Carepatron offers a unique blend of user-friendly design and advanced features like the online patient portal and telehealth platform, ensuring a seamless experience for both patients and professionals.
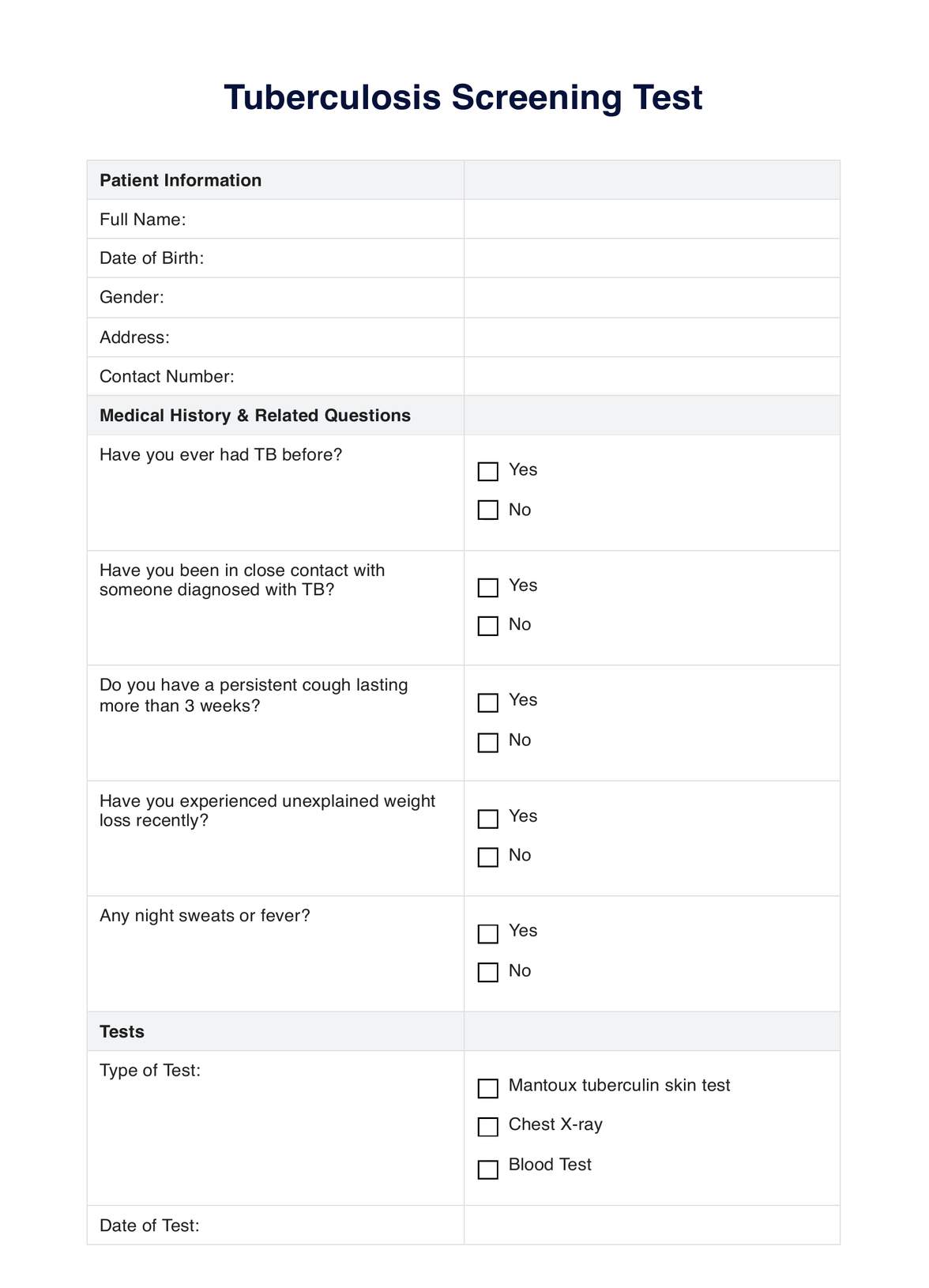
Explore the comprehensive guide on Tuberculosis Screening with Carepatron. Streamline your screenings with our advanced patient portal and telehealth platform.
Carepatron offers a unique blend of user-friendly design and advanced features like the online patient portal and telehealth platform, ensuring a seamless experience for both patients and professionals.
Carepatron prioritizes data security, ensuring that all patient information and medical records are stored with the highest level of encryption and protection.
Absolutely! Carepatron is versatile and can be used for various medical screenings, consultations, and healthcare management tasks.
EHR and practice management software
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments