood.
3. Blood Processing
The collected blood sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
4. Laboratory Analysis
The blood sample is centrifuged in the laboratory to separate the serum from the blood cells.
5. Enzyme Measurement
The serum is then tested for the presence and levels of AST. This is typically done using automated analyzers, which provide precise measurements.
6. Results Interpretation
The results are reported in units per liter (U/L) or international units per liter (IU/L). Normal AST levels vary by age and gender, but elevated levels may indicate underlying liver or heart problems.
7. Clinical Assessment
A healthcare provider reviews the test results in the context of the patient's medical history, symptoms, and other diagnostic tests. Elevated AST levels may prompt further investigation or medical intervention.
8. Follow-up Testing
In some cases, a follow-up AST test may be necessary to monitor the progression of a known medical condition or the effectiveness of treatment.
While the AST test is not typically a form or document, the results are usually provided on a lab report that can be printed for reference. Patients may receive a hard copy of their AST test results from their healthcare provider.
When Would You Use This Test?
The AST (Aspartate Aminotransferase) test is a valuable diagnostic tool used by healthcare practitioners across various medical specialties. It plays a crucial role in assessing the health of the liver and heart, making it appropriate to use in several clinical scenarios:
- Liver Disease Diagnosis: Gastroenterologists and hepatologists often use the AST test to diagnose liver diseases such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, and fatty liver disease. Elevated AST levels can indicate liver damage or inflammation, helping healthcare providers determine the nature and severity of the condition.
- Monitoring Liver Health: For patients with known liver conditions or those undergoing treatment, the AST test helps track liver health over time. It helps assess the effectiveness of therapies and identify disease progression or regression.
- Heart Disease Assessment: Cardiologists may order the AST test to assess heart health, especially in suspected heart muscle damage cases. Elevated AST levels can indicate myocardial infarction (heart attack) or other cardiac conditions, helping guide treatment decisions.
- Emergency Medicine: In emergency departments, the AST test is crucial for rapidly diagnosing and treating acute conditions like heart attacks or severe liver trauma. It aids in identifying life-threatening situations and guides immediate interventions.
- General Healthcare: Primary care physicians may use the AST test for routine check-ups or when patients exhibit symptoms such as jaundice, abdominal pain, or unexplained fatigue. It serves as a screening tool for potential liver or heart issues.
- Medication Monitoring: Some medications, including certain chemotherapy drugs and statins, can affect liver function. Doctors prescribing these medications may use the AST test to monitor liver health and adjust treatment.
What do the results mean?
The results of an AST (Aspartate Aminotransferase) test are essential for assessing the health of the liver and heart. They are reported in units per liter (U/L) or international units per liter (IU/L), providing valuable insights into a patient's medical condition. Here's what expected AST test results mean:
- Normal Range: In healthy individuals, AST levels typically fall within a specific reference range, which can vary slightly from one laboratory to another but is generally around 10 to 40 U/L. Normal AST levels indicate the liver and heart function within expected parameters, suggesting no significant damage or inflammation.
- Elevated AST Levels: Elevated AST levels may signify several underlying medical conditions:
- Liver Damage: Significant increases in AST levels can indicate liver damage or disease. Conditions like hepatitis, cirrhosis, or fatty liver disease can cause a rise in AST levels.
- Heart Issues: An elevated AST may also be seen in acute myocardial infarction (heart attack) or other heart conditions that damage cardiac muscle.
- Muscle Injury: AST is also present in skeletal muscles. Consequently, trauma or muscle injury, such as in accidents or strenuous exercise, can temporarily raise AST levels.
- Ratios with ALT: Doctors often consider the AST to ALT (Alanine Aminotransferase) balance when interpreting results. A significantly higher AST-to-ALT ratio may suggest alcoholic liver disease or cirrhosis, while a lower percentage may indicate viral hepatitis.
Understanding that elevated AST levels are not specific to a single condition is crucial. Additional diagnostic tests, medical history, and clinical symptoms are typically needed to pinpoint the underlying cause accurately.
Research & Evidence
The Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) test, also known as the SGOT (Serum Glutamic Oxaloacetic Transaminase) test, has a well-established history in clinical diagnostics. Its origins date back to the mid-20th century when medical researchers explored ways to assess liver and heart health more effectively.
In the 1950s and 1960s, researchers began developing enzymatic assays to measure specific enzymes present in the liver and heart. This led to the discovery of AST, an enzyme abundant in these organs. The AST test was initially used primarily for diagnosing liver diseases, particularly hepatitis and cirrhosis. Over time, the test's utility expanded to include the assessment of cardiac muscle health, specifically in diagnosing myocardial infarction (heart attack).
A substantial body of research has supported the clinical utility of the AST test over the years. Studies have demonstrated its effectiveness in detecting liver and heart conditions. Research has also highlighted the importance of AST-to-ALT (Alanine Aminotransferase) ratios in distinguishing between different liver diseases.
For example, a higher AST-to-ALT ratio may indicate alcoholic liver disease, while a lower ratio could suggest viral hepatitis. The AST test's accuracy and reliability have been validated through numerous clinical trials and comparative studies, establishing its place as a vital diagnostic tool.
The AST test continues to be widely used today due to its proven track record in diagnosing and monitoring liver and heart conditions. Ongoing research ensures that it remains a valuable resource in the ever-evolving field of clinical medicine. Its history and extensive evidence supporting its use have solidified its role in healthcare, allowing physicians to make informed patient care and treatment decisions.
References
- Advisory and peer review committees and review Boards | NHLBI, NIH. (n.d.). NHLBI, NIH. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/about/advisory-and-peer-review-committees
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) blood test: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. (n.d.). https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003472.htm
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (GOT), serum - Mayo Clinic Laboratories | Endocrinology Catalog. (n.d.). https://endocrinology.testcatalog.org/show/AST
- Aspartate transaminase - Health Encyclopedia - University of Rochester Medical Center. (n.d.). https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=167&contentid=aspartate_transaminase
- Connecticut Children??s. (2008, November 10). Blood Test: Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST, or SGOT) - Connecticut Children's. https://www.connecticutchildrens.org/health-library/en/parents/test-ast/
- National Library of Medicine. (n.d.). Liver diseases. https://medlineplus.gov/liverdiseases.html
- Testing.com. (2022a, November 24). Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) test - Testing.com. https://www.testing.com/tests/aspartate-aminotransferase-ast/
- Testing.com. (2022b, November 24). Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) test - Testing.com. https://www.testing.com/tests/aspartate-aminotransferase-ast/
- VA.gov | Veterans Affairs. (n.d.). https://www.hepatitis.va.gov/hcv/patient/diagnosis/labtests-AST.asp
- What is an aspartate aminotransferase (AST) test? (2017, March 16). WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/aspartate_aminotransferse-test
Commonly asked questions
AST tests are typically requested by healthcare providers such as doctors, nurses, and specialists, including gastroenterologists and cardiologists.
AST Tests are used to assess liver and heart health. They are employed when patients exhibit symptoms or risk factors associated with liver or heart conditions, during routine check-ups, or in emergencies like suspected heart attacks.
AST Tests involve collecting a blood sample, usually from a vein in the arm. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results help diagnose and monitor liver and heart conditions.
The actual blood collection for an AST Test typically takes just a few minutes. However, the time for results to become available can vary, with most results being ready within a day or two, depending on the laboratory's processing times.























-template.jpg)