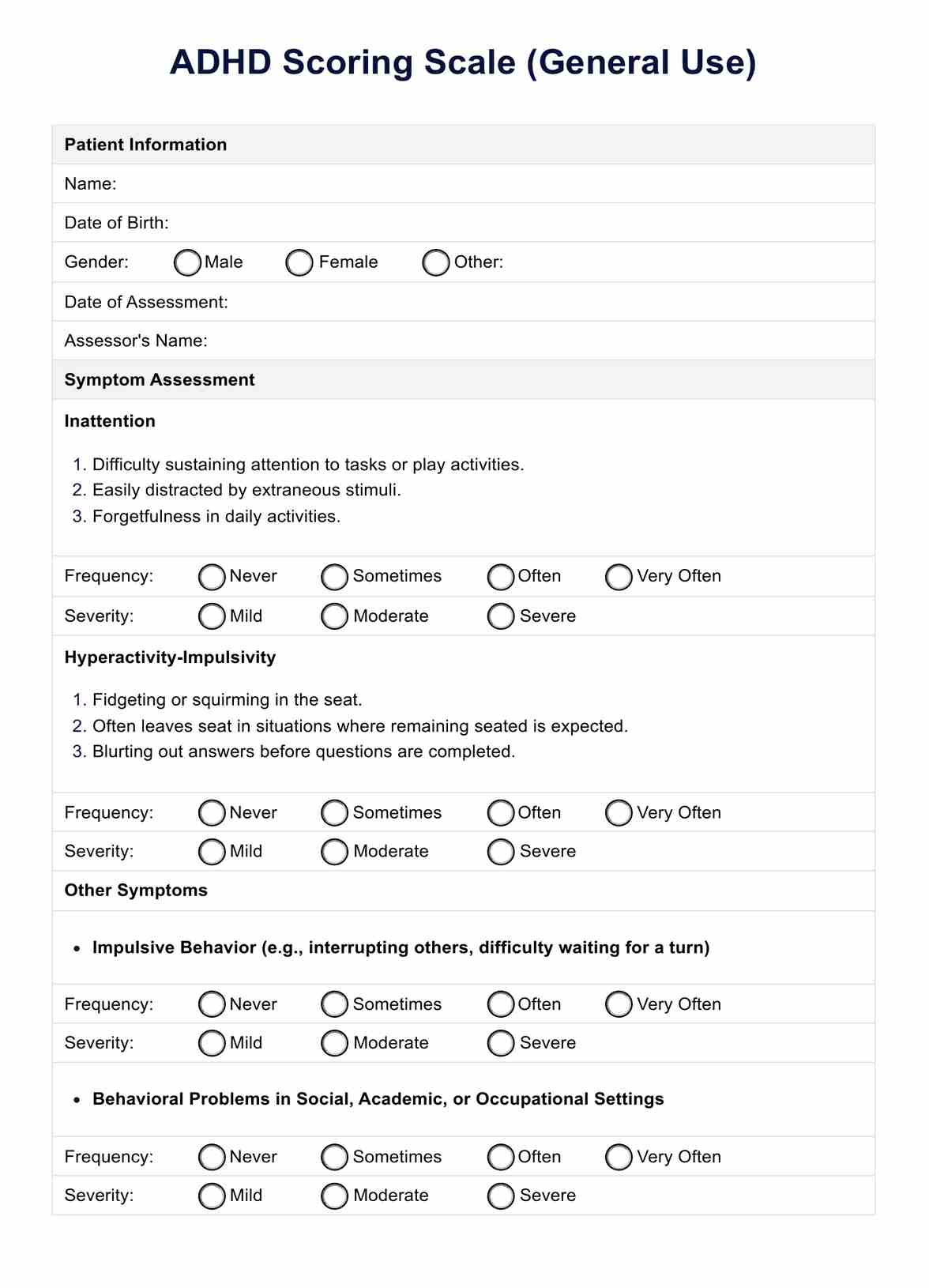
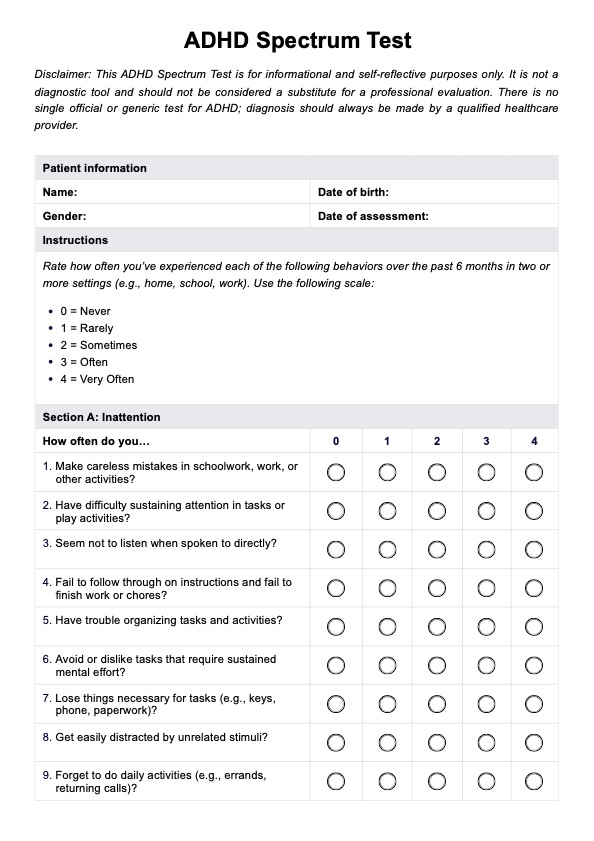
ADHD Scoring Scale
Explore the ADHD Scoring Scale, a comprehensive tool for assessing symptoms and severity of ADHD. Enhance understanding and treatment strategies.


What is the ADHD Scoring Scale?
The ADHD Scoring Scale is a tool used in the diagnostic process for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in both children and adults. It encompasses various rating scales, such as the Vanderbilt Assessment Scale, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM), and the ADHD Rating Scale-IV. These rating scales evaluate ADHD-related behaviors and symptoms across different age groups.
Healthcare professionals often utilize separate forms for children ages six and adults, considering age-specific criteria and symptoms. The assessment includes questions about classroom performance, social settings, and behavioral patterns such as excessive talking or careless mistakes. It aims to monitor improvement and provide an objective diagnosis by monitoring progress and evaluating the severity of ADHD symptoms.
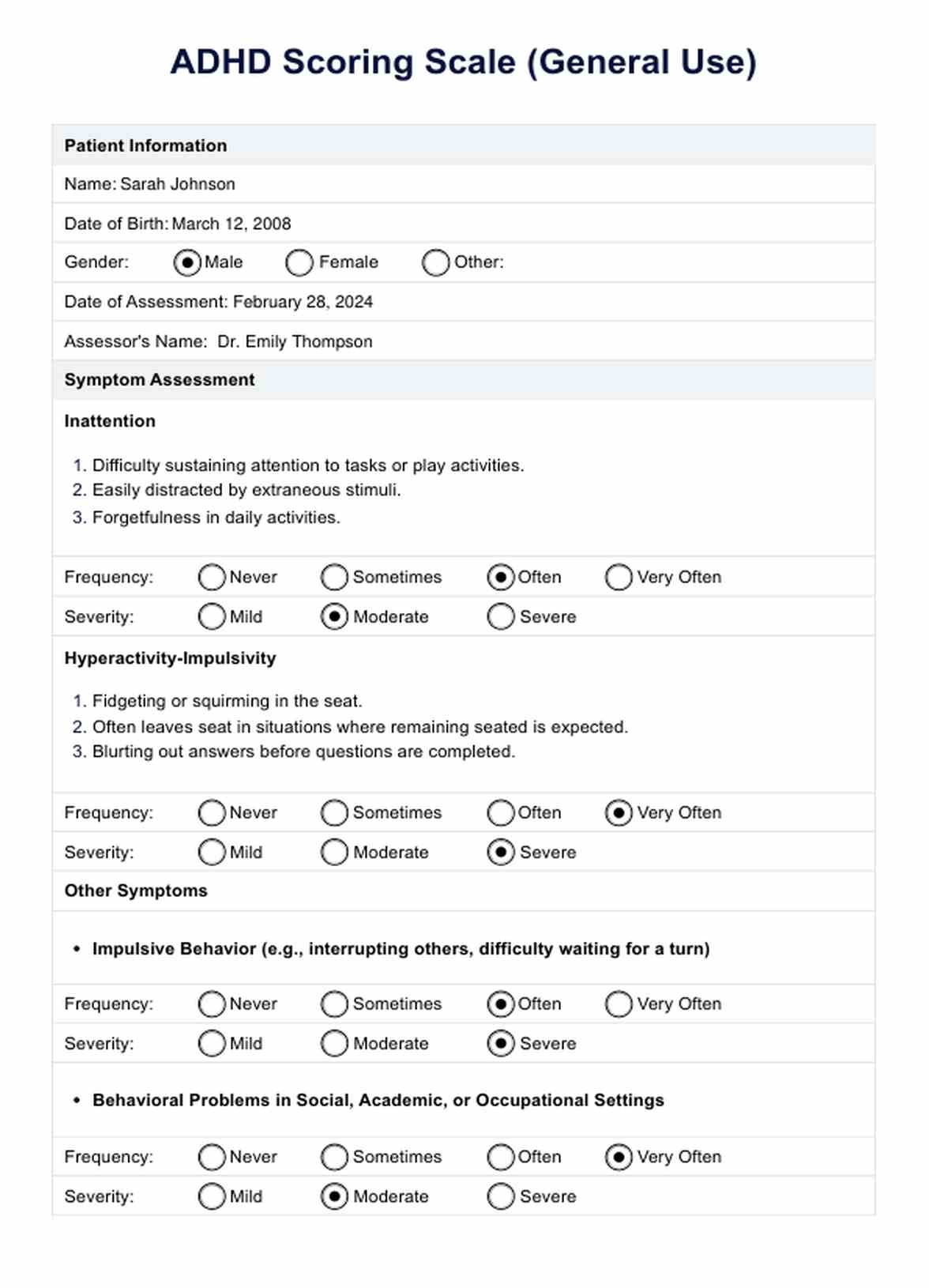
The ADHD Scoring Scale consists of items assessing inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. These questions cover a range of behaviors and symptoms, allowing for a comprehensive evaluation of ADHD-related difficulties.
Various psychometric properties, such as reliability and validity, are considered in the development and refinement of ADHD rating scales, ensuring their accuracy in diagnosing ADHD and related disorders like conduct disorder or learning disabilities.
Additionally, the rating scale may include performance questions and clinical history to assist healthcare professionals in making an accurate diagnosis and designing further appropriate interventions for individuals with ADHD.
ADHD Scoring Scale Template
ADHD Scoring Scale Example
How is the ADHD Scoring Scale used in diagnosing ADHD?
The ADHD Scoring Scale is a valuable tool used by healthcare professionals in diagnosing ADHD by systematically evaluating symptoms and behaviors associated with the disorder. Here's how it scores what's typically used in the diagnostic process:
- Initial screening: The ADHD Scoring Scale is often employed as an initial screening tool to assess whether an individual may exhibit symptoms indicative of ADHD. It helps healthcare professionals quickly identify potential cases that warrant further evaluation.
- Comprehensive evaluation: Upon identifying potential ADHD symptoms, healthcare professionals administer the ADHD Scoring Scale to gather detailed information about the individual's behaviors across various settings (e.g., school, home, and social environments). This comprehensive evaluation aids in understanding the frequency and severity of ADHD-related symptoms.
- Objective assessment: The ADHD Scoring Scale provides a standardized method for evaluating ADHD symptoms, ensuring a consistent and accurate evaluation. By using established rating scales and criteria, healthcare professionals can make informed judgments about the presence and severity of ADHD symptoms.
- Diagnosis confirmation: The results of the ADHD Scoring Scale, along with clinical observations and other relevant information (such as medical history and behavioral assessments), help healthcare professionals confirm or rule out an ADHD diagnosis. The scale assists in distinguishing ADHD from other mental health conditions with similar symptoms, such as anxiety disorders or learning disabilities.
- Treatment planning: Following a confirmed diagnosis, the ADHD Scoring Scale continues to help develop tailored treatment plans. It provides baseline data for monitoring symptom severity over time and evaluating the effectiveness of interventions, such as medication, behavioral therapy, or accommodations in educational or work settings.
Key components assessed by the ADHD Scoring Scale
The ADHD Scoring Scale assesses various vital components and criteria associated with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). These typically include:
Core symptoms of ADHD
ADHD features include inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, pivotal for diagnosis and understanding its impact on behavior.
- Inattention: This component evaluates difficulties in sustaining attention, organizing tasks, following instructions, and completing tasks accurately. Symptoms may include making careless mistakes, being easily distracted, forgetfulness, and difficulty listening or paying attention to details.
- Hyperactivity: This criterion assesses excessive motor activity, such as fidgeting, restlessness, and difficulty remaining seated in situations where it is expected. Individuals with ADHD may often feel restless and have trouble engaging in quiet activities.
- Impulsivity: Impulsivity refers to acting without forethought or consideration of consequences. It includes interrupting others, blurting out answers, difficulty waiting for one's turn, and making impulsive decisions without considering the potential outcomes.
Associated behavioral problems
These components encompass additional challenges, such as behavioral problems and functional impairments, providing insight into the broader spectrum of difficulties individuals with ADHD may face beyond the core symptoms.
- Behavioral problems: The scale may also evaluate other behavioral problems commonly associated with ADHD, such as difficulties in social interactions, aggression, defiance, and emotional dysregulation.
- Functional impairment: Assessment of functional impairment is crucial, as ADHD symptoms can significantly impact daily functioning in various settings, including school, work, relationships, and social activities.
Assessment considerations
Addressing age-appropriate criteria, frequency, severity, and contextual factors, this category guides clinicians in comprehensively evaluating ADHD symptoms to tailor interventions effectively for the individual's needs.
- Age-appropriate criteria: The scale considers age-specific criteria and developmental norms, as symptoms of ADHD can manifest differently across different developmental stages.
- Frequency and severity: The scale assesses the frequency and severity of ADHD symptoms to determine their impact on the individual's daily life and functioning.
- Contextual considerations: It evaluates ADHD symptoms across different contexts, such as home, school, work, and social settings, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the individual's behavior and functioning.
Is the ADHD Scoring Scale suitable for use in both children and adults?
Yes, the ADHD Scoring Scale is designed to be used in both children and adults. ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder that can persist into adulthood, and its symptoms may manifest differently across various age groups. Different versions or adaptations of the ADHD Scoring Scale exist to accommodate the specific needs and characteristics of children and adults with mental disorders.
For children, the ADHD Scoring Scale typically includes items from the child behavior checklist that assess symptoms commonly observed in childhood, such as inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and behavioral difficulties in school and social settings. These scales may incorporate input from parents, teachers, and other caregivers to gather information about the child's behavior across different environments.
In contrast, the ADHD Scoring Scale for adults may focus more on symptoms and behaviors relevant to adult functioning, such as challenges in organization, time management, sustaining attention in work or academic settings, and difficulties in relationships or managing responsibilities.
While the core components of ADHD—such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity—remain consistent across age groups, the specific items and language used in the scale may be tailored to reflect age-appropriate experiences and behaviors.
Additionally, the criteria for diagnosing ADHD in adults may differ slightly from those used for children, considering developmental differences in other age groups and the evolving presentation of symptoms over time.
How reliable and valid is the ADHD Scoring Scale in assessing ADHD symptoms?
ADHD Scoring Scales are generally reliable and valid in assessing ADHD symptoms. Studies show strong psychometric properties of these scales, supporting their use in different populations and settings.
It has high reliability and validity, accurately measuring symptoms and distinguishing individuals with ADHD. They are also sensitive to change, making them useful for monitoring treatment outcomes.
However, it's essential to note that the reliability and validity of the ADHD Scoring Scale may vary depending on the specific scale used, the population being assessed (e.g., children, adults), and the context in which the scale is administered.
Therefore, healthcare professionals must select appropriate ADHD scoring scales based on their psychometric properties, scales, and the characteristics of the individuals being evaluated.
ADHD Scoring Scale versions
There are several versions and variations of the ADHD Scoring Scale available, each tailored to specific age groups, settings, and purposes. Some of the most commonly used versions of the scoring system include:
Child and adolescent assessment scales
These assessment scales, such as the Vanderbilt assessment scale, ADHD rating scale IV (ADHD-RS-IV), NICHQ Vanderbilt assessment scale, Conners comprehensive behavior rating scales (CBRS), and Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham (SNAP-IV), are widely utilized tools specifically designed to evaluate ADHD symptoms in children and adolescents across various settings, including home and school environments.
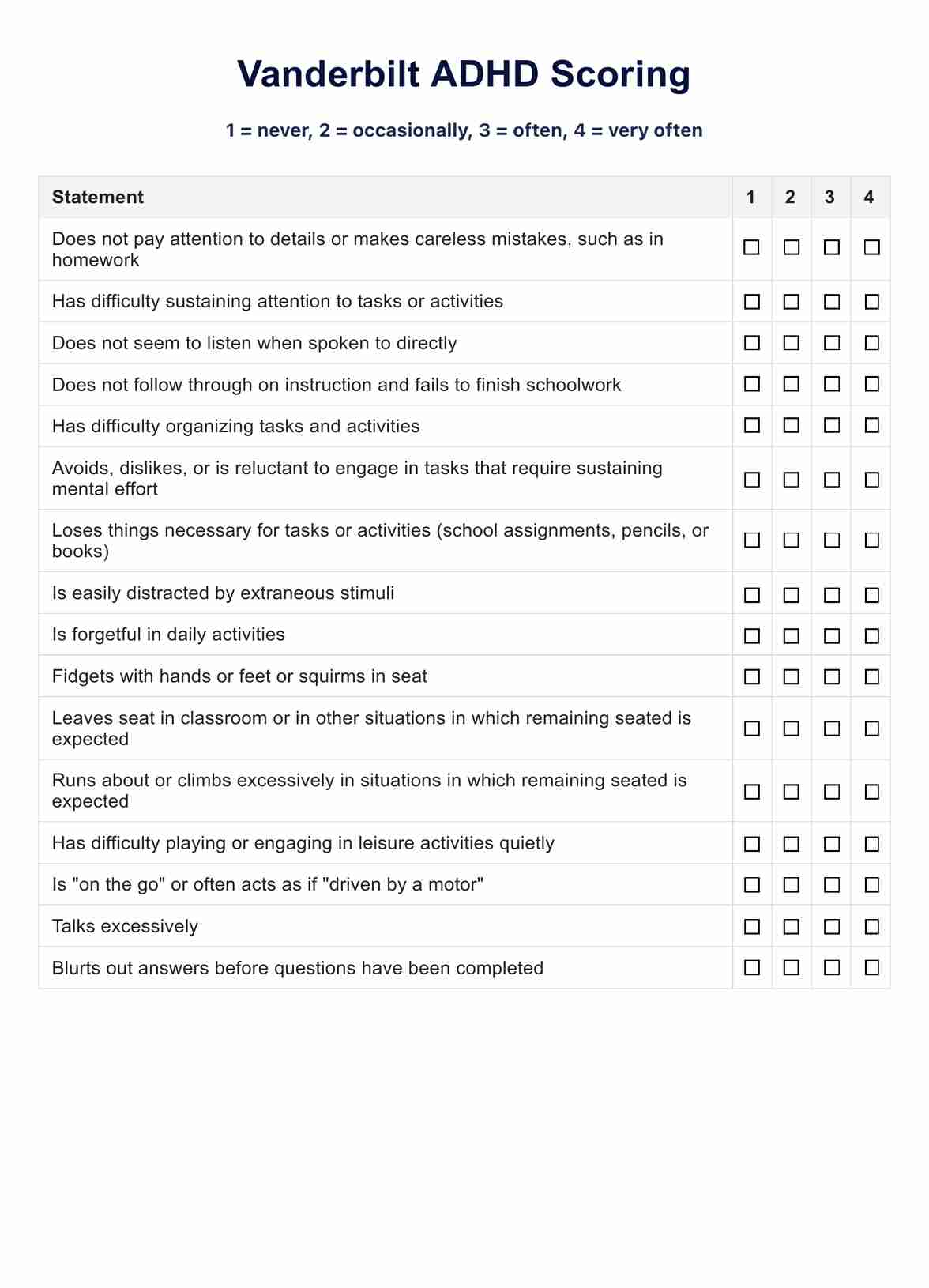
- Vanderbilt assessment scale: This scale is widely used for assessing ADHD symptoms in children and adolescents. It includes versions for parents and teachers, allowing for a comprehensive evaluation of behavior in home and school settings.
- ADHD rating scale IV (ADHD-RS-IV): The ADHD-RS-IV is a standardized tool for assessing ADHD symptoms in children and adolescents. It consists of items that measure both inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive symptoms.
- NICHQ vanderbilt assessment scale: Similar to the Vanderbilt Assessment Scale, this tool assesses ADHD symptoms in children. It includes forms for parents and teachers to provide a comprehensive view of the child's behavior.
- Conners comprehensive behavior rating scales (CBRS): This assessment tool evaluates various behavioral issues, including ADHD symptoms, in children and adolescents. It includes parent, teacher, and self-report forms.
- Swanson, nolan, and pelham (SNAP-IV): Originally developed to measure ADHD symptoms in children, the SNAP-IV is widely used in clinical and research settings. It includes items assessing both inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive symptoms.
Adult assessment scales
- Tailored for adults, the Adult ADHD Self-report Scale (ASRS) and Brown attention-deficit disorder Scale (BADDS) serve as practical screening tools to identify ADHD symptoms in individuals aged 18 and older, providing insights into areas such as executive functioning and time management.
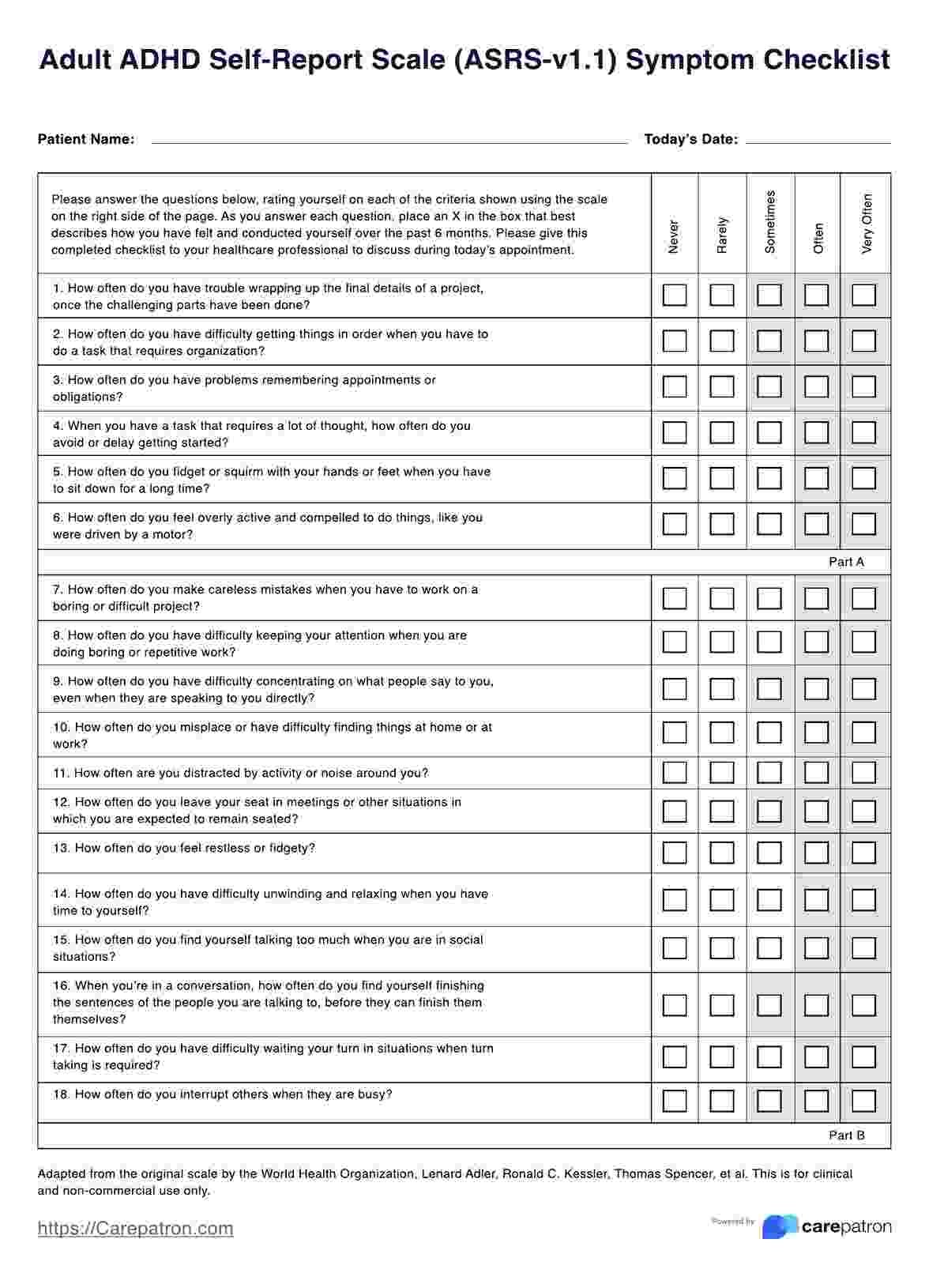
- Adult ADHD self-report scale (ASRS): Designed specifically for adults, the ASRS is a screening tool that assesses ADHD symptoms in individuals aged 18 and older. It includes a short version with six items and an extended version with 18.
- Brown attention-deficit disorder scale (BADDS): The BADDS is a self-report scale designed for adults to assess symptoms of ADHD, particularly inattentive symptoms. It evaluates various domains of functioning affected by ADHD, such as executive functioning and time management.
These are just a few examples of the many versions and variations of the ADHD Scoring Scale. Healthcare professionals may select the most appropriate scale based on factors such as the age of the child's behavior checklist, the age of the individual being assessed, the setting where
Using the ADHD Scoring Scale to track changes in ADHD symptoms over time
The frequency of administering the ADHD Scoring Scale to track changes in ADHD symptoms over time depends on several factors, including the individual's age, treatment plan, symptom severity, and treatment response.
Generally, the scale may be administered regularly to monitor progress and adjust treatment interventions as needed. Some guidelines for the frequency of administration include:
- At the start of treatment: The ADHD Scoring Scale is often administered at the beginning of treatment to establish a baseline assessment of ADHD symptoms and functional impairment. This initial assessment provides a reference point for tracking changes over time.
- Regular follow-up visits: Healthcare professionals may schedule regular follow-up visits to monitor the individual's response to treatment and assess changes in ADHD symptoms. The frequency of follow-up visits may vary but is typically every few weeks or months, depending on the treatment plan and clinical needs.
- During medication titration: If medication is prescribed as part of the treatment plan, the ADHD Scoring Scale may be administered more frequently during the titration phase to monitor the individual's response to medication and adjust the dosage as needed.
- During transitions: The ADHD Scoring Scale may be administered during transitions, such as changes in medication, dosage adjustments, or changes in treatment interventions, to evaluate the impact of these changes on ADHD symptoms.
As needed: In addition to scheduled assessments, the ADHD Scoring Scale may be administered in response to changes in symptoms, functional impairment, or other factors affecting ADHD management.
Commonly asked questions
The best ADHD rating score and scale depends on individual needs and preferences. Commonly used scales include the Vanderbilt Assessment and ADHD Rating Scale-IV.
ADHD diagnosis in the DSM-5 involves assessing symptoms across two main domains: inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity. A diagnosis is based on the presence of specific criteria outlined in the manual.
ADHD diagnosis is typically measured using standardized rating scales, clinical interviews, behavioral observations, and assessment of functional impairment.





























-template.jpg)