Sexual Sadism Disorder DSM-5 Criteria
Download a handy reference tool with our Sexual Sadism Disorder DSM-5 Criteria for guidance in identifying and managing the condition.


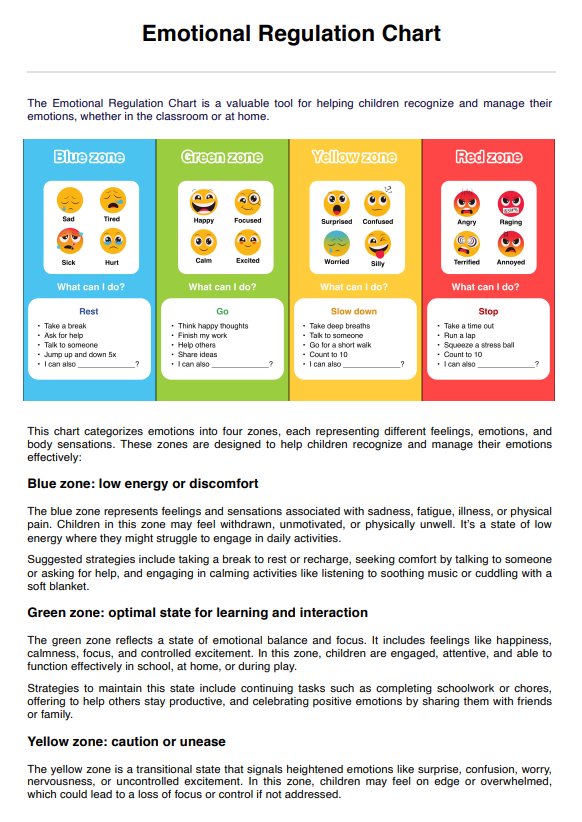
What is sexual sadism disorder?
Sexual sadism disorder is a paraphilic disorder defined by recurrent and intense sexual arousal derived from inflicting physical or psychological suffering on another person. This is included among other paraphilic disorders in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), with others including sexual masochism disorder and voyeuristic disorder.
Symptoms of sexual sadism disorder range from arousal that may manifest through intense sexually arousing fantasies, urges, or behaviors of a sadistic nature to acting on these urges and fantasies. It is considered a mental health disorder when these fantasies or behaviors cause significant distress to the individual, impair their social, occupational, or personal functioning, or involve nonconsenting individuals.
Sadistic sexual behaviors can range from verbal humiliation to acts of physical harm, with severity varying between individuals. While consensual sadistic practices within mutual agreements do not qualify as a disorder, sexual sadism disorder specifically involves nonconsensual acts or causes harm or distress to the individual or others.
Risk factors for developing sexual sadism disorder may include a history of trauma, exposure to violence, or co-occurring mental health conditions. Without treatment, the disorder may escalate, increasing the risk of legal, ethical, and interpersonal consequences among sexual sadists.
Treatment often involves psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), to address the underlying causes of sadistic sexual interests and teach healthier coping mechanisms. In some cases, medications like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or anti-androgens may be prescribed to help regulate intense sexual urges. Early intervention and ongoing support are essential for managing the disorder and preventing harm.
Sexual Sadism Disorder DSM-5 Criteria Template
Sexual Sadism Disorder DSM-5 Criteria Example
How is sexual sadism disorder diagnosed?
Sexual Sadism Disorder is diagnosed by a trained mental health practitioner, typically through a comprehensive assessment involving a detailed clinical interview and relevant diagnostic tools. Practitioners evaluate the individual’s history of sexual behaviors, fantasies, and urges, focusing on whether these involve inflicting physical or psychological pain on another person.
A thorough examination includes exploring whether these sadistic sexual behaviors have caused significant distress or impairment in the individual's personal, social, or occupational life. Additionally, practitioners will assess the presence of non-consensual acts and examine any legal, ethical, or interpersonal consequences associated with the behavior. Risk factors, such as previous trauma or co-occurring mental health disorders, are also considered during the assessment.
Practitioners may use validated questionnaires or self-report measures to gather information about the frequency and intensity of sadistic sexual fantasies and urges. The diagnosis is made based on whether these behaviors meet the criteria outlined in the DSM-5, which helps differentiate sexual sadism disorder from other sexual preferences or behaviors.
DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for sexual sadism disorder
The following are the key diagnostic features of the disorder:
- Intense sexual arousal: Over a period of at least six months, the individual experiences recurrent, intense sexual arousal from inflicting physical or psychological suffering on another person. This arousal is manifest through sadistic sexual fantasies, urges, or behaviors.
- Distress or impairment: The individual’s sadistic sexual urges or behaviors cause significant distress or impairment in their social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.
- Nonconsensual acts or harm: The individual may have acted on these urges with a nonconsenting person or experienced significant distress related to the fantasies.
The following are specifiers and additional considerations in diagnosing patients:
- In a controlled environment: The diagnosis can specify if the individual is living in a controlled environment, such as a prison, where opportunities to act on sadistic urges are restricted.
- In full remission: If the individual has not acted on sadistic urges or experienced distress for at least five years in an uncontrolled environment, they may be considered in remission.
How is sexual sadism disorder treated and managed?
Treatment for Sexual Sadism Disorder focuses on reducing harmful behaviors, managing intense sexual arousal from inflicting physical or psychological suffering, and addressing underlying psychological issues. This aims to reduce sadistic sexual fantasies, urges, and behaviors, thereby alleviating clinically significant distress and impairment in social, occupational, or personal functioning.
Psychological treatment
The primary approach to managing sexual sadism disorder is a psychological treatment, particularly cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). CBT helps individuals identify and challenge harmful thought patterns and develop healthier coping mechanisms. Cognitive restructuring techniques are used to modify sadistic sexual interests and reduce the intensity of sexual excitement linked to inflicting physical or psychological harm. Therapy also addresses any co-occurring mental disorders, such as antisocial personality disorder, which are common in individuals with sadistic sexual behaviors.
Medication
In some cases, anti-androgenic drugs or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) may be prescribed to help regulate sexual urges and reduce the impulsivity associated with sadistic sexual fantasies. These medications are used to decrease sexual arousal linked to sadistic sexual interests, ultimately helping individuals manage their sex drive and reduce the risk of acting on their urges in a nonconsenting context.
Inpatient or residential treatment
For individuals with severe sexual sadism or those who have committed sexually motivated crimes, inpatient treatment in a controlled environment may be necessary. Residential programs provide a structured setting where individuals can receive intensive therapy and monitor their progress in managing sadistic acts. This setting may also be required for those at high risk of sexually motivated homicides or engaging in sexual assault.
Long-term management
Long-term treatment may involve regular therapy sessions, continued medication, and monitoring for relapse or escalation of sadistic behaviors. The aim is to reduce impulsive behavior, manage sexual sadism in the context of consenting adults, and help individuals with paraphilic disorders reintegrate into society without posing a risk of harm to others.
Commonly asked questions
Sexual sadism disorder is often caused by a combination of biological, psychological, and environmental factors, including past trauma and co-occurring mental disorders.
Yes, sexual sadism disorder treatment involves cognitive behavioral therapy and medications like anti-androgens to reduce sexual urges and harmful behaviors.
Yes, it can be dangerous as it involves nonconsensual sadistic sexual behaviors and may lead to psychological harm or sexually motivated crimes.














-template.jpg)