Depression Treatment Guidelines
Learn about Depression Treatment Guidelines for effective management and treatment of depressive disorders. Download a free handout here.


Understanding Depression Treatment Guidelines
Depression Treatment Guidelines are evidence-based recommendations used by healthcare providers to effectively manage depressive disorders, such as major depressive disorder (MDD).
These guidelines contain a wide range of therapeutic options, including pharmaceutical treatments, psychological therapies, and complementary treatments, to address the complexity of depression and its varying symptom intensity. Common treatments include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and mindfulness-based cognitive behavior therapy.
Ensuring the right fit for each patient requires clinicians to closely evaluate depression symptoms, consider the diagnostic criteria, and adhere to clinical practice guidelines to achieve the best possible depression outcomes. Additionally, treating depression involves a comprehensive approach that also addresses comorbid conditions like anxiety treatments and chronic depression, ensuring a holistic view of the patient's mental health.
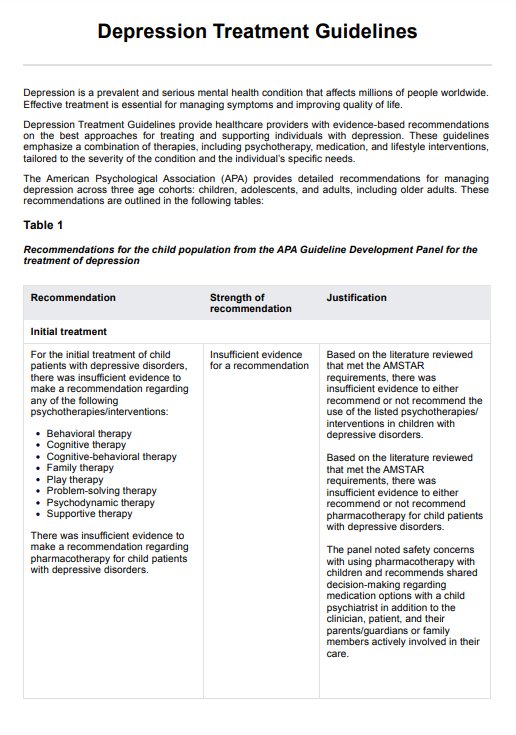
Depression Treatment Guidelines Template
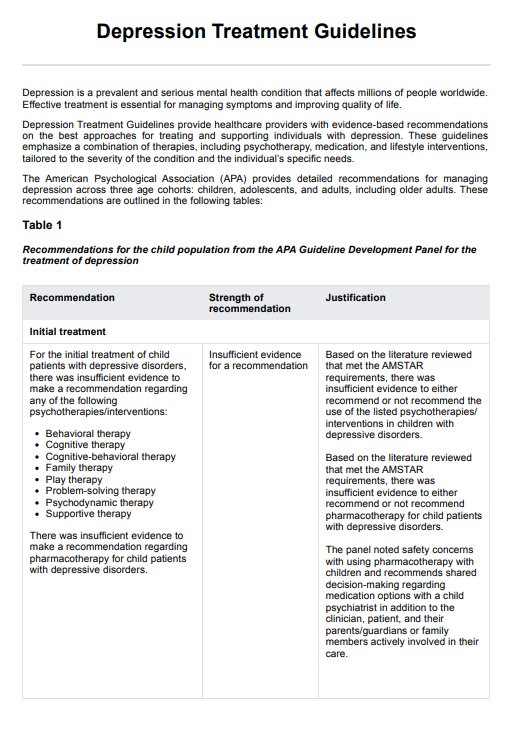
Depression Treatment Guidelines Example
Treatment guidelines for major depressive disorder (MDD)
As mentioned, major depressive disorder is a major mental health illness that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It is characterized by persistent melancholy and a loss of interest in previously loved activities. The American Psychiatric Association's Clinical Practice Guidelines for treating MDD offer a comprehensive strategy including pharmaceutical and psychological therapy. Here are some treatment guidelines for MDD (Mcquaid et al., 2019):
Initial treatment options
Antidepressant drugs and psychotherapy are commonly used as first-line treatments for MDD. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are popular antidepressants due to their demonstrated efficacy and mild side effect profiles.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a leading psychotherapy for treating depression, as it helps patients change negative thought patterns that contribute to depressive symptoms. Other psychotherapies, including Interpersonal Psychotherapy (IPT), mindfulness-based cognitive therapy, and psychodynamic therapy, are also considered based on individual needs (Mcquaid et al., 2019).
For more severe cases, combined treatment involving both antidepressants and psychotherapy is often recommended. The APA guidelines emphasize the use of CBT or IPT alongside antidepressant treatment for optimal results.
Treatment-resistant depression
When patients do not respond to initial treatments, they are considered to have treatment-resistant depression. In such cases, adjunctive treatments, like electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) or repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS), may be recommended, particularly for those with severe depression or psychotic symptoms. These treatments provide additional support when standard medications and therapies have not produced adequate results.
Addressing symptom severity
The APA guidelines propose adjusting treatment strategies based on the severity of depression symptoms. For people with mild depression, therapy alone, such as behavioral activation or problem-solving therapy, may suffice. However, for moderate to severe depression, a combination of medication and psychotherapy is frequently required to effectively treat symptoms.
Depression with comorbid conditions
Many individuals with MDD also have comorbid conditions, such as anxiety disorders or substance use disorders. Treatment plans should address these comorbidities to improve overall outcomes. For example, CBT can be adapted to treat both depression and anxiety. Additionally, supportive psychotherapy can help patients manage the emotional burden of these co-occurring conditions.
Long-term management and prevention
For patients who respond positively to initial treatments, preventing relapse is crucial. The APA guidelines recommend psychotherapy (e.g., CBT or mindfulness-based cognitive therapy) as the primary strategy for preventing relapse rather than relying solely on antidepressant medication. Maintenance therapy is particularly important for individuals with chronic or recurrent depressive symptoms, as it helps maintain long-term mental health and reduce the likelihood of recurrence.
Patient preferences and treatment adherence
A critical aspect of treatment is shared decision-making between the clinician and the patient, ensuring patient preferences are considered when developing the treatment plan. This approach enhances treatment adherence, essential for improving depression outcomes (Mcquaid et al., 2019). It's vital that patients feel empowered and confident in their treatment choices to ensure the best possible outcomes.
To learn more about Depression Treatment Guidelines, download our handout by clicking the “Use template” where you can access it via the Carepatron app. For a PDF copy, click the "Download" button.
Reference
Mcquaid, J., Lin, E., Washington, K., Jones, V., Kessler, M., York, N., & Mufson, L. (2019). Clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of depression across three age cohorts. https://www.apa.org/depression-guideline/guideline.pdf
Commonly asked questions
Depression treatment guidelines provide evidence-based recommendations for healthcare professionals on how to effectively treat major depressive disorder using a combination of pharmacological treatments, psychological treatments, and adjunctive treatments.
The most common depression therapies include cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT), and electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) for severe or treatment-resistant cases.
Treatment for depression is adjusted based on the intensity of the symptoms, the patient's preferences, and the treatment response. Options range from psychotherapy and antidepressant medication to more advanced treatments such as repeated transcranial magnetic stimulation. This approach is essential for managing mental disorders, ensuring that the treatment plan aligns with the specific needs of the patient.



















-template.jpg)