A normal Renal Function Test (RFT) report indicates that the kidneys are effectively filtering waste products, maintaining electrolyte balance, and performing other essential functions. Below is an overview of the typical components of a normal RFT report, including their normal ranges and brief explanations.
Renal Function Test (RFT)
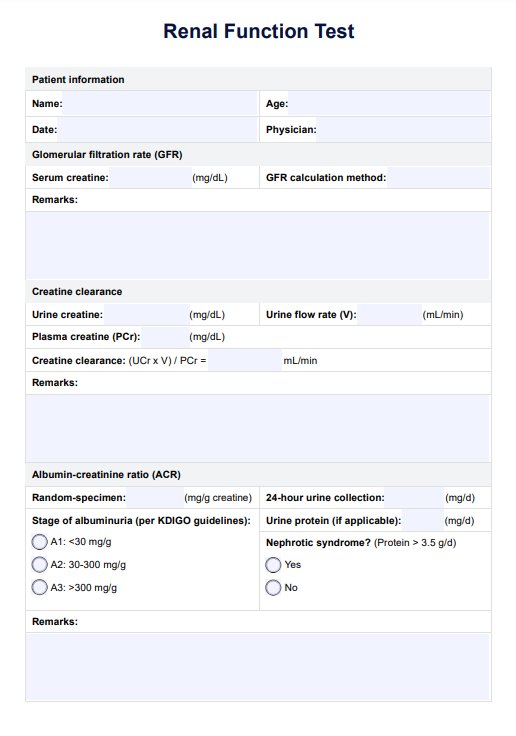
Learn about the Renal Function Test (RFT), a group of blood and urine tests used to evaluate the function of the kidneys. Download our free RFT test template today!
Renal Function Test (RFT) Template
Commonly asked questions
Renal Function Tests are used by healthcare providers to assess kidney health by measuring specific biomarkers in blood and urine samples. Practitioners typically follow a structured protocol, utilizing standardized templates to ensure comprehensive data collection and accurate interpretation of results.
RFT tests for key indicators of kidney health, including serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, and electrolyte levels, which provide insights into kidney function. Additionally, urine tests evaluate the presence of proteins, blood, or other abnormalities that can indicate underlying renal issues or diseases.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











