These valuable plan templates can be used at any point in the treatment journey for patients with infections to track, monitor, and plan all interventions by healthcare professionals and patient needs.
Risk For Infection Nursing Care Plan
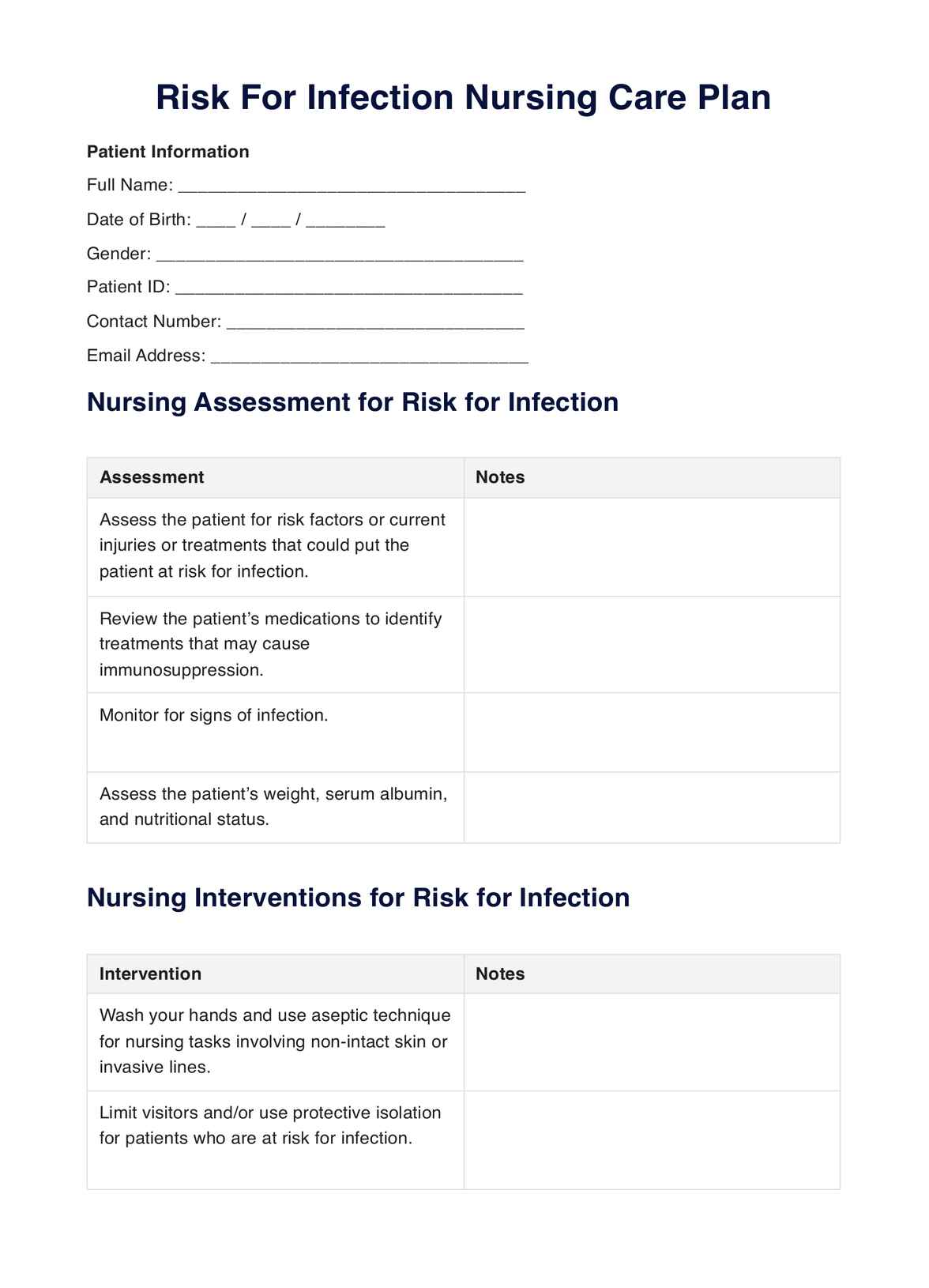
Streamline nursing diagnosis with our Risk For Infection Nursing Care Plan Template. Enhance patient care and safety. Download now!
Risk For Infection Nursing Care Plan Template
Commonly asked questions
Nurses typically use this infection risk care plan to help outline nurse planning. Yet, the template can be easily used and managed by any healthcare professional, even as an educational tool for the patient's self-management.
The primary nursing goals for preventing infection involve minimizing pathogen exposure, enhancing immune response, educating patients on prevention strategies, and monitoring for early signs of infection. By focusing on these areas, nurses play a crucial role in infection prevention and promoting patient wellbeing.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











