It is widely respected for its detailed approach to understanding ankle injuries through mechanical forces.
Lauge-Hansen Classification
Explore the Lauge-Hansen Classification for ankle fractures. Download a free PDF example of using this essential tool in orthopedic surgery for better diagnosis and treatment planning.
Use Template
Lauge-Hansen Classification Template
Commonly asked questions
While useful, it is most applicable to rotational injuries and might complement other classification systems for comprehensive assessment.
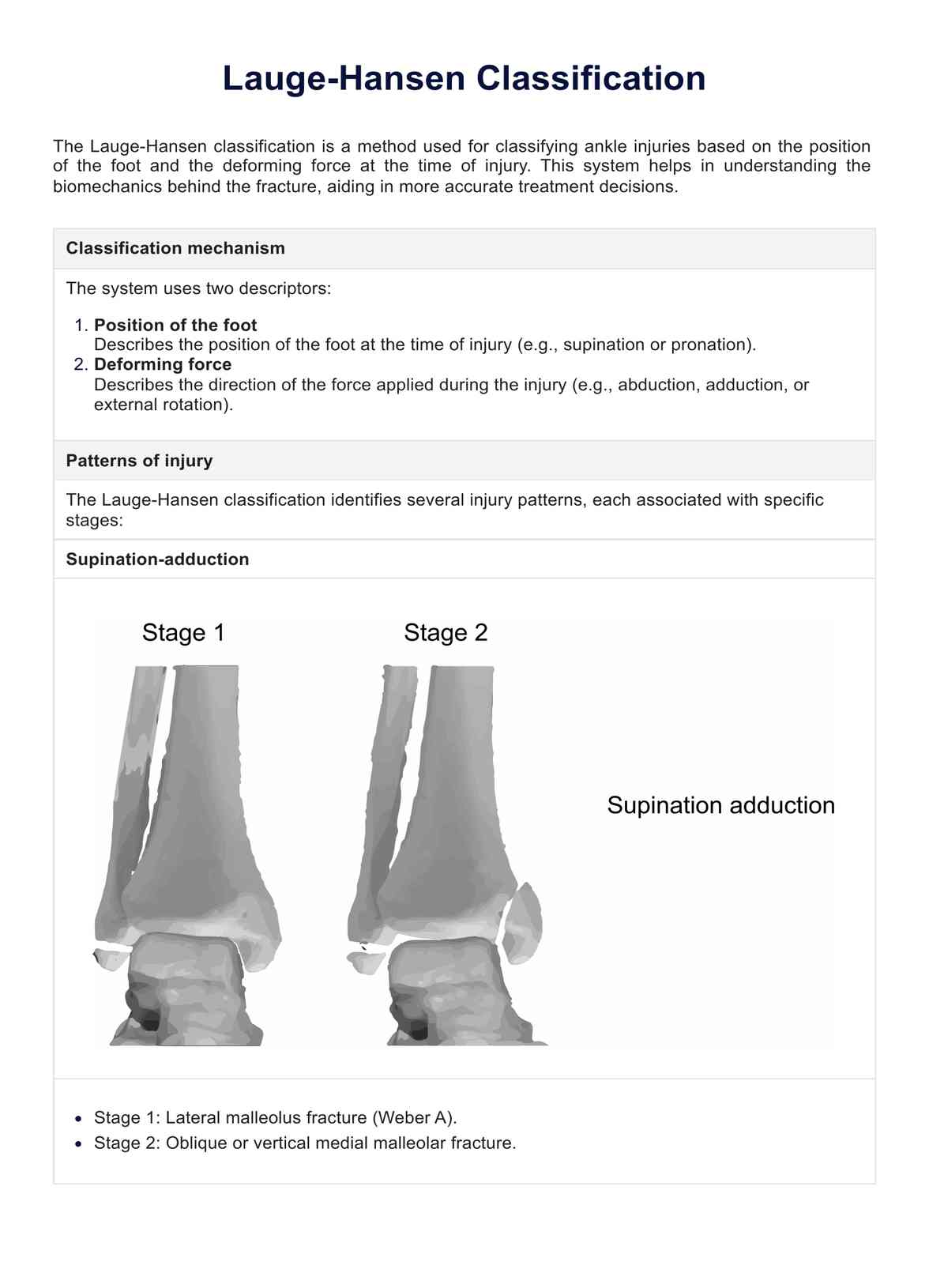
Based on the injury mechanism, the Lauge-Hansen Classification can predict specific ligament injuries, such as those involving the medial malleolar fracture. This understanding is crucial for devising precise treatment strategies in orthopedic surgery.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











