Full Scale Intelligence Quotient (FSIQ) Score Chart
Explore how full-scale IQ (FSIQ) scores are interpreted using our FSIQ Score Chart, highlighting intellectual levels and their significance in assessments.


Understanding IQ test scores
Intelligence Quotient (IQ) scores are widely used to assess cognitive abilities, offering a snapshot of an individual’s intellectual performance relative to others. Derived from standardized tests, IQ scores measure problem-solving skills, logical reasoning, memory, and the ability to process information. These scores help professionals evaluate cognitive strengths and areas that may require further development.
IQ testing categorizes individuals across a range of abilities, providing valuable insights into how a person’s cognitive function compares with the general population. Whether used in education, clinical settings, or career assessments of job performance, IQ scores are a key tool for understanding intellectual potential and creating personalized development plans.
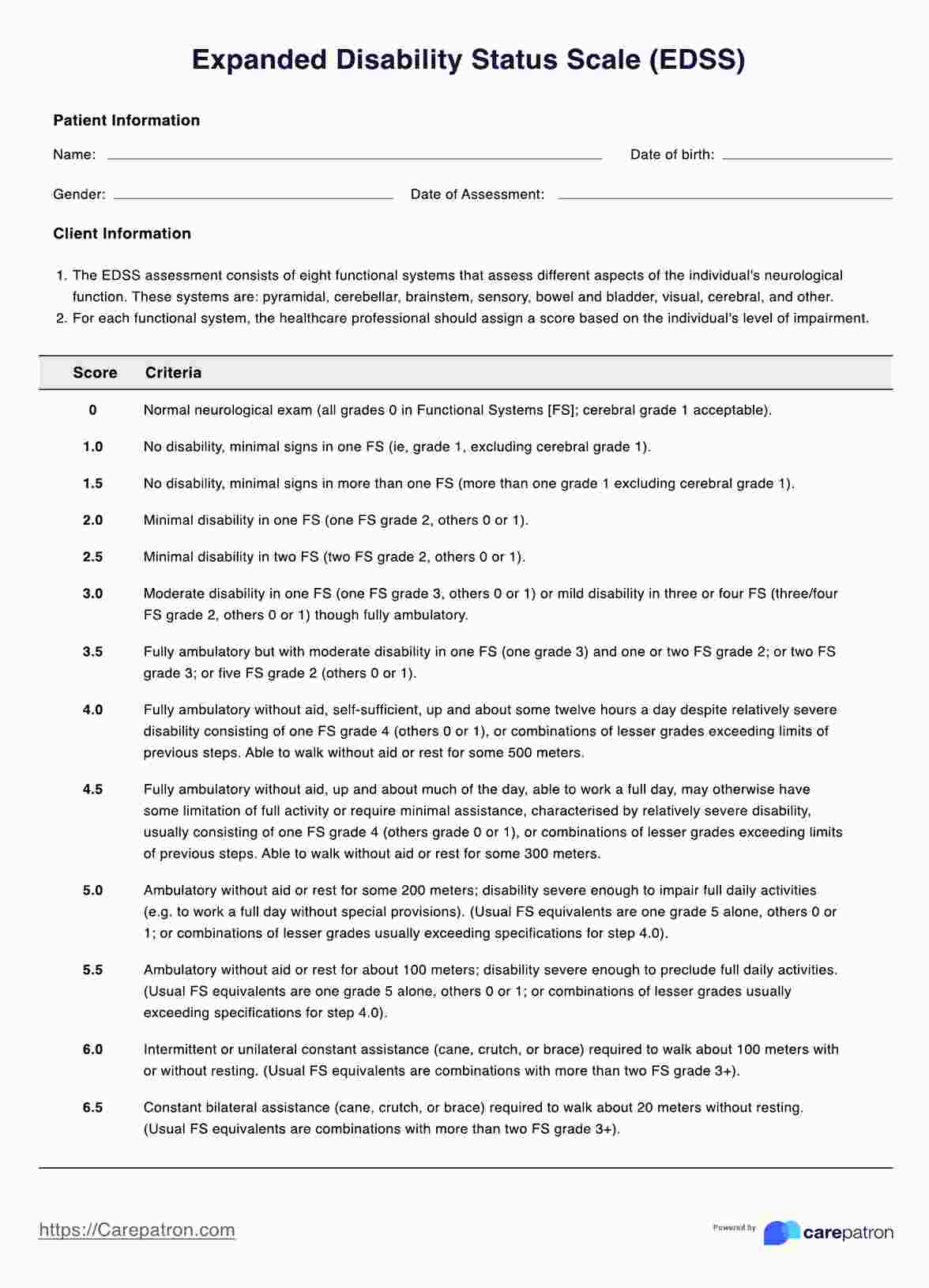
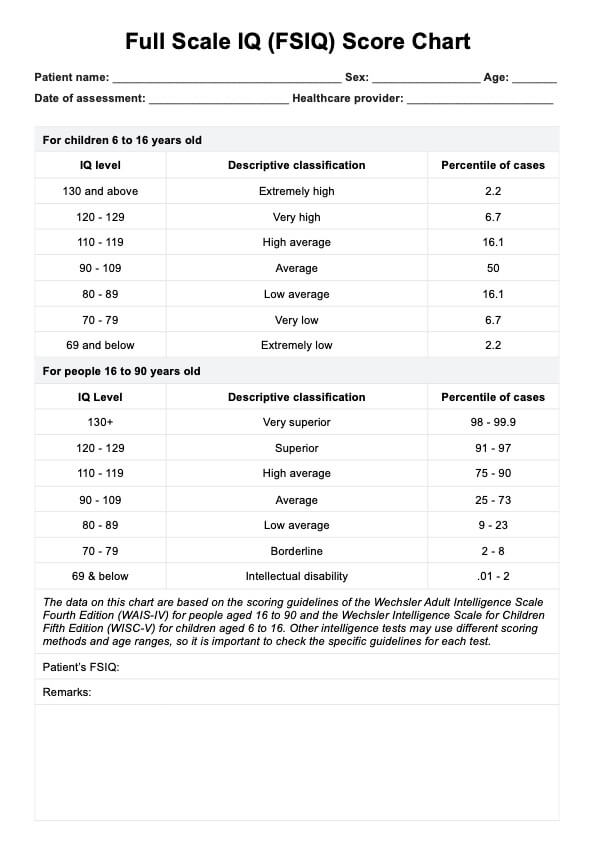
Full Scale Intelligence Quotient (FSIQ) Score Chart Template
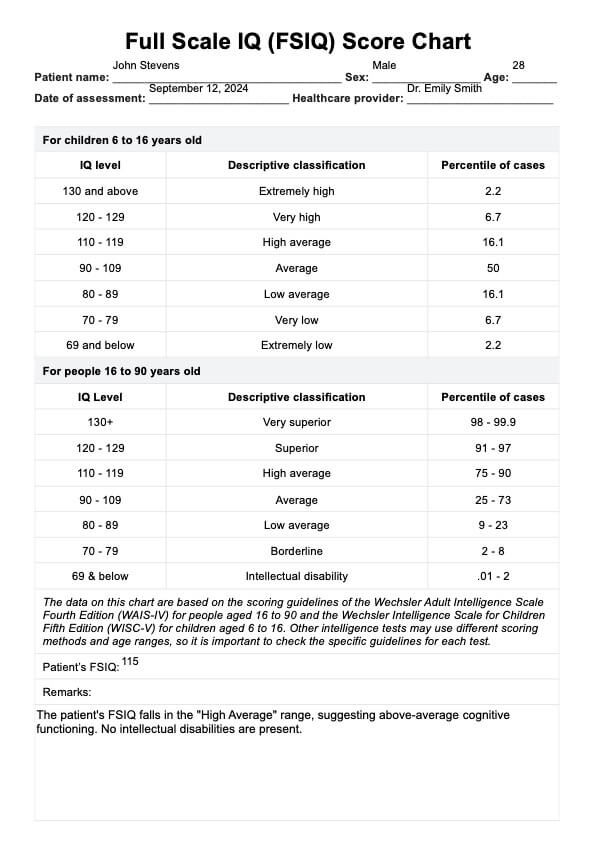
Full Scale Intelligence Quotient (FSIQ) Score Chart Example
What is a full-scale IQ (FSIQ) score?
The full-scale IQ (FSIQ) is a measure of overall cognitive ability derived from standardized intelligence tests like the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children Fifth Edition (WISC-V) or the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale Fourth Edition (WAIS-IV). FSIQ is calculated by averaging an individual's scores across several subtests that measure different cognitive abilities.
The WISC-V is administered to children between the ages of 6 and 16 years old, while the WAIS-IV is used for individuals aged 16 years and older. These tests are designed to assess an individual's cognitive abilities in areas such as verbal comprehension, perceptual reasoning, working memory, and processing speed. The subtests within these categories may include tasks such as identifying patterns, solving logic problems, vocabulary and general knowledge questions, visual-motor integration tasks, and recalling information from short-term memory.
Obtaining a full-scale IQ score can provide valuable information about an individual's overall cognitive functioning, as well as strengths and weaknesses in specific cognitive areas. It can also be used to identify learning disabilities, intellectual giftedness, and developmental disorders such as autism spectrum disorder.
It is important to note that FSIQ scores should not be viewed as the sole measure of intelligence or used to label individuals.
How to use our full-scale intelligence quotient (FSIQ) Score Chart
Our FSIQ Score Chart is an easy-to-use tool to help you interpret and record intelligence scores quickly and accurately. This chart includes FSIQ scores based on the WAIS and WISC, allowing you to
Step 1: Download the chart
Start by downloading the FSIQ Score Chart from the Carepatron platform. It’s available in a simple format that can be printed or used digitally to assist in interpreting FSIQ results.
Step 2: Enter the test scores
Once you have the individual's WAIS-IV results or similar IQ test scores, use the chart as a reference to determine their FSIQ score.
Step 3: Use for clinical or educational purposes
The chart can be part of a comprehensive psychological or educational assessment. Whether creating a treatment plan, supporting an academic strategy, or diagnosing cognitive conditions, this chart will help you interpret and communicate the FSIQ results effectively.
How is the FSIQ score interpreted?
FSIQ scores are interpreted based on specific ranges and corresponding descriptive categories. In the WAIS-IV, these categories include "Very Superior" for scores of 130 and above, representing the top 2% of the population, and "Average" for scores between 90 and 109, which reflect the cognitive abilities of a significant portion of the population. Scores below 70, categorized as "Extremely Low," may indicate cognitive impairments or intellectual disabilities requiring further clinical evaluation or intervention.
For the WAIC-V, the categories are slightly different, with "Extremely High" for scores of 130 and above, "Very High" for scores between 120 and 129, and "Average" for scores between 90 and 119. Scores below 70 are also considered "Very Low" in this test.
Interpreting the FSIQ score is critical in both clinical and educational settings. In schools, the score helps create individualized education plans (IEPs) for students with learning challenges. Clinically, FSIQ scores are used to diagnose various cognitive disorders, track intellectual development, or determine eligibility for services. Understanding the interpretation of FSIQ scores enables professionals to provide appropriate support for individuals across multiple contexts
Benefits of using our FSIQ Score Chart
This free FSIQ score chart is a useful tool for interpreting and understanding FSIQ scores. Here are some benefits of using this printable chart:
Streamlined documentation
Healthcare professionals often use FSIQ scores to assess an individual's cognitive abilities. With our printable chart, all the essential information is displayed in a clear and concise format, making it easier to document and share with other professionals.
Helpful for tracking progress
Our FSIQ Score Chart can be a useful tool for tracking progress over time for individuals undergoing cognitive therapy or interventions. By comparing previous and current scores, therapists, educators, and healthcare professionals can determine whether an individual's intellectual abilities have improved.
A quick reference guide
For those unfamiliar with FSIQ scores, our chart provides a quick reference guide for understanding where an individual's score falls in relation to the average range. This can be particularly helpful for parents or caregivers of children who may have received an FSIQ score.
Commonly asked questions
Calculating the full-scale IQ (FSIQ) score involves adding together the scores of specific subtests from a cognitive assessment, such as the WAIS-IV. The WAIS-IV has 10 core subtests that measure verbal comprehension, perceptual reasoning, working memory, and processing speed. Each subtest is scored separately, and the FSIQ score is then calculated by combining these individual scores. This combined score reflects overall cognitive ability compared to the general population.
IQ scores represent an individual's cognitive ability based on standardized IQ tests, while percentile ranks show how that IQ compares to the general population. For example, a score in the 75th percentile means the individual scored higher than 75% of people in their age group.
There is no specific "good" full scale IQ (FSIQ) score as it can vary based on individual factors and context. For example, a score of 110 may be considered average in the general population, but for someone with a learning disability or intellectual impairment, it could be considered above-average. Additionally, FSIQ scores should not be used as the sole measure of intelligence, as they do not capture other important aspects such as creativity and emotional intelligence.



















-template.jpg)