High Functioning ADHD Test
Explore our comprehensive guide on High Functioning ADHD, including symptoms, assessments, and a free downloadable test example.


Introduction to high functioning ADHD
High Functioning ADHD is a unique subtype of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) characterized by a person's ability to manage symptoms to a degree that allows them to function effectively in everyday life. Despite this, individuals with High Functioning ADHD still face considerable challenges that can impact their work, relationships, and self-esteem. Unlike more overt forms of ADHD, High Functioning ADHD is often subtler, making it harder to recognize and diagnose.
People with this condition may have developed coping strategies that mask their symptoms, which can include internalizing their hyperactivity or finding creative ways to manage attention deficits. Because their struggles are less visible, they often go unrecognized by peers, educators, and even healthcare professionals. This lack of recognition can lead to a lack of support and understanding, making it essential to raise awareness and understanding of High Functioning ADHD.
Proper management of High Functioning ADHD requires a nuanced approach. It involves recognizing the subtle manifestations of the disorder and understanding how it affects various aspects of life, including academic and professional achievements, social interactions, and personal relationships. Early identification and tailored interventions are key to helping individuals with High Functioning ADHD achieve their full potential.
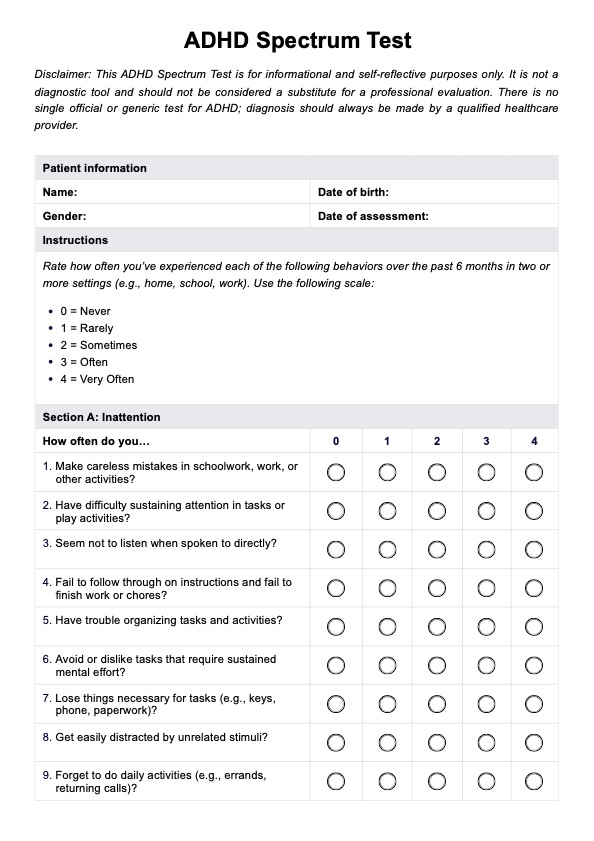
High Functioning ADHD Test Template
High Functioning ADHD Test Example
High Functioning ADHD Symptoms
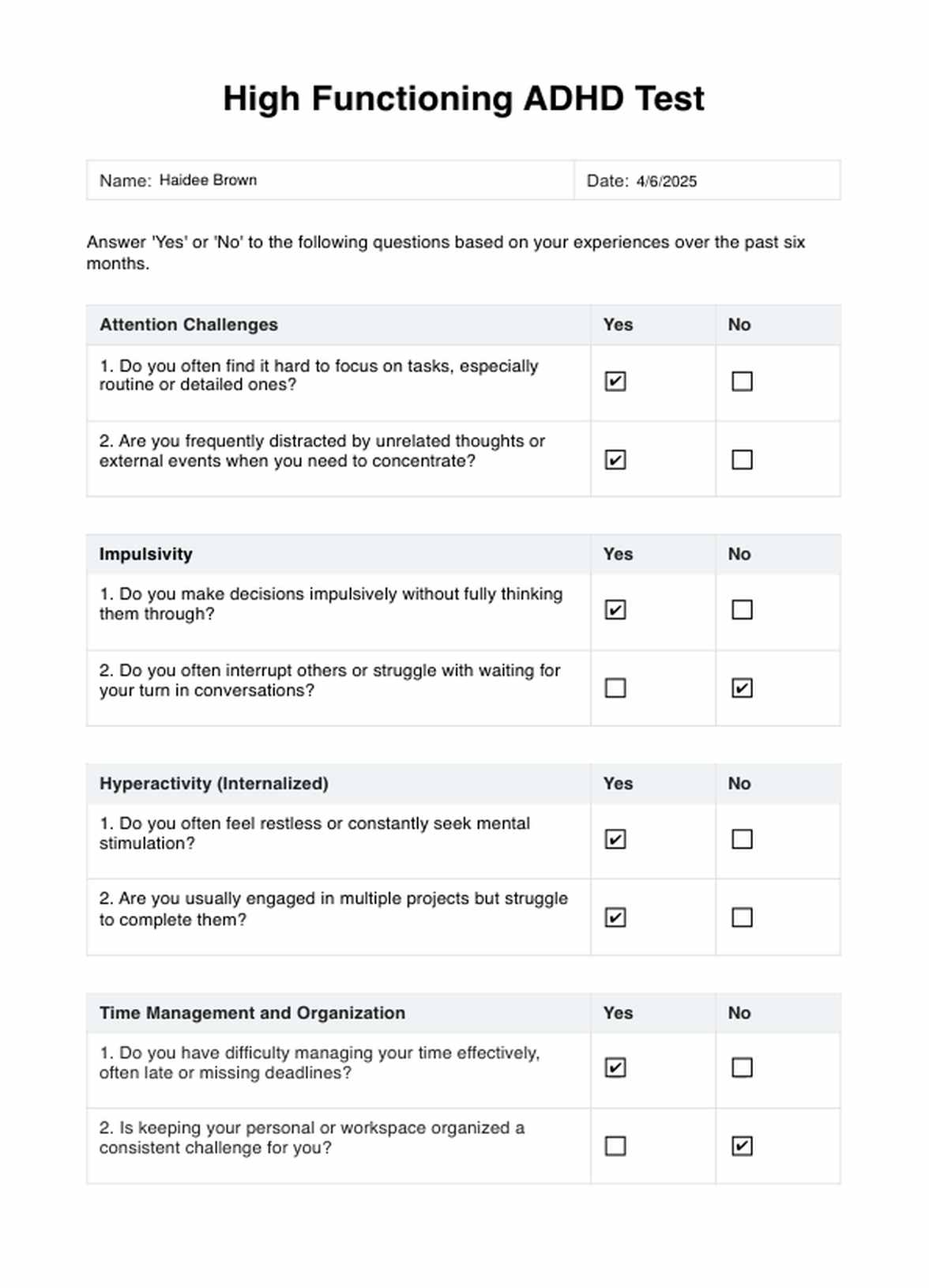
Symptoms of High Functioning ADHD, though often less visible and disruptive than those of classical ADHD, can significantly affect a person's life. The main symptoms include challenges in maintaining attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity, each manifesting uniquely in this subtype.
Affected individuals often struggle to sustain attention, especially in mundane or low-stimulation tasks, leading to frequent mind-wandering, daydreaming, or distractibility. This can result in difficulties with task completion, adherence to instructions, and organizational skills. Impulsivity may not be outwardly disruptive but can appear as impatience, difficulty waiting for conversation, hasty decision-making, or a tendency for spontaneous actions.
Hyperactivity in High Functioning ADHD tends to be more internalized, contrasting with the physical restlessness observed in more typical ADHD cases. Individuals may experience mental restlessness, feeling a constant inner agitation or a relentless need for mental engagement. This often drives them to continuously search for new ideas or initiate numerous projects.
High Functioning ADHD can coexist with other mental health conditions like anxiety and depression, further complicating symptom management. Understanding and recognizing these nuanced symptoms is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management, leading to better support, customized interventions, and an improved quality of life for those affected.
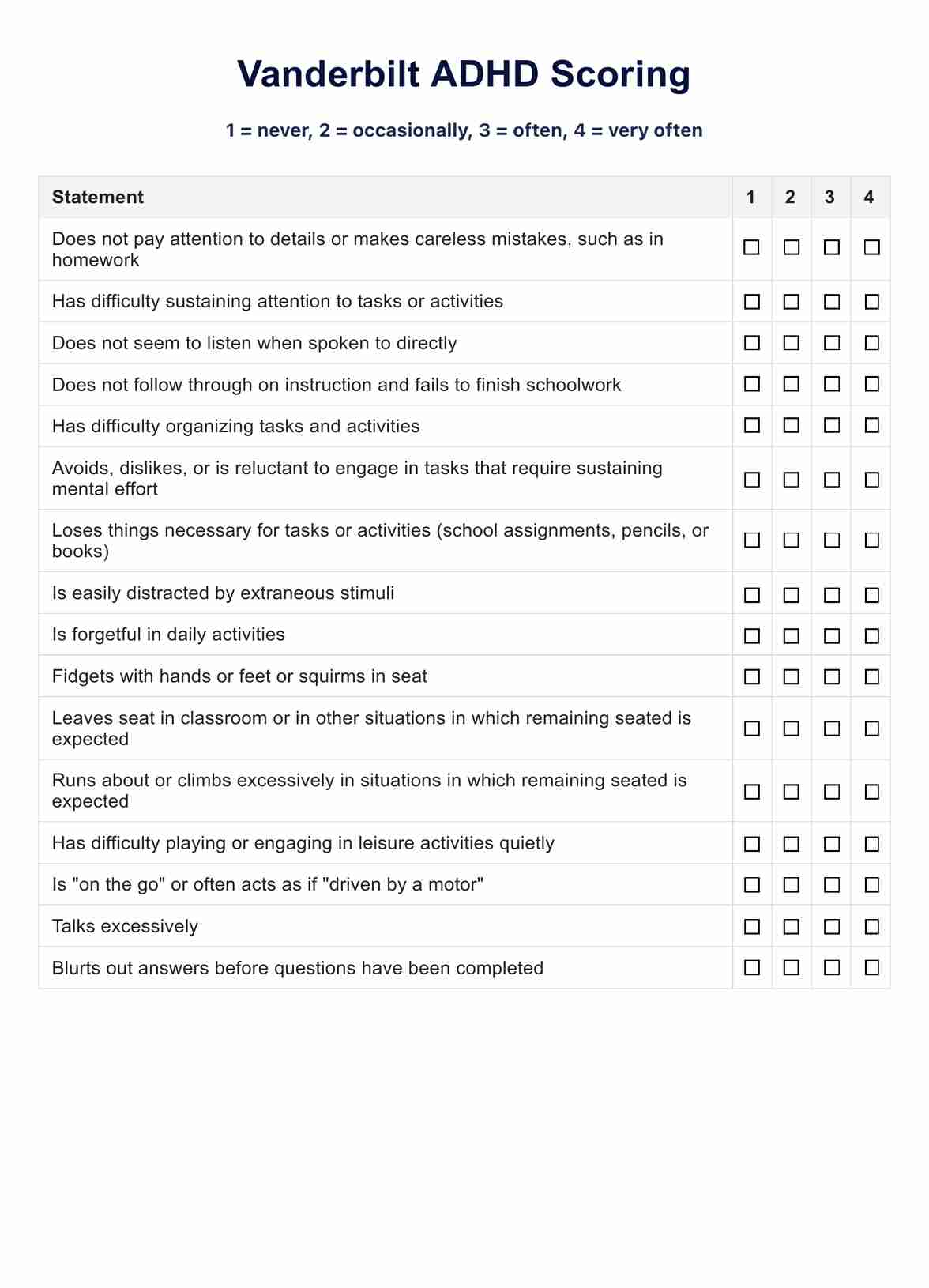
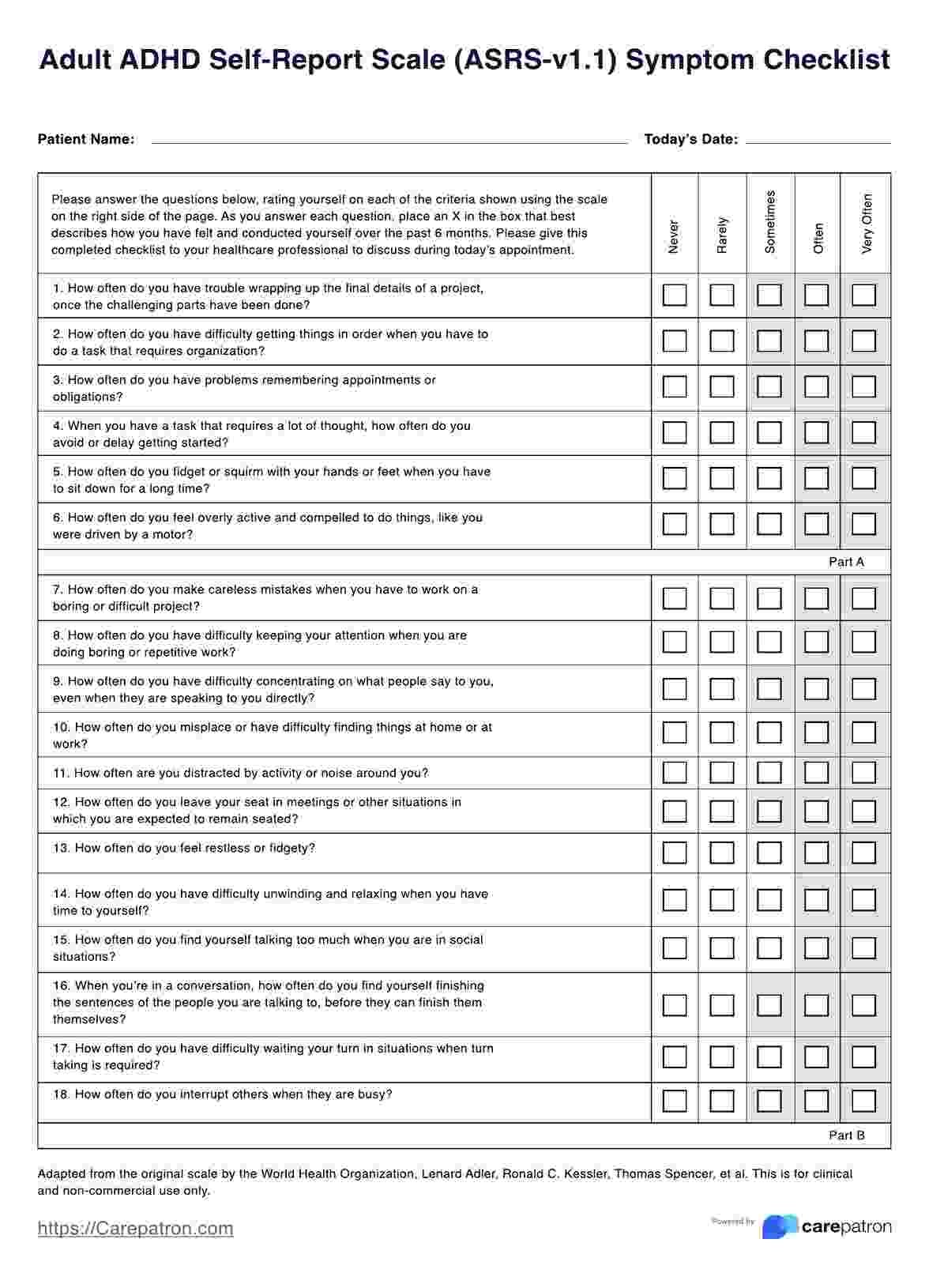
Common ADHD rating scale tests
Various ADHD rating scales are crucial in diagnosing and understanding the severity of ADHD symptoms. Key among these are:
- ADHD Symptom Checklist: A comprehensive tool capturing a range of ADHD behaviors and symptoms, aiding in identifying specific issues an individual might face.
- ADHD Spectrum Test: This test evaluates symptoms across the ADHD spectrum, which is crucial for tailoring personalized treatment approaches.
- ADHD Screening Test: Primarily a preliminary tool, it helps in the early detection of ADHD symptoms and determines the need for a more detailed assessment.
- DSM-5 ADHD Checklist: Based on the DSM-5 criteria, this checklist is a standardized tool for clinicians to diagnose ADHD.
- Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale: Specifically for adults, it assists in self-identifying symptoms that might affect daily life.
How does this ADHD test work?
ADHD management is an ongoing process. Continuous evaluation and adjustments to the treatment plan are made based on changes in symptoms, lifestyle, or other factors.
Step 1: Initial consultation
Begin with an initial consultation with a mental health professional. This step involves discussing symptoms, concerns, and the individual's medical history. It sets the stage for understanding the need for ADHD testing.
Step 2: Selection of the appropriate ADHD test
The mental health professional selects the most suitable ADHD test based on the individual's age, symptoms, and specific concerns. This could be one of the standardized tests like the ADHD Symptom Checklist or the Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale.
Step 3: Administration of the test
The selected test is administered in a clinical setting or as a take-home questionnaire. The test consists of structured questions or statements related to ADHD symptoms as outlined in the DSM-5.
Step 4: Response and rating
Individuals respond to the test items by rating their experiences against specified criteria. This usually involves grading the frequency or severity of symptoms over a certain period.
Step 5: Analysis of responses
The mental health professional analyzes the responses to identify patterns consistent with ADHD symptoms. This analysis is crucial to understand how closely the individual's symptoms align with the diagnostic criteria for ADHD.
Step 6: Differential diagnosis
To differentiate ADHD from other mental health disorders with similar symptoms, further assessment may be conducted. This step ensures that the diagnosis is accurate and specific to ADHD.
Step 7: Developing treatment strategies
If ADHD is diagnosed, the next step involves working with the individual to develop strategies to manage the condition. This includes creating compensation strategies for daily challenges and tailoring interventions to the individual’s needs.
Step 8: Follow-up and adjustment
Regular follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor progress. Treatment strategies and compensation methods are adjusted based on the individual's response to interventions.
Step 9: Ongoing support and education
The mental health professional provides ongoing support and education about ADHD. This helps the individual better understand their condition and fosters self-awareness, crucial for effective management.
Interpreting the results
Interpreting the results of ADHD assessments is a nuanced process that involves analyzing the scores within the framework of established clinical criteria for ADHD. This is more than just a numerical exercise; it requires carefully considering various factors, including the individual's age, which can influence how symptoms manifest and are perceived.
Lifestyle factors, such as daily routines and stress levels, also play a crucial role in how ADHD symptoms present. Additionally, co-existing conditions, often referred to as comorbidities, must be taken into account. These can include other mental health disorders like anxiety or depression, which may exacerbate or mask ADHD symptoms.
Understanding the interplay of these elements is essential for an accurate interpretation of the assessment results, ensuring that they reflect the individual’s true clinical picture.
Diagnosing ADHD
Diagnosing ADHD is comprehensive and should only be performed by a qualified healthcare professional. This professional will consider various elements, including the results from ADHD assessments, a thorough clinical evaluation, and an extensive review of the individual's medical history.
The clinical evaluation typically involves discussing symptoms, their impact on daily life, and any patterns observed over time. Medical history is reviewed to rule out other conditions that could mimic ADHD symptoms.
A formal diagnosis of ADHD is not based solely on the results of the assessments but is a conclusion drawn from a holistic view of the individual's psychological, physical, and emotional health.
Treatment for ADHD
Effective ADHD treatment encompasses a range of options, including medication management, behavioral therapy, and lifestyle changes. Medications like stimulants or non-stimulants play a key role in managing core symptoms, particularly for those with more severe symptoms of ADHD. However, it's crucial to tailor medication to individual needs, as it's not a universal solution.
Behavioral therapy, particularly cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), is effective in altering thinking patterns associated with ADHD. It's beneficial for developing time management and organization skills, which are crucial for daily life and professionally successful adults.
Lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and sufficient sleep, also significantly contribute to managing ADHD symptoms. These changes are significant for adults balancing professional responsibilities, as they help maintain focus and reduce impulsivity.
Ultimately, a personalized approach to treating ADHD, considering each individual's unique symptom profile and lifestyle, is essential. This combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments forms a comprehensive strategy for effectively managing ADHD.
Benefits of this ADHD assessment
- Structured symptom identification: ADHD assessments systematically identify ADHD symptoms, including those requiring sustained mental effort. This ensures a comprehensive evaluation of all potential areas of concern, from mild symptoms to more pronounced ones.
- Facilitation of early intervention: Identifying ADHD symptoms early, especially those related to challenges in sustained mental effort, facilitates timely intervention essential for the effective management of this mental health condition.
- Timely diagnosis and treatment: Early detection and diagnosis through these assessments lead to quicker treatment initiation, significantly improving outcomes, particularly in managing symptoms that hinder daily functioning.
- Mitigation of impact on daily life: An accurate and early ADHD diagnosis can help mitigate the disorder's impact on crucial aspects such as academic performance, career progression, and personal relationships, especially when symptoms affect daily life activities.
- Enhanced understanding of ADHD symptoms: These assessments aid in gaining a deeper understanding of the individual’s specific ADHD symptoms, including those that require sustained mental effort, which is critical for effective management.
- Development of personalized treatment plans: Insights from these assessments enable healthcare providers to create tailored treatment plans. These plans specifically address unique challenges in daily functioning and coping mechanisms needed by each individual with ADHD.
- Improved management strategies: Personalized management strategies, informed by these assessments, enhance the overall efficacy of ADHD treatment, particularly in helping individuals manage daily life with the condition.
- Increased self-awareness: Undergoing these assessments can increase self-awareness about ADHD, empowering individuals in self-management, especially in activities requiring sustained mental effort.
- Support in educational and workplace settings: The assessments provide essential documentation for support and accommodations in educational and workplace environments, aiding those with ADHD in contexts that require sustained mental effort and coping mechanisms.
- Guidance for families and caregivers: Results from ADHD assessments offer valuable insights for families and caregivers, helping them understand and support individuals with ADHD in their daily functioning and coping with mental health conditions.
Commonly asked questions
Signs of High Functioning ADHD include difficulty maintaining attention, especially in routine tasks, and internalized symptoms like mental restlessness or impulsivity in decision-making. Individuals may also struggle with organizational skills and time management.
Adult ADHD diagnosis can be challenging because symptoms often overlap with other mental health conditions, and adults might have developed coping mechanisms that mask ADHD symptoms. Additionally, there's less awareness and recognition of ADHD in adults compared to children.
The most legitimate ADHD test is a comprehensive evaluation by a qualified mental health professional, which includes clinical interviews, standardized rating scales, and observation. No test can diagnose ADHD; a thorough assessment considering various aspects is essential.
























-template.jpg)