Clonus is usually caused by lesions affecting the upper motor neurons in the central nervous system. Conditions such as multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, stroke, and cerebral palsy can lead to clonus.
Clonus Reflex Test
Learn about the Clonus Reflex Test, its procedure, benefits, and management. Discover how Carepatron's template streamlines assessments for healthcare professionals.
Clonus Reflex Test Template
Commonly asked questions
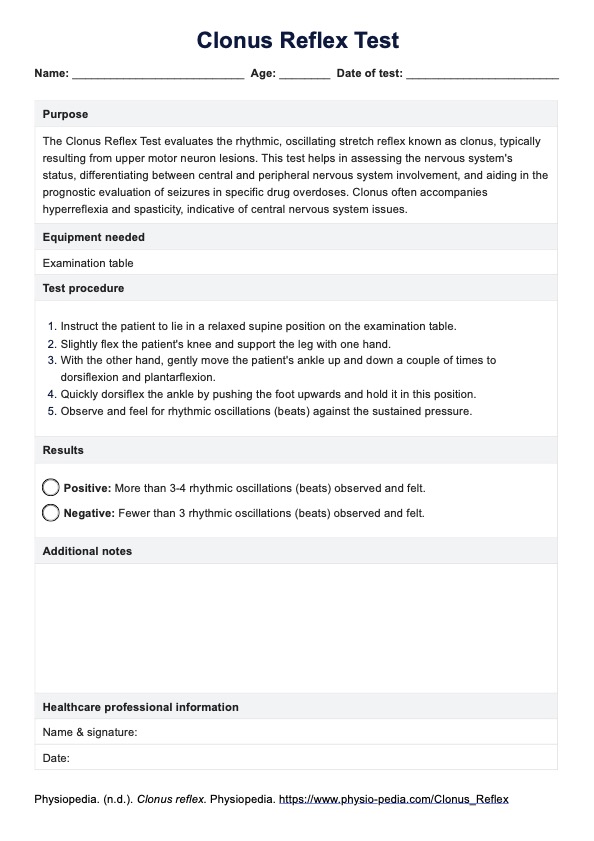
The test involves slightly flexing the patient’s knee, moving the ankle in dorsiflexion and plantarflexion, and then rapidly dorsiflexing the ankle while observing for rhythmic oscillations.
A positive test, indicated by more than 3-4 rhythmic oscillations, suggests hyperreflexia and spasticity due to upper motor neuron lesions. It helps diagnose and assess conditions like multiple sclerosis and spinal cord injuries.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











