Let clients focus on emotions they experience regularly (happy, sad, anxious, etc.) They can also track specific emotions or activities influencing their mood, especially during significant experiences.
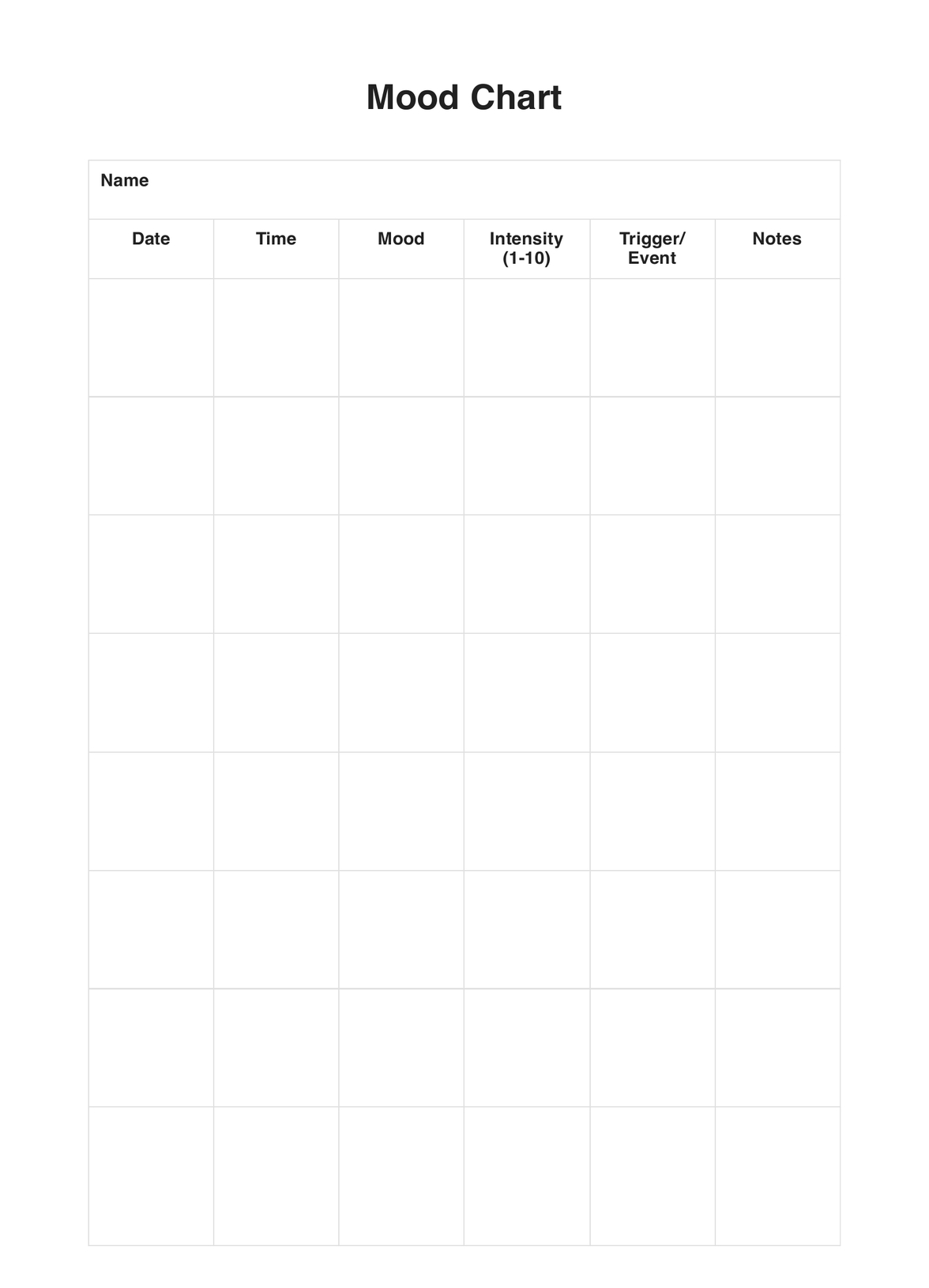
Mood Charts
Understand how a Mood Chart works and get access to a free PDF to help your clients track how they're feeling.
Mood Charts Template
Commonly asked questions
To fill out a Mood Chart, clients typically rate their mood on a scale (e.g., 1-10 or using descriptive labels) at specific times throughout the day or week. Some charts also include space to note potential triggers, activities, or other relevant information that may have influenced their mood.
Moods can significantly impact the body through the mind-body connection. Positive moods can enhance well-being, boost immune function, and promote physical health. In contrast, negative moods like stress or anxiety can lead to increased cortisol levels and muscle tension and even impact cardiovascular health.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











