List of Behavior Intervention Strategies PDF
Explore a comprehensive guide to help you encourage positive change with our List of Behavior Intervention Strategies. Access our free resource here!


What are behavior interventions?
Behavior interventions are structured approaches to address challenging behaviors in various settings, especially in schools, clinics, and special education programs. These interventions focus on reinforcing positive behavior while systematically reducing negative behaviors. Positive behavioral interventions commonly encourage individuals to replace problem behavior with more appropriate behaviors that align with established behavioral expectations.
Healthcare professionals often use positive behavior interventions when managing individuals with autism spectrum disorders, disruptive behavior, or other negative behavior. These interventions can be part of an individualized education program (IEP) and are essential for teaching students how to interact appropriately in various situations. They are also valuable in classrooms as a classroom management strategy, helping to create a supportive and structured environment.
Behavioral strategies to reduce challenging behaviors have numerous benefits. First, they promote desired behaviors by reinforcing appropriate behavior, thus enhancing the individual's ability to function in social or academic settings. By focusing on positive behavior, these interventions minimize the occurrence of negative behaviors and improve overall student interaction. Additionally, behavior contracts and charts can provide a clear visual of progress, helping students and educators track improvements.
Behavior management techniques, such as setting clear behavioral expectations and using rewards for positive behavior, encourage individuals to develop appropriate behaviors. These interventions also help minimize problem behavior and make maintaining a consistent classroom routine easier. When tailored to the individual’s needs, they can significantly improve academic performance and social interactions, fostering a more inclusive and effective learning environment.
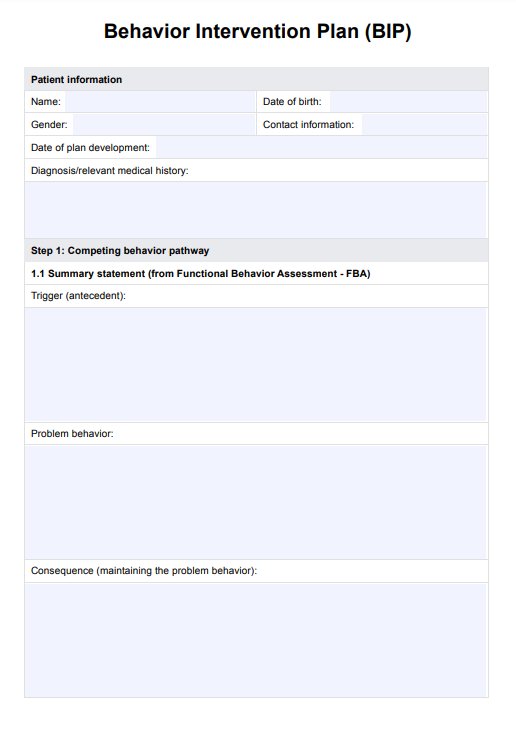
List of Behavior Intervention Strategies PDF Template
List of Behavior Intervention Strategies PDF Example
How does our List of Behavior Intervention Strategies PDF work?
Our List of Behavior Intervention Strategies PDF is a comprehensive reference designed to assist healthcare practitioners in promoting positive changes in behavior. It provides specific strategies for encouraging positive actions and reducing disruptive behaviors in various settings, including classrooms.
Step 1: Access the template
To begin, access the PDF through Carepatron. Once logged in, click "Use Template" in the article to use the handout into your classroom environment or clinical setting.
Step 2: Identify the target behavior
Identify the specific strategies that apply to the behavior you are aiming to address, whether it is to reduce disruptive behaviors or to encourage positive behaviors during an academic task. Understanding the behavior will guide the selection of appropriate interventions.
Step 3: Select the appropriate strategy
Choose from positive reinforcement strategies, negative reinforcement strategies, or antecedent-based strategies based on the individual’s needs. For example, use proximity control in the classroom environment to minimize disruptions or implement behavior charts to track progress.
Step 4: Apply the strategy consistently
Consistency is key to ensuring long-term behavioral improvement. Implement the chosen strategy across various scenarios and settings, such as during specific academic tasks or within a structured daily routine. This increases the effectiveness of the intervention.
Step 5: Monitor and adjust as needed
Evaluate the effectiveness of the strategy by monitoring positive changes in the individual’s behavior. Adjust as necessary to ensure the intervention remains relevant and impactful over time. Use tools like behavior charts to document progress and adjust interventions when needed.
List of Behavior Intervention Strategies
Behavior intervention strategies are essential tools in managing and modifying undesired behaviors. They emphasize promoting positive behavior and reducing problem behaviors through structured methods. (Idaho (SESTA), 2024) Below are several effective strategies:
Positive reinforcement strategies
Positive reinforcement encourages desired behaviors by providing rewards or recognition when they occur. This strategy can be applied by:
- Praise and recognition: Acknowledge and commend individuals for demonstrating the specific behavior to encourage repetition.
- Rewards and incentives: Offer tangible rewards, such as extra privileges or small treats, for consistent positive behavior.
- Increased positive attention: Provide more positive social interaction when desired behaviors are displayed.
- Token economy systems: Implement a system where tokens are earned for positive behaviors and exchanged for rewards.
Negative reinforcement strategies
Negative reinforcement focuses on removing an unfavorable condition after demonstrating positive behaviors, which strengthens the likelihood of that behavior recurring. It can be done through:
- Extinction: Gradually remove any positive praise or reinforcement that might be maintaining the undesired behaviors.
- Time-out: Briefly remove an individual from the situation when they exhibit unwanted behaviors.
- Response cost: Take away a preferred activity or privilege when undesirable behaviors occur, ensuring fairness.
Antecedent-based strategies
Antecedent interventions involve adjusting the environment or conditions before behaviors occur to prevent problem behaviors from arising. Methods include:
- Environmental cues: Modify the environment to reduce triggers for unwanted behavior.
- Visual schedules and prompts: Use visual tools to provide clear expectations and routines.
- Activity schedules: Structure transitions and activities to minimize chances of undesired behavior.
Emotional regulation strategies
Emotional regulation helps individuals manage their emotions, reducing the likelihood of problem behaviors. Methods include:
- Self-awareness exercises: Teach individuals to recognize emotional triggers.
- Mindfulness activities: Incorporate practices like deep breathing or meditation to calm down.
- Journaling: Encourage individuals to express their emotions through writing as part of self-management strategies.
Self-management strategies
Self-management strategies empower individuals to take control of their own behavior through monitoring and evaluating their actions. This can be done by:
- Self-monitoring: Teach individuals to track their behaviors, increasing self-awareness and responsibility.
- Self-evaluation: Encourage individuals to assess their own progress and areas for improvement.
- Self-reward systems: Allow individuals to develop their own rewards to reinforce positive behavior choices.
Strategies for successful behavioral interventions
Conducting successful interventions to manage a specific behavior is essential. Positive behavior interventions must be combined with well-planned, individualized behavior strategies to create long-lasting change. Below are key strategies to ensure the effectiveness of behavioral interventions.
Define the behavior
Identifying the behavior is the first step. This allows for accurate measurement and helps track progress over time. Ensure all team members understand and agree on the specific behavior being addressed.
Use positive praise
Positive praise reinforces desired behaviors and increases their likelihood. When a student's behavior aligns with expectations, providing verbal acknowledgment or small rewards encourages repetition of the behavior.
Apply positive phrasing
Framing requests with positive phrasing guides individuals toward positive behavior. Instead of focusing on what not to do, clear instructions on what is expected foster a more cooperative environment.
Implement negative reinforcement
Negative reinforcement can remove an unfavorable condition when the target behavior occurs, encouraging individuals to continue exhibiting positive behaviors.
Provide ongoing support
Ongoing support is critical for sustaining successful interventions. Continuous feedback, strategy adjustment, and progress monitoring ensure that the interventions remain effective and adaptable to changing needs.
Reference
Idaho (SESTA). (2024, May). Behavior Intervention Strategies (BIS) Tool. Idaho Training Clearinghouse (Special Education Training and Technical Assistance). https://idahotc.com/Portals/0/Resources/1304/SESTA_Behavior_Intervention_Strategies_Tool.pdf
Commonly asked questions
Positive behavior interventions focus on reinforcing desirable behaviors through positive praise, rewards, or recognition while reducing the frequency of negative consequences or problem behaviors. They aim to create a structured environment where individuals can thrive.
Ongoing support ensures that interventions remain effective over time. Regular monitoring and adjustments help adapt strategies to meet changing needs and provide continuous reinforcement of positive behavior.
Some common strategies include positive reinforcement (rewarding appropriate behaviors), antecedent interventions (modifying environments to reduce unwanted behaviors), extinction techniques (removing rewards for unwanted behaviors), and self-management strategies (teaching skills for managing behaviors).

























-template.jpg)