Anoscopy
Discover everything about anoscopy tests, including the when, why, and how behind this vital medical procedure.


What is an Anoscopy Test?
An anoscopy is a medical procedure to examine the rectum's lower part and the anal canal. This test is primarily performed to diagnose and evaluate conditions affecting the anal and rectal region, such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, polyps, and certain cancers. Anoscopy is a relatively simple and quick procedure that provides valuable information to healthcare providers.
During an anoscopy, a thin, flexible tube called an anoscope is inserted into the anus. The anoscope is typically about 3 to 4 inches long and has a light source at its tip to illuminate the examined area. The anoscope helps the healthcare provider visualize the inner lining of the anal canal and rectum. If necessary, a lubricated, gloved finger may help guide the anoscope.
The entire anoscopy procedure usually takes only a few minutes and is often done in an outpatient setting. It is generally well-tolerated by patients and does not typically require anesthesia, although a local anesthetic may be used to minimize discomfort.
An can be a crucial diagnostic tool for various conditions involving the anal and rectal regions. It allows healthcare providers to directly visualize the area, assess any abnormalities, and collect tissue samples if needed for further analysis. The information obtained through anoscopy helps in the accurate diagnosis of conditions. It guides treatment decisions, whether it involves managing hemorrhoids, removing polyps, or further investigating suspicious lesions.
Anoscopy Template
Anoscopy Template Example
How Does It Work?
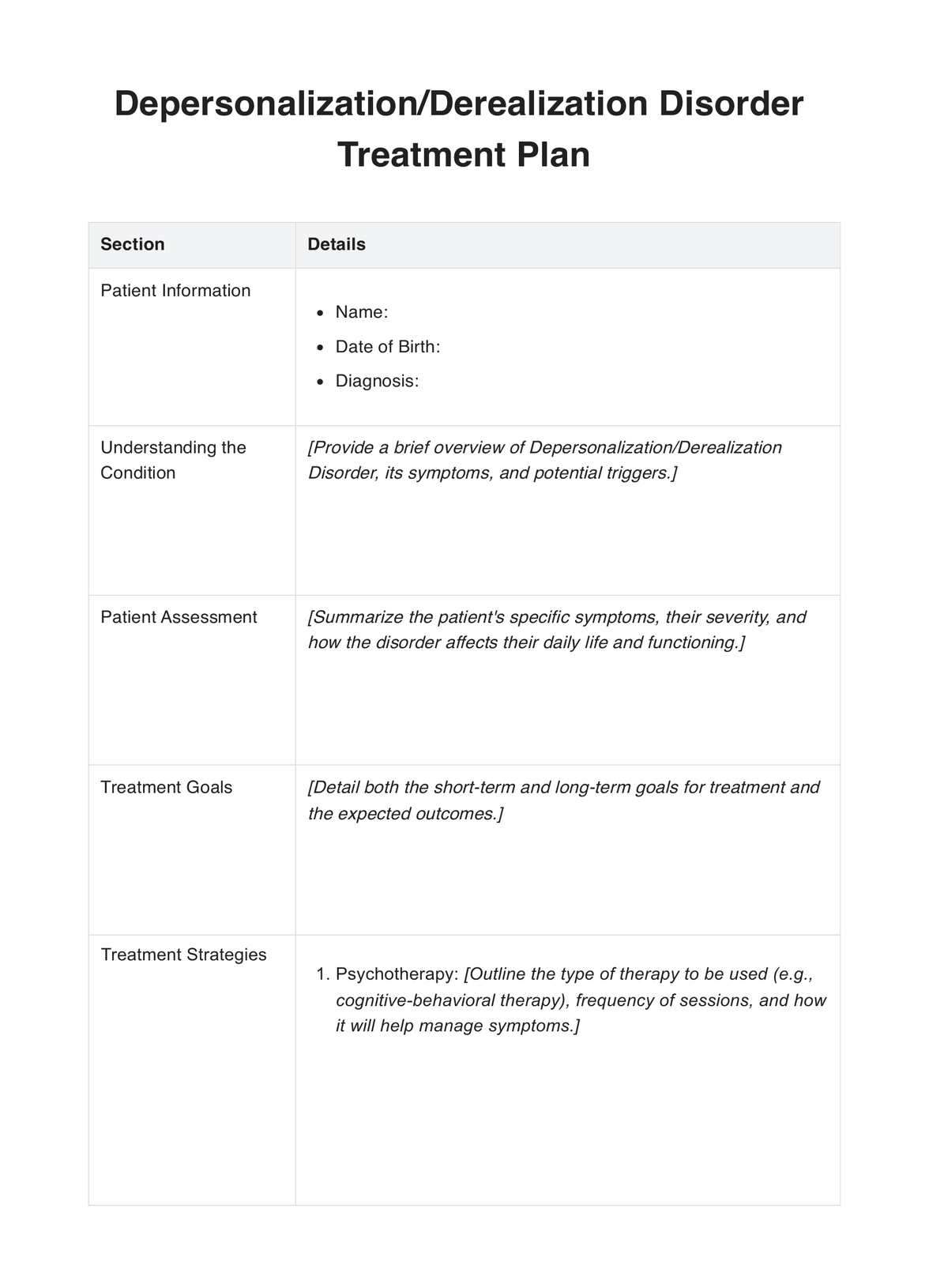
1. Patient Identification
To ensure accurate documentation, record the patient's personal information, including their name, date of birth, and medical record number.
2. Pre-procedure Details
Document the date and time of the anoscopy procedure. Note the reason for the anoscopy, such as symptoms or suspected conditions. Indicate any relevant medical history, allergies, or pre-existing conditions that might impact the procedure.
3. Informed Consent
Verify that the patient has provided informed consent for the anoscopy procedure, acknowledging that they understand the risks and benefits.
4. Procedure Description
Describe the procedure briefly, including using an anoscope, any lubrication, and whether a local anesthetic was administered.
5. Visualization and Findings
Record detailed observations of the anal canal and rectum using the anoscope. Note any abnormalities, such as hemorrhoids, polyps, fissures, or other lesions. Include information about any identified issues' color, size, location, and characteristics.
6. Biopsy or Sampling
If necessary, document the collection of tissue samples or biopsies during the anoscopy. Note the method used and the samples taken for laboratory analysis.
7. Patient Comfort and Monitoring
Assess and record the patient's comfort level throughout the procedure. Monitor vital signs if required, especially if the patient experiences adverse reactions.
8. Post-procedure Instructions
Provide the patient with post-procedure care instructions, including any restrictions on activities or medications. Document any recommendations for follow-up appointments or treatments.
9. Signature and Verification
The healthcare provider should sign and date the form, confirming the accuracy of the information. If applicable, the patient may also sign to acknowledge receipt of post-procedure instructions.
A printable anoscopy test form is critical for healthcare providers to document their findings, ensure proper patient care, and maintain a comprehensive medical record. Accurate and thorough documentation is essential for diagnosis, treatment planning, and ongoing patient management.
This medical record template provides valuable support to enhance your practice and client results.
When Would You Use This Test?
The Anoscopy Test is used by healthcare practitioners in various scenarios when they need to evaluate and diagnose conditions specifically related to the anal canal and rectum. Here are vital situations when the use of the Anoscopy Test is appropriate:
- Evaluation of Rectal Bleeding: When a patient presents with rectal bleeding, which can indicate various conditions such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, or colorectal cancer, healthcare providers may use anoscopy to inspect and determine the cause of bleeding visually.
- Assessment of Anal Pain: Patients experiencing persistent anal pain, discomfort, or itching may undergo an anoscopy to identify the source of their symptoms. This is crucial for diagnosing conditions like anal fissures, abscesses, or infections.
- Colorectal Cancer Screening: As part of routine colorectal cancer screening, healthcare providers may recommend anoscopy to examine the anal and rectal area for abnormalities, polyps, or early signs of cancer, particularly in high-risk individuals.
- Diagnosis of Anal Lesions: Anoscopy is commonly employed to evaluate and diagnose anal lesions, including anal warts associated with HPV and other growths or abnormalities that may require treatment or monitoring.
- Monitoring of Anal and Rectal Conditions: For patients with known anal or rectal conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or colorectal polyps, repeated anoscopy examinations may be used to monitor the progression of these conditions and guide treatment decisions.
- Pre-operative Assessment: Before certain surgeries involving the anus or rectum, surgeons may perform anoscopy to assess the area, plan the procedure, and ensure no unexpected issues.
- Assessment of Inflammatory Conditions: Anoscopy can also evaluate and diagnose inflammatory conditions affecting the anal canal and rectum, such as proctitis or Crohn's disease.
What fo the Results Mean?
The results of an Anoscopy Test provide crucial information about the condition of the anal canal and rectum, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of various medical issues. Here are typical results and their meanings:
- Normal Findings: If the Anoscopy Test reveals no abnormalities, it is considered normal. The anal canal and rectum appear healthy and free from significant issues. Typical results are reassuring and may suggest that symptoms such as rectal bleeding or anal pain are due to minor and non-serious causes like hemorrhoids or temporary irritation.
- Hemorrhoids: The most frequent finding during an anoscopy is the presence of hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoids are swollen blood vessels in the anal area and can be classified into internal or external hemorrhoids. The size and degree of prolapse (if any) are typically documented. The presence of hemorrhoids may explain symptoms like bleeding, itching, or discomfort.
- Anal Fissures: Anoscopy may reveal anal fissures, which are small tears or cracks in the lining of the anus. These can cause pain and bleeding during bowel movements. Identification of anal fissures guides appropriate treatment, often including lifestyle modifications and topical medications.
- Anal Polyps: Polyps, abnormal growths of tissue, can sometimes be found during an anoscopy. While most anal polyps are benign, they may need to be removed and examined to rule out cancer or precancerous changes.
- Infections or Lesions: Anoscopy can detect conditions like anal warts (caused by HPV) or other lesions. Such findings may necessitate further evaluation and treatment, including medication or procedures to remove the lesions.
- Abnormal Tissue Biopsy: A biopsy may be taken for pathological examination if suspicious tissue is identified during the anoscopy. Abnormal biopsy results could indicate precancerous or cancerous changes, requiring additional diagnostic tests and appropriate treatment.
Research & Evidence
Anoscopy has its roots in proctology, the branch of medicine specializing in disorders of the rectum and anus. It was traditionally performed using rigid anoscope-like instruments made of metal or glass. The early use of anoscopy focused on diagnosing and treating common anal conditions such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, and abscesses.
Over time, anoscopy techniques became more refined, and flexible anoscope designs were introduced, improving patient comfort and safety during the procedure.
Research supporting the efficacy of anoscopy in diagnosing and managing anal and rectal conditions is extensive. Clinical studies have documented the benefits of anoscopy in various contexts:
- Colorectal Cancer Screening: Anoscopy is a component of colorectal cancer screening programs and is effective in identifying early signs of cancer and precancerous lesions.
- Hemorrhoid Diagnosis: Numerous studies have examined the accuracy of anoscopy in diagnosing hemorrhoids and guiding appropriate treatment.
- Anal Fissure Management: Research has demonstrated the utility of anoscopy in diagnosing anal fissures and helping determine the most suitable treatments.
- Infectious Diseases: Anoscopy aids in identifying anal warts related to HPV and other infections, facilitating prompt treatment.
- Polyp Detection: Anoscopy plays a role in detecting and evaluating anal polyps, which may require further examination and management.
Modern anoscopy benefits from technological advancements such as improved lighting, flexible anoscope designs, and the availability of high-resolution imaging equipment. These innovations enhance the accuracy of diagnoses and patient comfort.
Anoscopy is often performed alongside other imaging techniques, such as endoscopy or sigmoidoscopy, to comprehensively evaluate the lower gastrointestinal tract.
References
- Anoscopy. (n.d.-a). https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/anoscopy/
- Anoscopy. (n.d.-b). Mount Sinai Health System. https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/tests/anoscopy
- Anoscopy and High-Resolution Anoscopy. (2022, March 15). Johns Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/anoscopy-high-resolution-anoscopy
- Anoscopy: What to expect before, during, and after. (n.d.). City of Hope. https://www.cancercenter.com/cancer-types/anal-cancer/diagnosis-and-detection/anoscopy
- Malik, Z. (2023, September 26). How To Do Anoscopy. MSD Manual Professional Edition. https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/gastrointestinal-disorders/how-to-do-gastrointestinal-procedures/how-to-do-anoscopy
- Mir, F., MD. (n.d.). Anoscopy: Background, indications, contraindications. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/79937-overview
- Professional, C. C. M. (n.d.). Anoscopy. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/24993-anoscopy
- Watt, T. (2020, November 12). Anoscopy. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/anoscopy
- WebMD Editorial Contributor. (2021, April 21). What is an anoscopy? WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/what-is-an-anoscopy
Commonly asked questions
Anoscopy Tests are typically requested by healthcare providers, including gastroenterologists, colorectal surgeons, proctologists, and primary care physicians, when patients present with anal or rectal symptoms or as part of colorectal cancer screening.
Anoscopy Tests are used when patients experience symptoms like rectal bleeding, anal pain, or discomfort. They are also employed in routine colorectal cancer screening and to diagnose conditions such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, polyps, and anal warts.
Anoscopy Tests involve the insertion of a thin, flexible anoscope into the anus to visually inspect the anal canal and rectum. The procedure helps healthcare providers diagnose and evaluate conditions affecting these areas, and it may include taking tissue samples or biopsies if necessary.
An Anoscopy Test is a relatively quick procedure, typically taking only a few minutes to complete. It is generally well-tolerated by patients and can often be performed in an outpatient setting.






















-template.jpg)