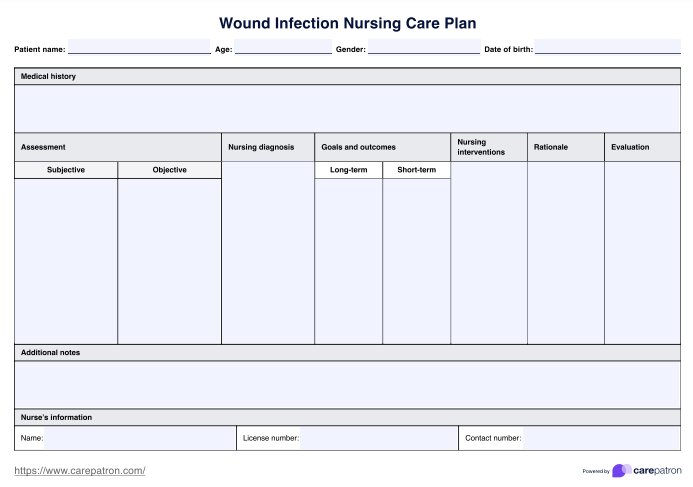
A Wound Infection Nursing Care Plan Template is a structured tool healthcare professionals use to assess, plan, and implement care for patients with wound infections. It guides nurses through each step of patient care, from initial assessment to treatment and follow-up.
Wound Infection Nursing Care Plan Template
Use our Wound Infection Nursing Care Plan Template to manage and treat wound infections effectively, ensuring optimal patient care and recovery.
Use Template
Wound Infection Nursing Care Plan Template Template
Commonly asked questions
This template is designed for nurses, wound care specialists, and other healthcare providers involved in treating patients with wound infections. It's also a valuable resource for nursing students and educators.
The template is designed to align with general healthcare documentation standards. However, practitioners should ensure that their documentation complies with specific local and institutional regulations.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











