Driving immediately after a dilated eye exam is not recommended due to temporary blurred vision and light sensitivity. It's advisable to arrange alternative transportation or wait until your vision returns to normal.
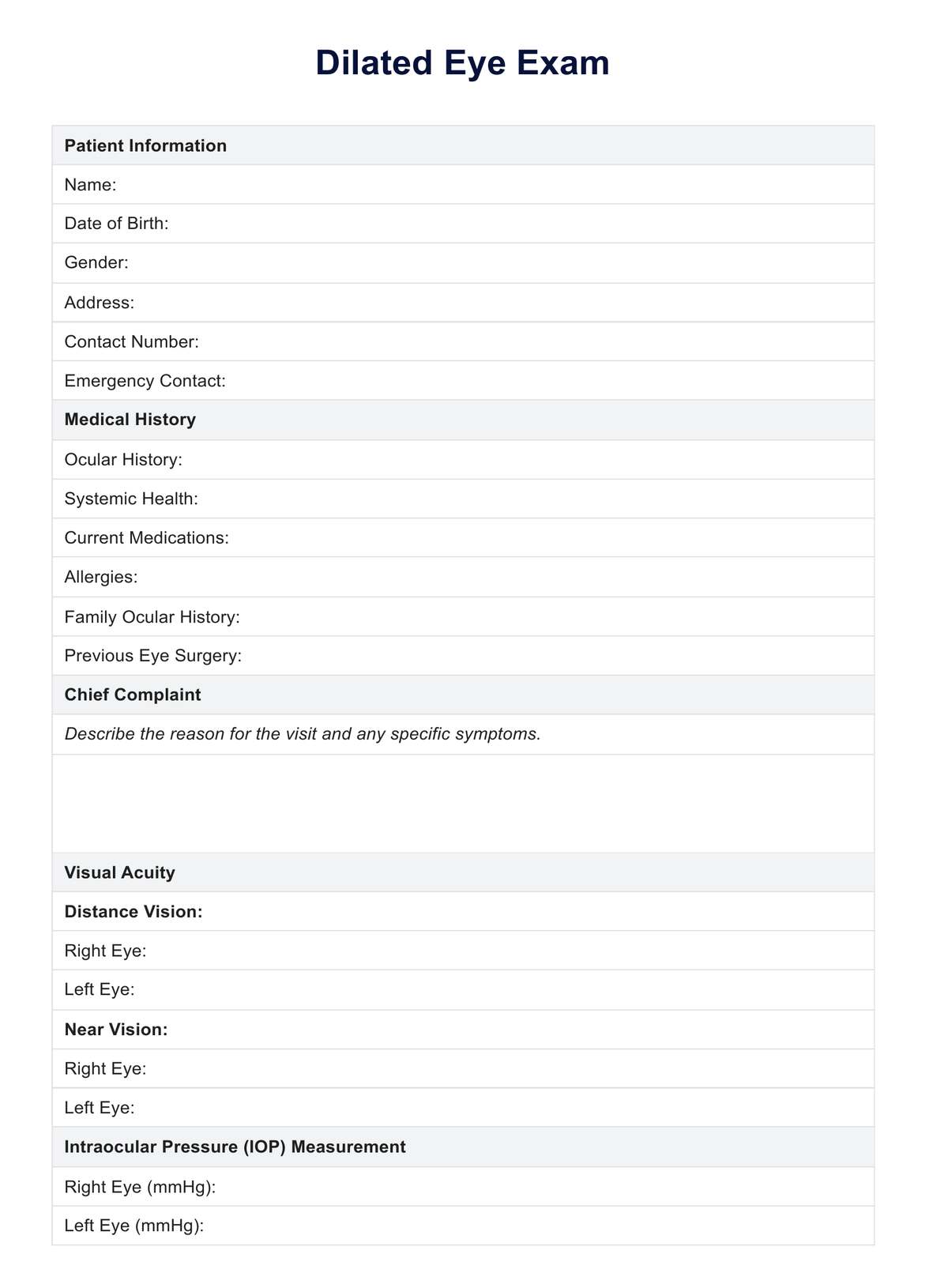
Dilate Eye Exam
Learn about dilate eye exams importance in detecting eye conditions. Download Carepatron's PDF to understand the procedure better.
Use Template
Dilate Eye Exam Template
Commonly asked questions
The effects of pupil dilation typically last for about 4 to 6 hours. However, individual responses may vary, and wearing sunglasses during this period is recommended to reduce discomfort from light sensitivity.
Avoid activities requiring sharp vision, such as reading fine print or using electronic devices, due to temporary blurred vision. Also, avoid prolonged exposure to bright lights, and consider wearing sunglasses for comfort.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











