Dental X-rays are generally affordable and are often covered by dental insurance as part of routine dental care.
Dental Radiograph Chart
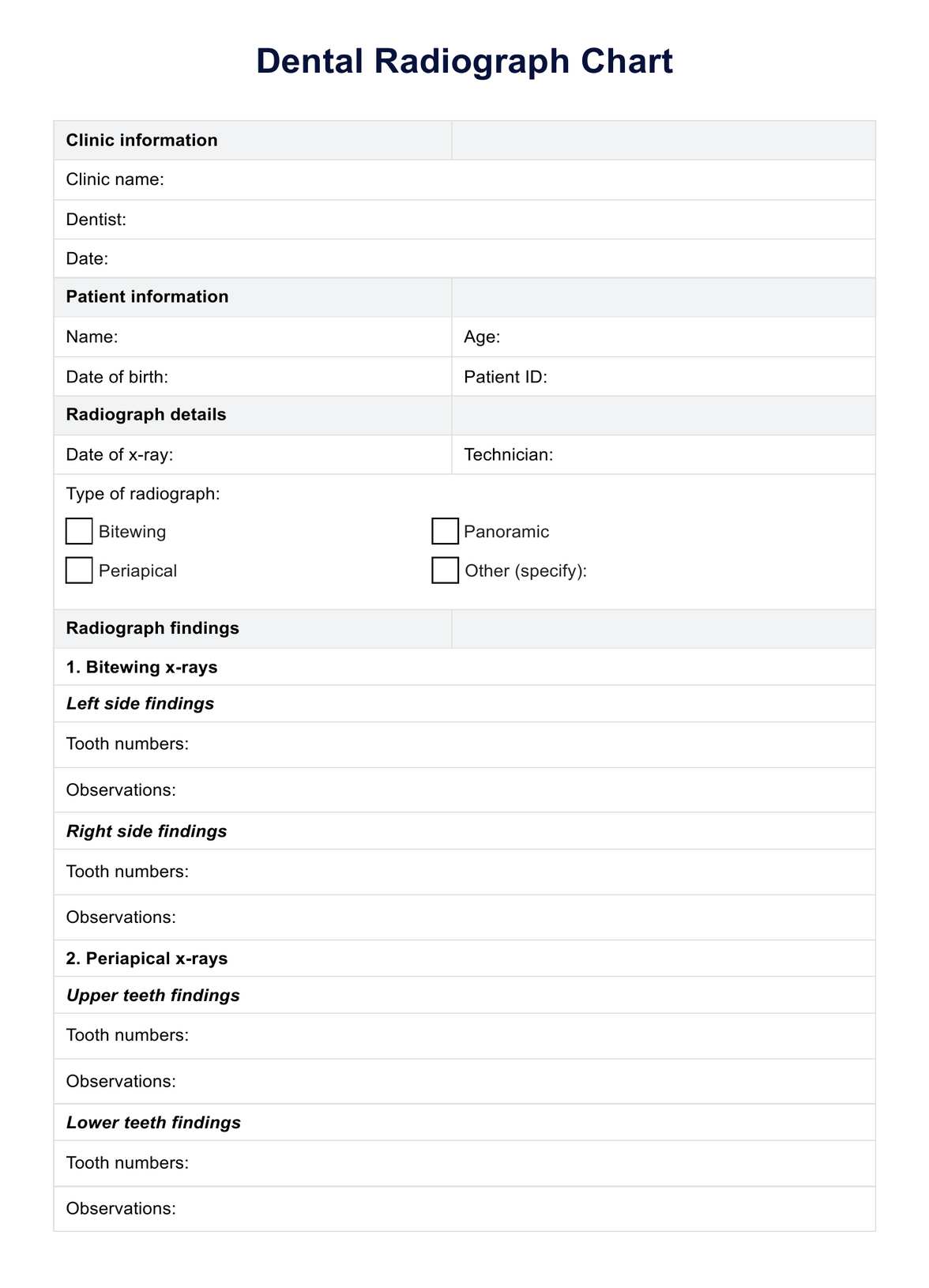
Discover how to use dental radiograph charts effectively in your practice. Download our free example and learn about the types, safety, and benefits of dental x-rays.
Use Template
Dental Radiograph Chart Template
Commonly asked questions
No, dental x-rays are painless. The process involves minimal discomfort, as it is non-invasive and quick.
The frequency of dental X-rays depends on the individual's oral health condition, age, risk for dental disease, and any signs of oral disease. Dentists typically recommend X-rays during routine dental check-ups.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











